The global multiparameter patient monitoring system market size was exhibited at USD 11.58 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 20.54 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
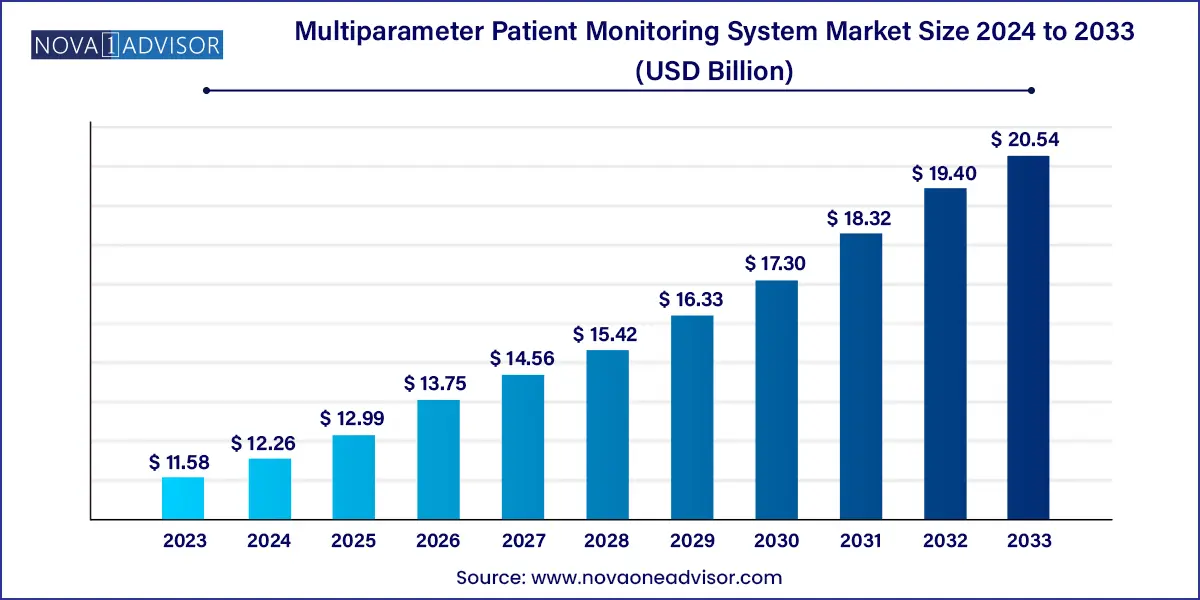
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the global market and accounted for 42.0% of the total share in 2023
- The portable segment dominated the revenue share in 2023 and accounted for 66.2% .
- The high acuity multiparameter patient monitoring systems segment dominated the market with a revenue share of over 45.7% in 2023.
- The geriatric segment accounted for the highest revenue share of 53.9% in 2023.
- The hospitals segment held the largest share of 41.0% in 2023.
Market Overview
The global multiparameter patient monitoring system market represents a critical component of modern healthcare infrastructure, enabling the continuous assessment of multiple physiological parameters in patients across care settings. These systems are vital in intensive care units (ICUs), emergency departments, surgical recovery rooms, and even homecare settings, where real-time monitoring can mean the difference between timely intervention and clinical deterioration.
Multiparameter patient monitoring systems (MPMS) typically track key metrics such as heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation (SpO2), temperature, and electrocardiogram (ECG) readings. These systems have evolved from bulky, single-location machines into compact, portable, and wireless-enabled solutions capable of integrating with electronic medical records (EMRs), cloud storage, and telehealth platforms.
The increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory conditions, combined with the growing aging population, has heightened the demand for constant monitoring, particularly for patients in critical or unstable conditions. Moreover, the global COVID-19 pandemic further underscored the need for reliable remote and in-hospital monitoring, prompting a wave of innovation and rapid adoption in this segment.
Today’s multiparameter monitors go beyond vital sign tracking. They include predictive analytics powered by AI, advanced alarm management systems to reduce fatigue, and interoperability with hospital networks for seamless data sharing. These technological enhancements are not only improving patient outcomes but are also aiding in resource optimization and cost containment in overwhelmed healthcare systems.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Adoption of wireless and wearable multiparameter monitors for remote and ambulatory care.
-
Integration with cloud platforms and EMRs, enabling real-time data sharing and predictive analytics.
-
Rising demand for portable devices in emergency transport, rural clinics, and homecare settings.
-
AI and machine learning algorithms for trend analysis, early warning scoring, and predictive alerts.
-
Miniaturization and battery efficiency improvements, allowing for compact, long-use monitors.
-
Increased use in ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) due to rising day-care surgeries and outpatient recovery needs.
-
Customized interfaces and dashboards for different acuity levels, improving usability in diverse care settings.
-
Government initiatives supporting remote patient monitoring, especially in chronic disease and elderly care management.
Multiparameter Patient Monitoring System Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 11.58 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 20.54 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 5.9% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Device, Acuity Level, Age Group, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Koninklijke Philips N.V.; GE Healthcare; Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.; Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA; Medtronic; Masimo; Skanray Technologies; SCHILLER; Spacelabs Healthcare; ICU Medical, Inc., SternMed GmbH. |
Segments Insights:
Device Type Insights
Portable multiparameter patient monitoring systems accounted for the largest market share, driven by increasing demand for flexibility and mobility in healthcare delivery. These devices are crucial in emergency care, ambulances, remote clinics, and homecare settings. Their portability allows healthcare professionals to track vital signs in real time across diverse care environments without compromising accuracy.
Portable monitors are also widely used in low-acuity hospital wards, outpatient surgical centers, and post-discharge monitoring programs. Advancements in lithium-ion battery efficiency, wireless data transfer, and compact display systems have made these devices more user-friendly and adaptable. For example, COVID-19 field hospitals around the world relied heavily on portable MPMS for continuous oxygen saturation and respiratory monitoring.
Meanwhile, fixed multiparameter monitors are growing steadily, particularly in high-acuity settings such as ICUs and operating rooms. These systems offer superior integration capabilities with ventilators, infusion pumps, and imaging systems. They are often equipped with multi-screen interfaces, higher parameter sensitivity, and robust alarm algorithms. However, their growth is comparatively slower due to higher setup costs and limited mobility.
Acuity Level Insights
High-acuity monitoring devices led the market by a wide margin due to their critical importance in intensive care units, emergency rooms, and surgical theaters. These devices can track up to 12 or more parameters, including advanced metrics like cardiac output, intracranial pressure, capnography, and central venous pressure. They are indispensable for patients on life support, undergoing complex surgeries, or those in unstable post-operative states.
Hospitals and trauma centers continue to invest in high-acuity systems, often with AI-powered analytics and alarm fatigue management features. For example, smart MPMS units used in neurosurgical ICUs are capable of combining vital sign data with imaging and lab reports, providing clinicians a holistic patient view.
However, medium-acuity systems are the fastest-growing segment. These are increasingly used in step-down units, rehabilitation wards, and ambulatory care settings, offering a cost-effective alternative for stable patients who still require regular monitoring. Medium-acuity monitors typically support five to seven parameters and are favored for managing chronic diseases or post-discharge transitions. Their growing use in emerging markets—where ICU infrastructure may be limited—adds to their momentum.
Age Group Insights
The adult age group dominated the market, reflecting the high burden of chronic diseases and surgical procedures among this demographic. Adult patients form the majority population in ICUs, general wards, and ambulatory surgery centers. Monitoring systems for this group are designed to accommodate variable physiological baselines and larger body sizes, making them standard equipment across all hospital types.
Conditions such as heart disease, hypertension, and respiratory ailments—common in adults—necessitate multiparameter tracking to ensure timely clinical intervention. These devices also support post-anesthesia recovery, where parameters like respiration rate and ECG must be closely watched.
Conversely, geriatric monitoring is the fastest-growing age segment. As populations age, especially in countries like Japan, Italy, and the U.S., the need for continuous, non-invasive monitoring of elderly patients is surging. Elderly patients are at higher risk of polypharmacy interactions, falls, and co-morbidities, requiring robust monitoring systems that can detect subtle changes in health status. Portable and wireless MPMS with AI-based alerts are proving especially effective in home and nursing home environments, driving segment growth.
End-use Insights
Hospitals are the primary end-users of multiparameter patient monitoring systems, contributing the largest market share. These institutions house ICUs, emergency rooms, and surgical suites where continuous monitoring is indispensable. Hospitals typically purchase a range of MPMS devices from fixed high-acuity systems for critical care to portable monitors for general wards. The scale of patient inflow, the need for triage, and compliance with quality standards make these devices a core investment.
Integration of MPMS into hospital information systems (HIS) and electronic health records (EHRs) has further solidified their value. For example, many hospitals use AI-enabled monitors that predict sepsis or cardiac arrest based on parameter trends, reducing mortality rates and litigation risks.
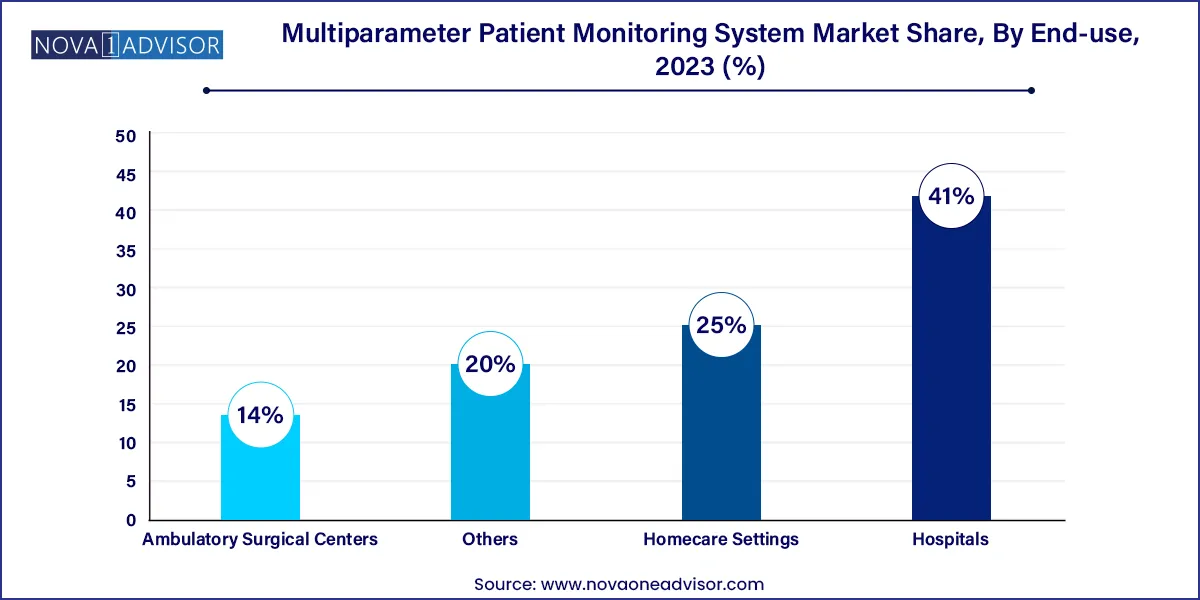
Homecare settings, however, are the fastest-growing end-use category. Advances in telemonitoring, IoT-based sensors, and government subsidies are allowing patients to receive hospital-level care in their homes. Chronic disease patients, post-op recovery cases, and palliative care individuals are increasingly being managed with home-based multiparameter monitors connected to central monitoring hubs. This shift is reshaping healthcare delivery by reducing pressure on hospitals while empowering patients and caregivers.
Regional Insights
North America led the global multiparameter patient monitoring system market due to its mature healthcare infrastructure, high technology adoption, and strong presence of leading market players. The United States is home to some of the largest hospital chains and medical research institutions that invest heavily in critical care and patient safety technologies.
The region’s robust reimbursement environment and growing geriatric population further support adoption. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) covers remote patient monitoring services, driving demand in both hospitals and homecare. Additionally, widespread integration of digital health records enables seamless interoperability of MPMS with other systems, enhancing care coordination.
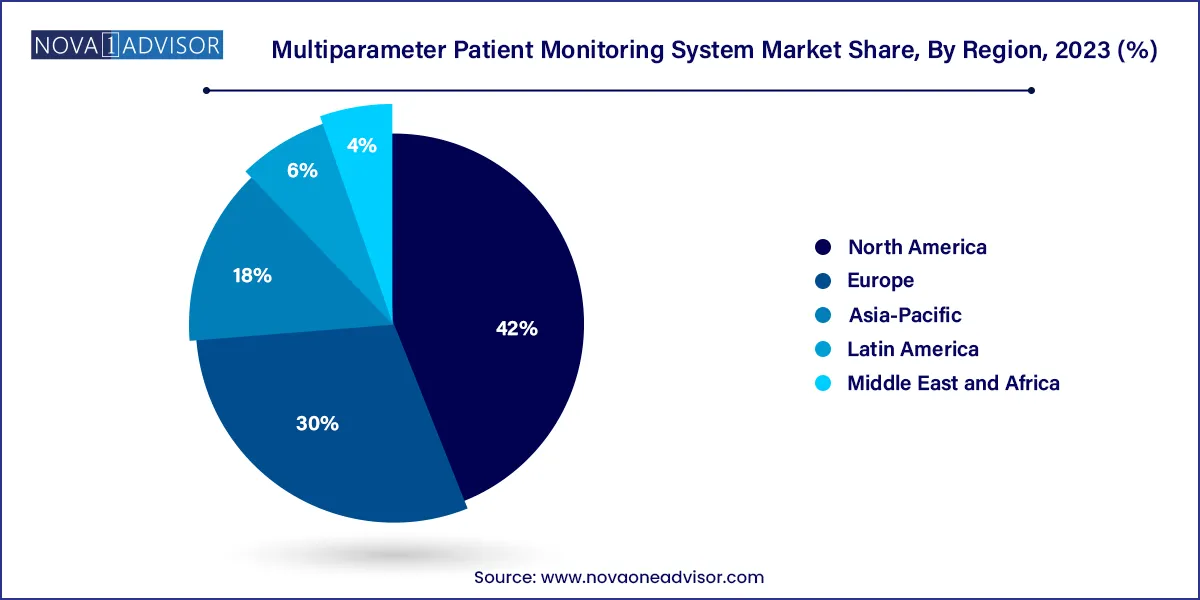
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by expanding healthcare access, rapid urbanization, and rising chronic disease prevalence. Countries like China, India, and Indonesia are investing significantly in upgrading hospital infrastructure, including ICUs and surgical units, where MPMS are essential.
Rising awareness of patient monitoring in both urban and rural settings, coupled with a growing medical tourism industry, is catalyzing demand for portable and affordable monitoring solutions. Local startups and multinational companies are introducing cost-effective, compact MPMS tailored to regional needs. Government-backed programs in India (Ayushman Bharat) and China's healthcare reforms are also subsidizing critical care expansion, further boosting market growth.
Some of the prominent players in the multiparameter patient monitoring system market include:
- SternMed GmbH
- Spacelabs Healthcare
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- ICU Medical, Inc.
- GE Healthcare
- Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA
- Medtronic
- MASIMO CORPORATION
- Skanray Technologies
- Schiller
- Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – Philips Healthcare launched its IntelliVue Guardian 5.0 system with predictive early warning scoring and cloud analytics integration for hospitals in Europe.
-
January 2025 – GE HealthCare announced the development of a compact, AI-powered portable MPMS unit optimized for homecare and ambulatory settings.
-
October 2024 – Mindray Medical International expanded its BeneVision series in the Asia-Pacific region, focusing on medium-acuity, wireless-connected monitors.
-
August 2024 – Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA introduced a modular patient monitoring platform with multi-parameter expansion modules and telehealth capabilities.
-
June 2024 – Nihon Kohden Corporation entered into a strategic partnership with a U.S.-based software firm to enhance AI-based alarm management in high-acuity MPMS devices.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global multiparameter patient monitoring system market.
Device
Acuity Level
Age Group
- Pediatric
- Adult
- Geriatric
End-Use
- Hospitals
- Homecare Settings
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



