Genetic Testing Market Size and Trends
The genetic testing market size was exhibited at USD 11.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 91.30 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 22.6% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
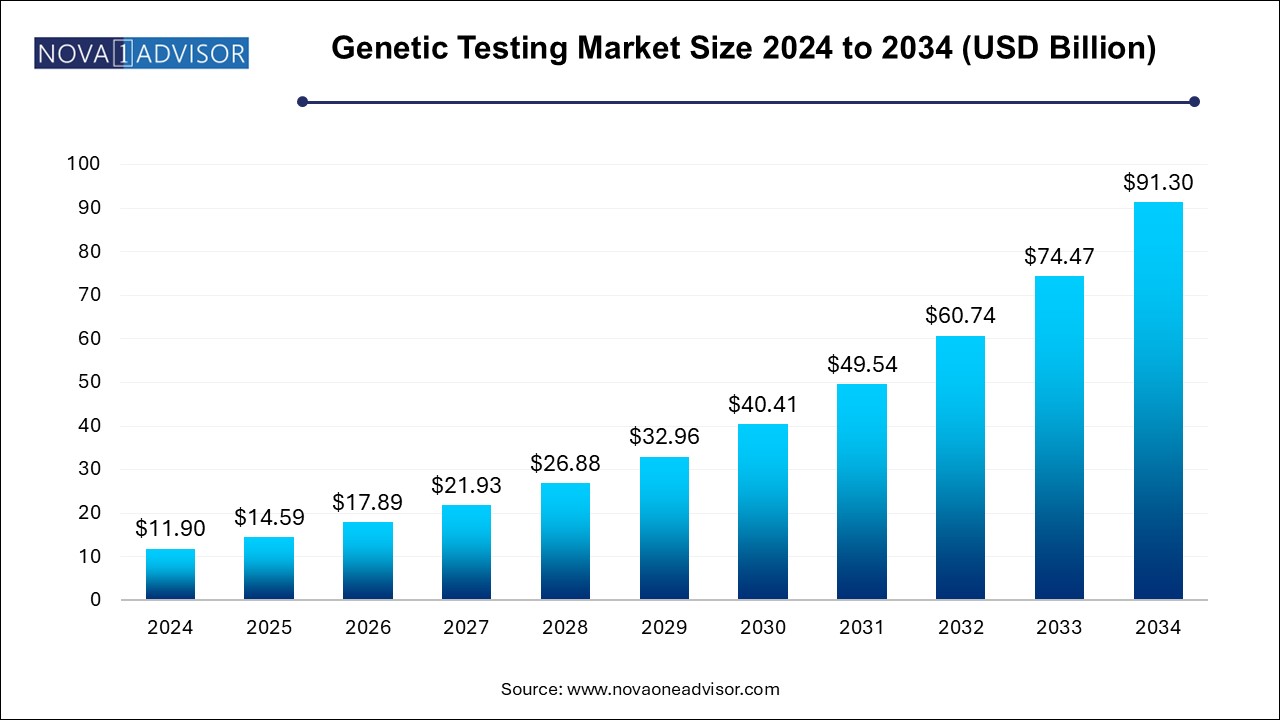
Genetic Testing Market Key Takeaways:
- Based on technology, the next generation sequencing segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 49.3% in 2024.
- The array technology segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- Based on application, the health and wellness-predisposition/risk/tendency segment led the market with the largest revenue share at 52.3% in 2024.
- The genetic disease carrier status segment is also expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 22.5% over the forecast period.
- The consumables segment led the market with the largest revenue share at 60.2% in 2024.
- The software & services segment is also expected to experience at a substantial CAGR of 24.8% during the forecast period.
- Based on channel, the offline segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 62.3% in 2024.
- The online channel is expected to exhibit at the fastest CAGR of 23.6% during the forecast period.
- Based on end use, the hospitals and clinics segment led the market with the largest revenue share at 44.0% in 2024.
- The diagnostic laboratories segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 22.7% during the forecast period
- North America genetic testing market dominated the global market with the largest revenue share of 45.38%% in 2024.
Market Overview
The global genetic testing market has undergone a transformative evolution, evolving from a niche, clinical diagnostic service into a mainstream healthcare, lifestyle, and consumer wellness offering. Genetic testing refers to the analysis of DNA, RNA, chromosomes, proteins, or metabolites to detect heritable or acquired genetic abnormalities. Initially confined to rare disease diagnosis and newborn screening, its application has now expanded into areas such as ancestry tracing, oncology, reproductive health, pharmacogenomics, and personalized wellness.
With the advent of precision medicine, rapid technological innovations like Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), and increasing awareness among consumers, genetic testing is reshaping how individuals and healthcare systems approach disease prevention, early detection, and treatment optimization. In recent years, genetic testing has become more affordable and accessible, with direct-to-consumer (DTC) platforms allowing people to gain insights into their heritage, predispositions to health conditions, and even behavioral traits—all from the convenience of their homes.
The global burden of genetic and chronic diseases, rising investments in genomics, the increasing availability of genomic databases, and growing collaborations between biotechnology firms and healthcare providers are major factors driving the market forward. As we move into an era of individualized medicine, the genetic testing market is positioned to play a central role in shaping healthcare delivery, research, and personal well-being.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Mainstreaming of Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing: Consumers are increasingly seeking genetic insights through DTC channels, fueling partnerships between biotech companies and retail pharmacy chains.
-
Integration of AI and Bioinformatics in Genomic Analysis: AI-powered algorithms are accelerating genomic interpretation, risk prediction, and personalized health recommendations.
-
Expansion of Prenatal and Carrier Screening: Rising awareness about inherited disorders is prompting more couples to opt for genetic testing during pregnancy and family planning.
-
Focus on Pharmacogenomics: Personalized drug therapies based on individual genetic profiles are gaining traction in oncology, cardiology, and psychiatry.
-
Rise of Wellness and Lifestyle Genomics: Consumers are now using genetic tests to understand nutrition compatibility, athletic potential, and behavioral traits.
-
Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns: As consumer genomic data grows, companies are enhancing privacy protocols and transparency to gain user trust.
-
Government Genomics Initiatives: Countries are launching national genomic databases and integrating genetic testing into public health programs.
Report Scope of Genetic Testing Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 14.59 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 91.30 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 22.6% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Technology, Application, Product, Channel, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
24 genetics; Circle DNA; tellmegene; 23andme; AncestryDNA; MyDNA; Everly Well; Igenomix; VitaGen; Myriad Genetics Inc.; Mapmygenome; Helix OpCo LLC; MyHeritage Ltd.; Illumina, Inc.; Color Genomics, Inc.; Amgen, Inc.; Beyond Nutrition Health and Wellness Services DMCC |
Market Driver: Rising Incidence of Genetic and Chronic Disorders
One of the strongest growth drivers in the genetic testing market is the increasing prevalence of genetic and chronic diseases globally. Conditions such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, BRCA-related breast cancer, and Lynch syndrome are being diagnosed with higher accuracy thanks to genetic screening. Moreover, complex multifactorial disorders like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s often have genetic predisposition components, which are now better understood through expanded genetic testing panels.
For instance, BRCA1/2 testing has become a key protocol in assessing breast and ovarian cancer risk in women with a family history. Similarly, genetic testing for familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is aiding early detection and prevention of cardiovascular complications. As healthcare systems shift towards preventive models, genetic testing is increasingly being integrated into routine care protocols, amplifying demand.
Market Restraint: Data Privacy and Ethical Challenges
Despite its immense potential, the genetic testing market faces significant ethical, legal, and data privacy challenges. Genetic data is deeply personal and, if mishandled, can lead to discrimination in insurance, employment, or social settings. Concerns have been raised over how DTC companies store, use, and potentially share consumer data with third parties, including pharmaceutical companies or law enforcement.
Cases such as the misuse of genetic data in criminal investigations or the unauthorized sale of data for research have sparked debates on consent, ownership, and privacy. While regulations like HIPAA (U.S.) and GDPR (EU) provide some safeguards, inconsistencies and loopholes across geographies remain. Addressing these issues is critical to sustaining public trust and long-term growth.
Market Opportunity: Integration of Genetic Testing in Personalized Medicine
A significant opportunity lies in the integration of genetic testing into precision medicine frameworks, particularly in oncology, cardiology, and rare disease diagnosis. Personalized medicine leverages genetic insights to tailor treatment plans that are more effective, have fewer side effects, and improve patient outcomes. The success of targeted cancer therapies based on tumor genomics such as PARP inhibitors for BRCA mutation carriers exemplifies the potential of this approach.
Hospitals and healthcare providers are investing in in-house genetic testing labs and bioinformatics teams to enable real-time decision-making. Additionally, the use of companion diagnostics for drug selection and dosing based on an individual’s genome is expected to grow rapidly. These applications are driving collaboration between pharmaceutical companies, diagnostic developers, and clinical researchers to develop comprehensive, actionable genetic testing solutions.
Genetic Testing Market By Technology Insights
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) led the technology segment due to its ability to process massive volumes of genetic data quickly and cost-effectively. NGS has revolutionized genetic diagnostics by enabling whole-genome, whole-exome, and targeted gene panel sequencing for both clinical and research applications. Its accuracy, scalability, and ability to detect rare mutations make it the preferred choice in oncology, inherited disorder screening, and pharmacogenomics.
NGS is increasingly being adopted by hospitals, academic institutions, and biotech firms to offer comprehensive genetic insights. Companies such as Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and BGI are at the forefront, offering NGS platforms that support high-throughput, multi-omics research, and personalized medicine programs.
While NGS dominates complex testing, PCR-based testing is growing rapidly due to its utility in point-of-care diagnostics and simpler mutation analysis. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is widely used for detecting known mutations, especially in reproductive health and infectious disease testing. Its speed, cost-efficiency, and compatibility with small labs make it ideal for decentralized settings.
The global response to COVID-19 elevated awareness and infrastructure for PCR technology, which is now being leveraged for expanded genetic applications. As newer versions like digital PCR and real-time PCR evolve, this segment is set to continue its upward trajectory.
Genetic Testing Market By Application Insights
Health and wellness-predisposition/risk analysis emerged as the dominant application, reflecting the growing consumer interest in understanding their genetic risks for chronic diseases, aging, metabolism, and lifestyle compatibility. Companies like 23andMe and AncestryDNA offer panels that inform users about their likelihood of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep disorders based on genetic markers.
This application is especially popular in regions with high health literacy and internet penetration. With consumers increasingly embracing preventive healthcare and self-monitoring, the demand for wellness genomics is expected to remain strong.
Newborn screening is the fastest-growing application segment, driven by government mandates, rising awareness, and technological improvements in early genetic diagnosis. Many countries have introduced policies requiring genetic screening for metabolic, endocrine, and blood disorders in newborns within the first days of life.
Early detection of disorders like phenylketonuria, congenital hypothyroidism, and cystic fibrosis can significantly reduce morbidity and improve outcomes. The increasing availability of portable screening devices and partnerships with maternity clinics are supporting expansion in this critical application area.
Genetic Testing Market By Product Insights
Consumables, including reagents, kits, and chips, dominated the product segment due to their recurring use in every genetic test conducted. Laboratories performing NGS, PCR, or microarray analysis require a consistent supply of these consumables for sample preparation, amplification, and sequencing. Their indispensable role and high usage frequency make them the largest revenue contributor in the value chain.
Major vendors offer bundled consumables optimized for proprietary platforms, creating long-term dependencies and stable revenue streams. This segment also benefits from advancements in multiplexing and high-sensitivity reagent design.
The software and services segment is expanding rapidly, driven by the need for genomic data analysis, interpretation, storage, and sharing. The complexity of NGS output and the emergence of multi-omics research require advanced bioinformatics tools and analytics services.
AI-powered platforms are being developed to predict disease risk, identify therapeutic targets, and visualize genomic variations. Cloud-based platforms such as BaseSpace by Illumina and Qiagen Digital Insights are enabling real-time collaboration between researchers and clinicians, thereby accelerating clinical translation.
Genetic Testing Market By Channel Insights
The online segment dominated the channel analysis as DTC genetic testing grew in popularity. Online ordering, at-home sample collection kits, and digital result portals have democratized access to genetic insights. Companies use user-friendly websites and apps to deliver complex genetic information through interactive dashboards, empowering consumers to make informed health and lifestyle choices.
The online model offers scalability, lower overheads, and direct consumer engagement, enabling companies to bypass traditional clinical gatekeeping. Strategic marketing on social media platforms has further fueled demand, especially among millennials and Gen Z.
Offline channels, such as hospitals, diagnostics centers, and specialized clinics, are growing rapidly due to their credibility, in-person support, and integration with physician-led care. For complex or sensitive genetic tests, such as those related to cancer or reproductive health, patients often prefer guidance from medical professionals.
Clinics also offer multi-disciplinary teams that can interpret results, recommend follow-ups, and provide counseling. Offline channels are crucial for integrating genetic testing into routine medical practice, driving adoption in conservative markets.
Genetic Testing Market By End-use Insights
Diagnostic laboratories dominated the end-use segment due to their specialization in processing high volumes of genetic tests, especially for clinical applications. Independent labs and hospital-affiliated labs are equipped with the infrastructure for advanced sequencing, analysis, and reporting.
Companies like Invitae, Myriad Genetics, and Labcorp have established extensive networks of labs offering a range of clinical tests from cancer panels to hereditary disorders. Their scalability, R&D capabilities, and partnerships with insurance providers ensure they maintain a central role in the market.
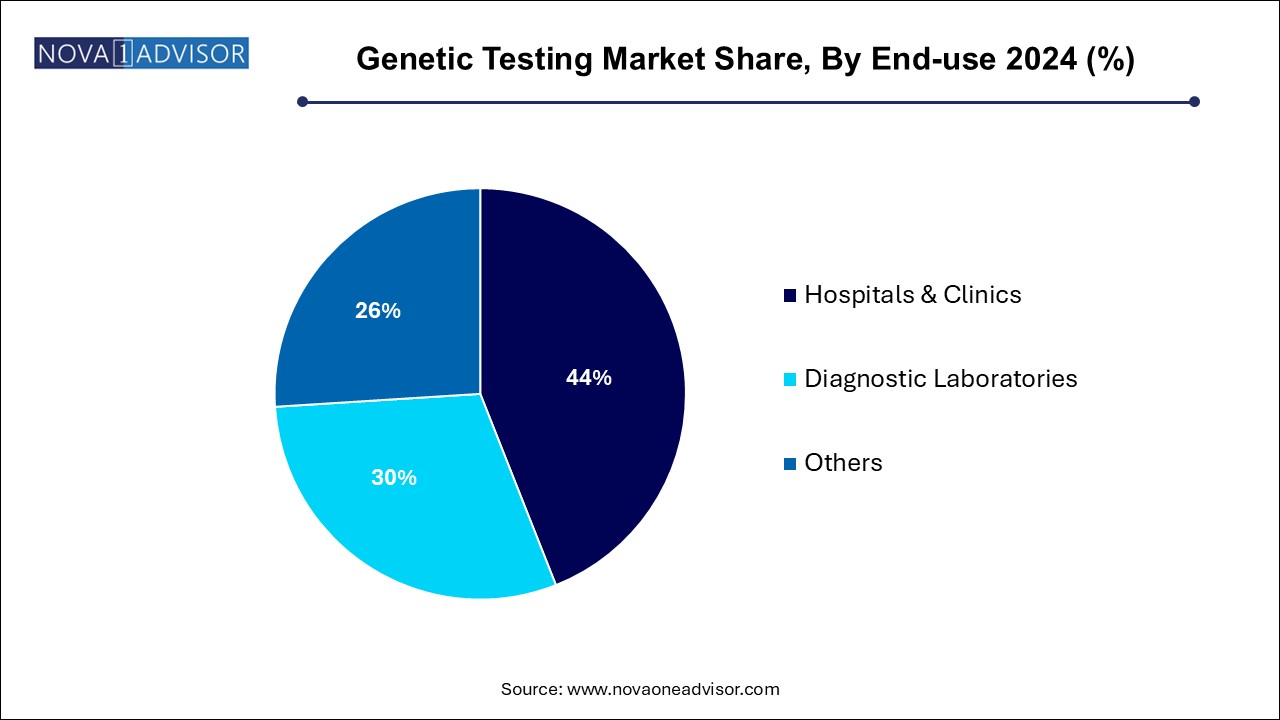
Hospitals and clinics are witnessing rapid growth in genetic testing adoption, driven by the integration of precision medicine into mainstream care. Hospitals are increasingly establishing genetic counseling units and investing in genomic infrastructure to support in-house testing.
Collaborations between hospitals and academic research centers are also facilitating the development of new gene panels and biomarker assays tailored for specific patient populations. As genetic data becomes a routine component of patient records, hospital use is expected to surge.
Genetic Testing Market By Regional Insights
North America, particularly the U.S., led the global genetic testing market owing to its strong healthcare infrastructure, early adoption of precision medicine, and the presence of major genomic companies. The region benefits from favorable reimbursement frameworks, government-backed genomics initiatives like the All of Us Research Program, and high public awareness.
Direct-to-consumer testing is especially popular in the U.S., with millions of people using services like 23andMe and AncestryDNA. The robust regulatory environment, along with strong investments in biotechnology and healthcare AI, makes North America a key innovation hub for genetic testing.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region due to rising healthcare expenditure, increasing incidence of genetic diseases, and growing awareness of preventive health. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing strong uptake of genetic tests, particularly in reproductive health and oncology.
Governments are investing in genomic databases and national screening programs. For instance, China's Precision Medicine Initiative aims to sequence over a million genomes by 2030. As genetic testing becomes more affordable and accessible, Asia-Pacific is poised for exponential growth.
Some of the prominent players in the genetic testing market include:
- 24 genetics
- Circle DNA
- Tellmegen
- 23andme
- AncestryDNA
- MyDNA
- Everly Well
- Igenomix
- VitaGen
- Myriad Genetics, Inc.
- Mapmygenome
- Helix OpCo LLC
- MyHeritage Ltd.
- Illumina, Inc.
- Color Genomics, Inc.
- Amgen, Inc.
- Beyond Nutrition Health and Wellness Services DMCC
Genetic Testing Market Recent Developments
-
23andMe (March 2025): Launched a new pharmacogenomics product line that helps users understand drug response profiles, expanding into personalized therapy.
-
Illumina (February 2025): Unveiled its latest high-throughput sequencer, the NovaSeq X2, promising faster genome sequencing at a fraction of previous costs.
-
Myriad Genetics (January 2025): Announced a strategic partnership with Mayo Clinic to expand hereditary cancer testing services across clinical networks.
-
Color Genomics (April 2025): Rolled out a workplace genomics program offering employees access to cardiovascular and cancer risk genetic screening.
-
Invitae (March 2025): Introduced a telehealth-based genetic counseling platform integrated with its diagnostic services for better patient navigation.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the genetic testing market
By Technology
- Next Generation Sequencing
- Array Technology
- PCR-based Testing
- FISH
- Others
By Application
- Ancestry & Ethnicity
- Traits Screening
- Genetic Disease Carrier Status
- New Baby Screening
- Health and Wellness-Predisposition/Risk/Tendency
By Product
- Consumables
- Equipment
- Software & Services
By Channel
By End-use
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


