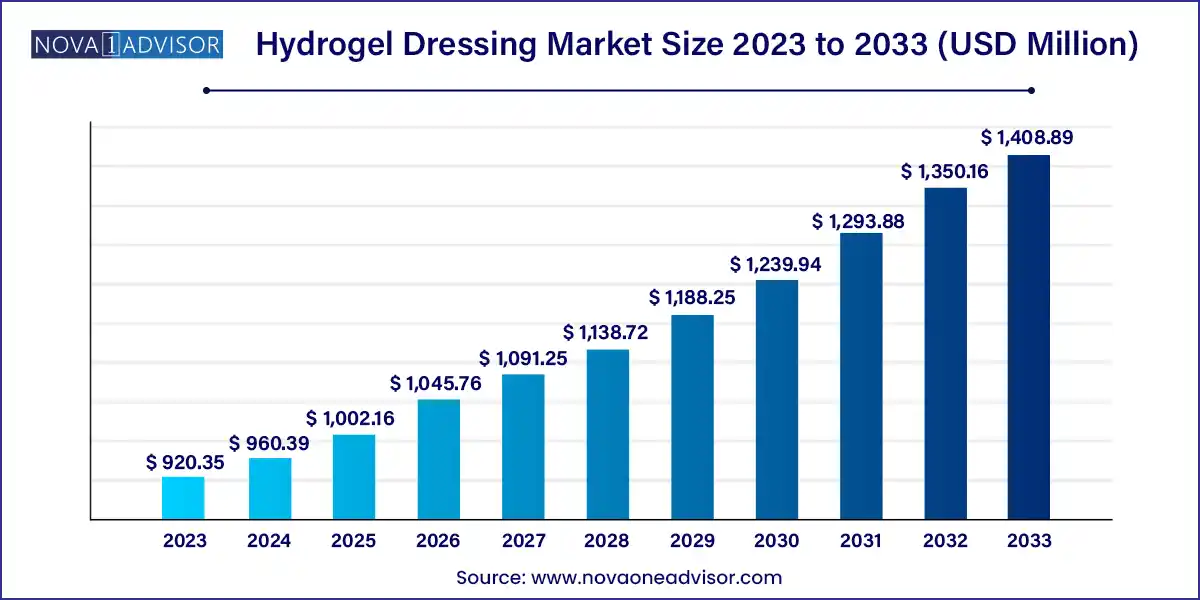
The global hydrogel dressing market size was exhibited at USD 920.35 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,408.89 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.35% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market in 2023 with a 48.0% share in 2023.
- The hospital segment dominated the market in 2023.
- Based on product, the amorphous hydrogel segment held a revenue share of 55.0% in 2023.
- The chronic wounds segment dominated the market in 2023 and is projected to show a considerable growth rate over the forecast years.
Market Overview
The Hydrogel Dressing Market is gaining substantial traction in the global advanced wound care sector, owing to its unique therapeutic properties and expanding range of applications. Hydrogel dressings, made primarily of water in a gel base, are known for their ability to maintain a moist wound environment, facilitate autolytic debridement, and relieve pain. These characteristics make them ideal for a wide variety of acute and chronic wounds, including burns, pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and surgical incisions.
The rise in chronic wound incidence fueled by aging populations, diabetes prevalence, obesity, and lifestyle disorders—is significantly contributing to market growth. At the same time, growing awareness among healthcare professionals and patients regarding wound healing solutions that improve comfort and reduce infection risks is driving adoption. Hydrogel dressings are particularly favored for wounds with minimal to moderate exudate, and their cooling effect helps reduce trauma and pain during dressing changes.
In recent years, technological advances have led to the development of next-generation hydrogel products with antimicrobial properties, higher absorbency, and better adhesion, expanding their usage in both inpatient and outpatient settings. Moreover, the shift toward home healthcare and telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of hydrogel dressings for at-home wound care. With rising investments in wound management technologies and strong demand from both developed and emerging markets, the hydrogel dressing market is positioned for consistent growth.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Demand for Advanced Wound Care Products: Hydrogel dressings are replacing traditional gauze and foam dressings due to their faster healing outcomes and patient comfort.
-
Development of Antimicrobial and Bioactive Hydrogels: Formulations infused with silver, iodine, and growth factors are being launched to prevent infections and stimulate tissue regeneration.
-
Home Healthcare Boom: Increasing preference for home-based wound care, especially among geriatric and post-surgical patients, is boosting demand for easy-to-use hydrogel products.
-
Smart Hydrogel Innovations: Emerging products integrate sensors to monitor wound healing parameters, moisture levels, and even detect infections in real-time.
-
Shift Toward Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Products: Sustainability concerns are prompting R&D into hydrogels that are both biodegradable and biocompatible.
-
Integration with Telehealth and Digital Wound Platforms: Hydrogel dressings are being used alongside remote monitoring apps and AI tools that track wound healing progress.
-
Government Initiatives to Tackle Chronic Wounds: Countries are launching national wound care programs to address pressure ulcers and diabetic wounds, especially in aging populations.
Hydrogel Dressing Market Report Scope
Market Driver: Increasing Incidence of Chronic Wounds Globally
A key driver of the hydrogel dressing market is the rising prevalence of chronic wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injuries, and venous leg ulcers. These wounds require prolonged management and significantly impact patient quality of life and healthcare costs. According to the U.S. National Institutes of Health, chronic wounds affect approximately 6.5 million Americans annually, with treatment costs exceeding $25 billion per year.
Diabetes a leading cause of foot ulcers is a major contributor to this trend. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that over 540 million adults worldwide had diabetes in 2023. Hydrogel dressings are particularly suited for these wounds, as they maintain an optimal moisture balance and help remove necrotic tissue without harming healthy cells. Their non-adherent nature also minimizes trauma during dressing changes. The global increase in elderly populations more prone to chronic wounds further elevates demand for advanced dressings like hydrogels in hospitals, long-term care, and home settings.
Market Restraint: Limited Absorptive Capacity and Cost Concerns
Despite their many benefits, hydrogel dressings face constraints due to their limited fluid-handling capacity, which restricts their use to wounds with minimal to moderate exudate. Heavily exuding wounds, such as infected ulcers or surgical sites with drainage, often require dressings with superior absorption capabilities like alginates or foam composites. This limits hydrogel adoption in high-exudate wound types and stages.
Moreover, hydrogel dressings are relatively more expensive than traditional dressings, creating cost barriers in resource-limited healthcare systems. In developing countries, where budget constraints are significant and access to advanced wound care remains limited, the higher price point of hydrogel products may deter large-scale adoption. Additionally, improper usage or inadequate training among caregivers and home users can lead to suboptimal outcomes, undermining clinical efficacy and patient confidence in these products.
Market Opportunity: Rising Adoption of Hydrogel Dressings in Home Healthcare
An exciting growth opportunity for the hydrogel dressing market lies in the expansion of home-based wound care, particularly for elderly, disabled, and post-operative patients. The shift toward outpatient care, driven by cost savings and patient comfort, has led to increased demand for dressings that are user-friendly, painless to apply and remove, and do not require frequent changes.
Hydrogel dressings, with their cooling effect, non-adherence, and soothing properties, are ideal for home use especially when managing pressure injuries, superficial burns, or diabetic ulcers. Their transparent or semi-transparent design also allows easy monitoring of wound condition without removal. With the proliferation of home healthcare providers, wound care kits, and telehealth consultations, manufacturers are targeting this segment with self-adhesive and pre-cut hydrogel formats that minimize application complexity. This shift is expected to accelerate hydrogel adoption in both developed countries with aging populations and emerging markets with growing access to home medical supplies.
Segments Insights:
By End-use
Hospitals currently dominate the end-use segment, owing to the high volume of chronic and acute wound cases treated in inpatient settings. Hospital protocols for advanced wound management frequently include hydrogel dressings, especially in intensive care units (ICUs), surgical wards, and burn units. Institutional procurement through group purchasing organizations (GPOs) and product bundling with wound care devices contributes to higher market share in this segment. Additionally, hospitals often drive early adoption of new hydrogel innovations through clinical trials and formulary evaluations.
However, home healthcare is the fastest-growing end-use segment, supported by an aging global population, increasing outpatient procedures, and growth in remote care models. As patients seek comfort and cost-efficiency outside hospital environments, home-based wound care is becoming standard for conditions like post-surgical wounds, pressure injuries, and minor burns. Hydrogel dressings, with their easy application and soothing effect, are ideal for at-home use. Telehealth platforms and wound care apps are enabling remote monitoring, making home healthcare a scalable and attractive market for hydrogel product manufacturers.
By Product Insights
Amorphous hydrogels dominate the market, favored for their versatility and ease of application across irregular or deep wounds. These free-flowing gel formulations can be directly applied to the wound bed or used with secondary dressings. They are commonly used in wound care clinics and hospitals for pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and radiation burns. Their soothing and cooling effect also makes them ideal for pain management, especially in first- and second-degree burns. Amorphous hydrogels are often preferred in long-term care and palliative settings where comfort and ease of application are top priorities.
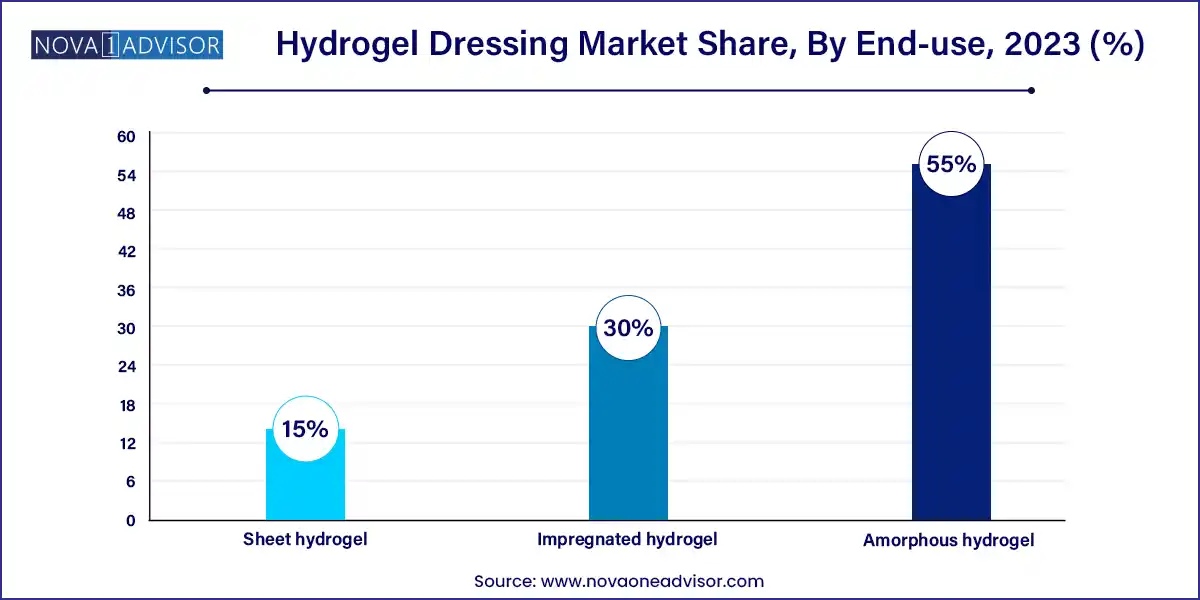
In contrast, sheet hydrogel products are the fastest-growing segment, thanks to their convenient handling, reduced risk of leakage, and improved cosmetic outcomes. These sheets are precut and often reinforced with supportive backing materials, making them easy to place and remove. Their semi-transparent nature allows wound monitoring without disruption, and newer antimicrobial versions infused with silver or honey offer additional therapeutic benefits. Sheet hydrogels are gaining popularity in outpatient wound clinics and home care settings due to their lower frequency of dressing changes and clean application process.
By Application Insights
Chronic wounds represent the largest application segment, reflecting the global burden of diabetes, vascular diseases, and immobility among aging populations. Chronic wounds, including pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and venous leg ulcers, often take weeks to months to heal and require ongoing care to prevent infection and promote tissue regeneration. Hydrogel dressings play a pivotal role in these cases by facilitating autolytic debridement and maintaining a moist wound environment. They are also useful in managing odor and reducing inflammation, key concerns in chronic wound care.
On the other hand, acute wounds are the fastest-growing application segment, driven by a rise in surgical procedures, trauma cases, and burn injuries worldwide. Post-operative wounds, abrasions, and superficial burns benefit significantly from hydrogel dressings due to their cooling, pain-relieving, and non-adherent properties. In surgical and trauma settings, hydrogel sheets are being increasingly used to promote healing and minimize scarring. The demand for faster wound healing, improved post-surgical outcomes, and patient comfort is pushing hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers to adopt hydrogel solutions more frequently.
By Regional Insights
North America holds the largest share of the hydrogel dressing market, driven by high healthcare expenditure, robust reimbursement systems, and strong awareness of advanced wound care solutions. The U.S. and Canada have large elderly populations, high diabetes prevalence, and well-developed hospital infrastructure—all of which contribute to consistent demand for hydrogel dressings. Leading companies like 3M, Smith & Nephew, and Coloplast have a strong retail and hospital presence across North America. In addition, favorable FDA regulations and widespread insurance coverage for chronic wound treatments support hydrogel product penetration.
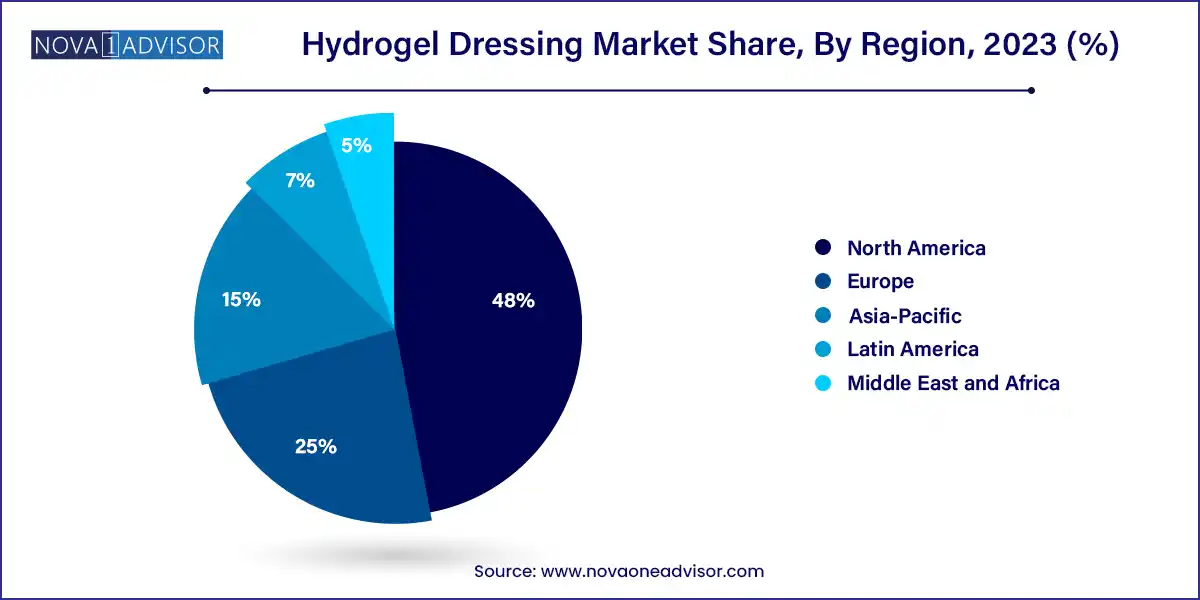
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, reflecting rising healthcare spending, expanding access to modern wound care, and growing incidences of diabetes and burns. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing in healthcare infrastructure and implementing national wound care guidelines. Rapid urbanization, increasing surgical volumes, and government-led diabetic foot care programs are further fueling regional demand. Multinational companies are entering into partnerships with local distributors, while regional players are launching affordable hydrogel products to cater to underserved populations. The shift toward home healthcare and rising e-commerce activity is also boosting retail sales of hydrogel dressings in Asia-Pacific.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – Smith & Nephew introduced a next-gen antimicrobial sheet hydrogel dressing with silver ions, aimed at reducing hospital-acquired infections in surgical wounds.
-
January 2025 – ConvaTec Group expanded its AQUACEL Hydrogel line in European markets with enhanced conformability and patient-reported comfort features for burn care.
-
October 2024 – 3M Health Care announced the acquisition of a mid-sized wound care startup focused on smart hydrogels that monitor moisture levels and healing progress via mobile app integration.
-
August 2024 – Medline Industries launched a biodegradable amorphous hydrogel gel tube in India as part of its cost-effective wound care product series for emerging markets.
-
June 2024 – B. Braun Melsungen AG received CE approval for a dual-action hydrogel dressing with embedded pain-relief agents, targeting post-surgical wound recovery.
Some of the prominent players in the Hydrogel dressing market include:
- Cardinal Health
- Smith & Nephew
- 3M
- ConvaTec Group PLC
- Medline Industries, Inc.
- Integra LifeSciences Corp.
- McKesson Medical-Surgical
- DermaRite Industries, LLC
- AMERX Health Care Corp.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global hydrogel dressing market.
Product
- Amorphous hydrogel
- Impregnated hydrogel
- Sheet hydrogel
Application
-
- Surgical & traumatic wounds
- Burns
-
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Pressure ulcers
- Venous leg ulcers
- Other chronic wounds
End-use
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Home Healthcare
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



