Nanomedicine Market Size and Growth
The global nanomedicine market size was valued at USD 191.19 billion in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 571.91 billion by 2033, registering a CAGR of 11.58% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
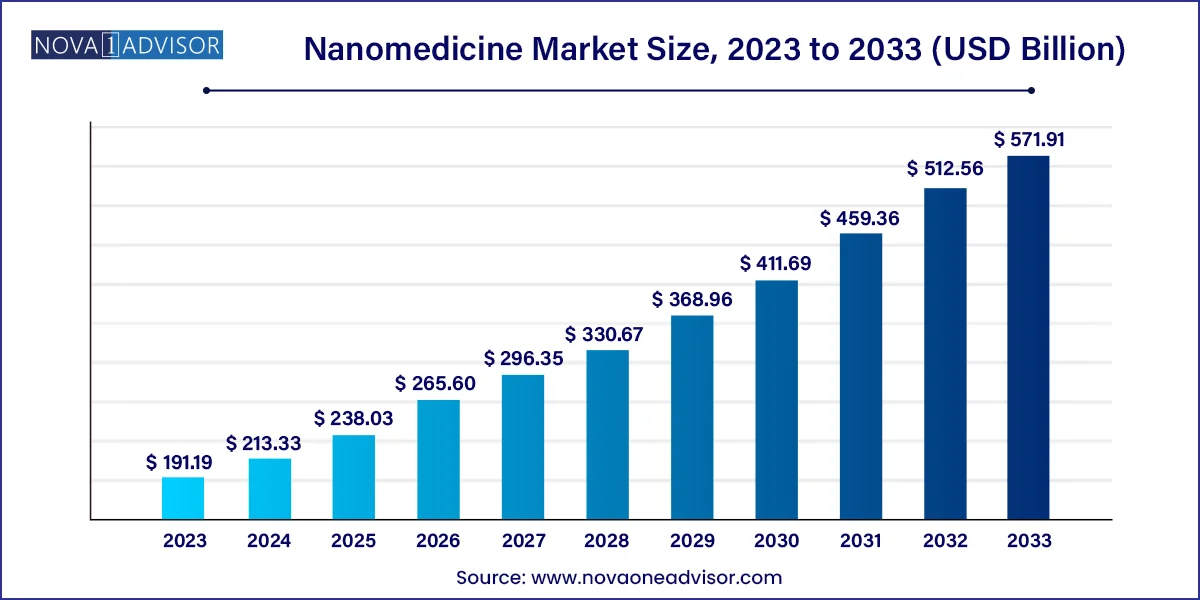
Nanomedicine Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the market with a share of 51.91% in 2023.
- The Asia Pacific market is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 14.08% during 2023-2033.
- The drug delivery segment dominated the nanomedicine market in 2023 with a share of 39.11%
- The therapeutics segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth rate of 12.79% from 2023 to 2033.
- The clinical oncology segment dominated the market with a share of 35.44% in 2023.
- The infectious disease segment is expected to grow at a rapid CAGR of 12.32% by 2033
- The nanoparticles segment captured the highest market share of 79.32% in 2023
- The nanotubes segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 10.90% from 2023 to 2033
Market Overview
The Nanomedicine Market represents one of the most advanced frontiers in biomedical innovation, combining the power of nanotechnology with the complexity of human biology to improve the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases. Nanomedicine involves the use of nanoscale materials—typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers—in the form of nanoparticles, liposomes, dendrimers, nanotubes, and other nano-constructs, to deliver drugs, enhance imaging, and repair tissues at the cellular and molecular levels.
Over the past two decades, nanomedicine has transitioned from academic research into a commercial reality. It now plays a crucial role in various applications such as targeted drug delivery, cancer therapy, molecular imaging, regenerative medicine, and biosensing. The ability to engineer nanoparticles to navigate biological barriers, target specific cells or tissues, and release therapeutic payloads in a controlled fashion has revolutionized treatment paradigms for cancer, infectious diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions.
Market expansion is driven by an increasing demand for personalized medicine, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and a growing need for minimally invasive treatments. The development of nanomedicine-enabled diagnostics and theranostic tools (combining therapy and diagnostics) is creating entirely new avenues for early detection and precise intervention. Moreover, regulatory approvals for nanomedicine-based drugs and devices, such as Doxil (liposomal doxorubicin) and Abraxane (albumin-bound paclitaxel), have validated the commercial potential of the sector.
As innovation accelerates, nanomedicine is expected to penetrate deeper into mainstream healthcare. However, challenges around scalability, regulatory clarity, and long-term safety remain, demanding coordinated efforts from academia, industry, and regulatory bodies. Nevertheless, the nanomedicine market is poised to become a cornerstone of next-generation healthcare, blending biotechnology, materials science, and clinical medicine in ways previously unimaginable.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Focus on Targeted Drug Delivery: Nanocarriers are increasingly used to deliver drugs specifically to disease sites, minimizing systemic toxicity and improving therapeutic efficacy.
-
Integration of Theranostics: Combining diagnostics and therapy in a single nanoplatform is gaining momentum, particularly in oncology for real-time tumor monitoring and treatment.
-
Nanomedicine in mRNA and Gene Therapy Delivery: Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), proven successful in COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, are being repurposed for a variety of genetic and infectious diseases.
-
Emergence of Smart Nanodevices: Programmable nanorobots and sensors are being developed for precision surgery, targeted drug release, and biosignal monitoring.
-
Personalized Nanomedicine: Leveraging patient-specific biomarkers to develop tailored nanotherapeutic and diagnostic solutions.
-
Biodegradable Nanoparticles: Growing demand for biodegradable and non-toxic nanoparticles to enhance biocompatibility and reduce accumulation in tissues.
-
Nanotechnology in Implantable Devices: Nanocoatings and nanostructures are improving the functionality and integration of orthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular implants.
-
Expansion in Infectious Disease Applications: COVID-19 demonstrated nanomedicine’s value in rapid vaccine delivery and is now being extended to influenza, tuberculosis, and emerging pathogens.
Nanomedicine Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 213.33 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 571.91 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 11.58% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Application, indication, molecule type, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott Laboratories; CombiMatrix Corporation; Celgene Corporation; Nanospectra Biosciences, Inc.; GE Healthcare; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals; Merck & Co., Inc.; Pfizer, Inc.; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.; Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
Market Driver: Increasing Prevalence of Chronic and Life-Threatening Diseases
A significant driver of the nanomedicine market is the growing burden of chronic and life-threatening illnesses, such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. These conditions often require long-term, systemic treatment with significant side effects. Nanomedicine offers a transformative approach by allowing site-specific delivery of therapeutics, which enhances efficacy while reducing toxicity.
For example, in oncology, traditional chemotherapy affects both cancerous and healthy cells, leading to adverse effects. Nanocarriers such as liposomes or polymeric nanoparticles can encapsulate chemotherapeutics and deliver them directly to tumor cells using targeting ligands, exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. This not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the safety profile of otherwise toxic drugs. With the global cancer burden expected to rise to over 28 million cases annually by 2040, nanomedicine’s ability to deliver precision treatment is a major market catalyst.
Market Restraint: Regulatory Complexity and High Development Costs
Despite its potential, nanomedicine faces a significant market restraint: regulatory ambiguity and high costs of development. Unlike traditional small-molecule drugs, nanomedicines do not always fit neatly into existing regulatory frameworks. Their novel mechanisms, multifunctionality, and complex interactions with biological systems demand comprehensive evaluation of toxicity, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and long-term safety.
Moreover, the manufacturing of nanomedicine involves intricate processes such as particle size control, surface modification, and sterility maintenance, which can be both expensive and technically challenging. Scaling up from lab-scale production to clinical-grade manufacturing often requires bespoke facilities and quality control systems, further driving up costs. These barriers can discourage smaller biotech firms from entering the market and extend timelines for product commercialization, limiting the pace of innovation.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of mRNA Technology and Nanocarriers in Vaccinology
One of the most promising opportunities in the nanomedicine market is the expansion of mRNA vaccine and gene therapy delivery using nanocarriers, especially lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). The success of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna both utilizing LNPs for delivery has validated the platform and opened doors for broader application.
Researchers are now exploring mRNA-LNP technologies for influenza, RSV, malaria, Zika, and cancer vaccines, among others. Nanocarriers improve the stability, cellular uptake, and controlled release of mRNA, solving the challenges of degradation and immunogenicity. This delivery method is also being adapted for CRISPR-based gene editing, where the precision and safety of the delivery vehicle are crucial. The global investment in vaccine platforms and gene therapy delivery systems is expected to surge in the coming years, creating ample growth opportunities for nanomedicine developers.
Segmental Analysis
By Application Scope
Therapeutics dominate the application scope of the nanomedicine market, especially in cancer, cardiovascular, and neurological disease management. Therapeutic nanomedicine includes drug delivery systems, nanoformulated chemotherapy agents, and nano-encapsulated anti-inflammatories. These products have already made it to the market, with several more in advanced clinical trials. The ability to modulate drug release kinetics and target-specific cells makes nanomedicine particularly effective in treating tumors, where traditional therapies have limited specificity.
In-vivo imaging is the fastest-growing application, thanks to its critical role in early diagnosis and disease monitoring. Nanoparticles enhance contrast in MRI, CT, PET, and optical imaging modalities by selectively accumulating in pathological tissues. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs), quantum dots, and gold nanoclusters are being explored to detect tumors at earlier stages with higher resolution. This segment is expected to grow rapidly as non-invasive imaging becomes central to personalized treatment planning and therapy tracking.
By Indication Scope
Clinical oncology is the largest segment by indication, reflecting the immense research and commercial activity in cancer nanomedicine. Numerous nanocarriers, including liposomes, dendrimers, and polymeric micelles, are being used to deliver chemotherapeutics, siRNA, and immunotherapies to tumor sites. FDA-approved products like Abraxane and Doxil have proven that nanomedicine can extend survival and improve quality of life in patients with advanced malignancies.
Infectious diseases are the fastest-growing indication, especially post-COVID-19. The pandemic underscored the value of rapid-response vaccine platforms and accelerated the global investment in nano-enabled delivery systems. Lipid nanoparticles used in COVID-19 vaccines have set a precedent for developing similar platforms for influenza, HIV, and neglected tropical diseases. Nanomedicine is also being explored to deliver antimicrobial peptides and improve the penetration of antibiotics into resistant bacterial biofilms.
By Molecule Type Scope
Nanoparticles dominate the molecule type segment, particularly liposomes, polymers, and metal oxide particles. Liposomal drug delivery has matured significantly, with applications ranging from antifungals to anticancer drugs. Polymer–drug conjugates offer high loading efficiency and controlled release, while metal nanoparticles like gold and silver are used in both diagnostics and photothermal therapies.
Nanodevices are the fastest-growing segment, driven by the advent of smart diagnostics and implantable nanosensors. These devices are capable of real-time biomarker monitoring, targeted drug release, and even performing nanoscale surgical interventions. Examples include glucose-monitoring nanochips, self-regulating insulin delivery nanodevices, and targeted photothermal therapy agents activated by laser light. Though still in early stages, nanodevices represent the future of precision medicine and digital health convergence.
Regional Analysis
North America leads the global nanomedicine market, underpinned by strong academic research ecosystems, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and significant public and private funding. The United States houses numerous nanotech pioneers and major pharmaceutical players investing in nanomedicine R&D. Institutions like the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) provide robust support for translational research and commercialization.
The region is also home to several FDA-approved nanomedicine products and maintains a favorable regulatory environment for novel therapies. With high adoption of personalized medicine, presence of cutting-edge clinical trial networks, and growing consumer awareness, North America is expected to retain its dominance throughout the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by rising healthcare expenditure, strong biotech industry growth, and government investment in nanotechnology. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are actively funding nanomedicine research and infrastructure development. China’s 14th Five-Year Plan includes specific provisions for nanotechnology development, while India’s DBT and DST are supporting translational nanomedicine research for diseases like tuberculosis and cancer.
The region is also experiencing a rising prevalence of chronic diseases and greater demand for affordable, innovative treatments. Asia-Pacific is rapidly adopting nano-based diagnostics and therapeutics, particularly in oncology and infectious disease management. Local players are also entering global partnerships to co-develop and manufacture nanomedicine products, further enhancing regional capabilities.
Nanomedicine Market Top Key Companies:
- Abbott Laboratories
- CombiMatrix Corporation
- Celgene Corporation
- Nanospectra Biosciences, Inc.
- GE Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Moderna announced a partnership with AstraZeneca to develop next-gen lipid nanoparticle platforms for mRNA cancer vaccines and personalized oncology therapeutics.
-
January 2025: Nanospectra Biosciences began Phase II clinical trials of its AuroLase® therapy, a nanoshell-based photothermal ablation treatment for prostate cancer.
-
November 2024: Samsung Biologics launched a nanotechnology-based formulation platform for improving bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs, in partnership with a U.S. biotech firm.
-
September 2024: India’s Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) approved funding for five nanomedicine projects targeting tuberculosis and cervical cancer.
-
July 2024: Nanobiotix, a French biotech company, received Fast Track designation from the FDA for its radio-enhancing nanoparticle NBTXR3, used in soft tissue sarcoma.
Nanomedicine Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Nanomedicine market.
By Application Scope
- Therapeutics
- In-vitro Diagnostics
- Drug Delivery
- In-vivo Imaging
- Implants
By Indication Scope
- Clinical Oncology
- Infectious Diseases
- Clinical Cardiology
- Orthopedics
- Others
By Molecule Type Scope
- Nanoparticles
- Metal & Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
- Liposomes
- Polymers & Polymer Drug Conjugates
- Hydrogel Nanoparticles
- Dendrimers
- Inorganic Nanoparticles
- Nanoshells
- Nanotubes
- Nanodevices
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

