The global nasal drug delivery technology market size was exhibited at USD 72.89 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 150.93 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.55% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
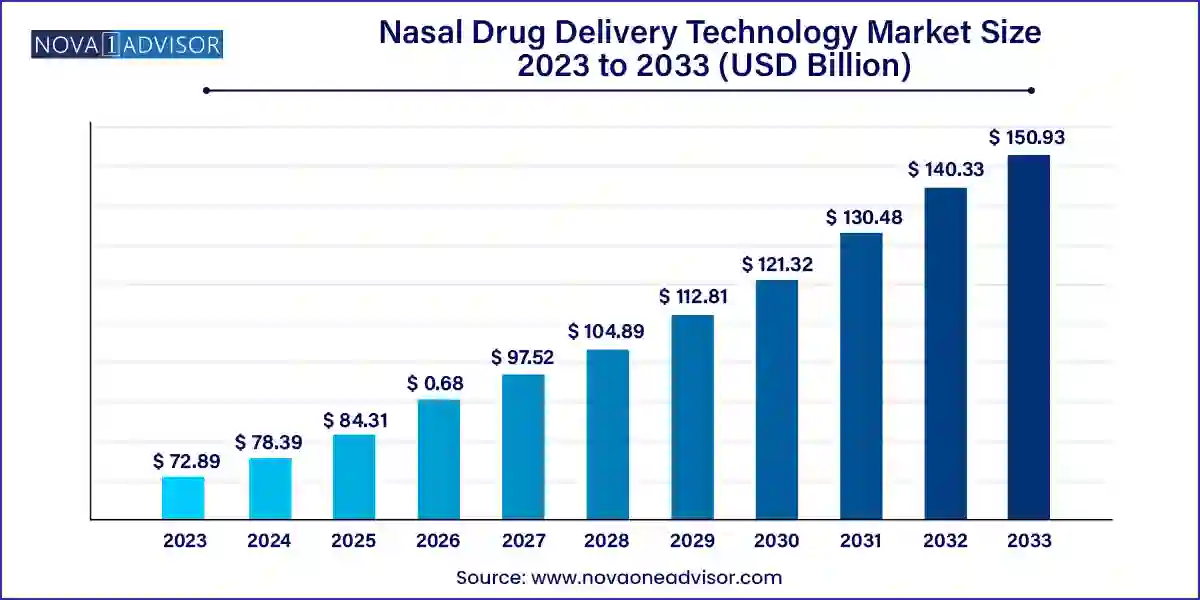
Key Takeaways:
- North America held the largest share of over 31.0% in 2023.
- The nasal spray segment held the largest revenue share of over 35.0% in 2023
- The non-pressurized container segment led the market with a revenue share of over 85.0% in 2023.
- The pressurized containers segment is estimated to register a notable CAGR of 7.38% over the forecast period.
- The retail pharmacies segment accounted for the largest share in 2023 owing to the easy availability and convenience.
- The rhinitis segment held the largest share of over 31.0% in 2023 due to the availability of related products for its treatment.
Market Overview
The nasal drug delivery technology market is becoming increasingly vital in the global pharmaceutical industry as it provides a non-invasive, fast-acting, and patient-compliant method of drug administration. Utilizing the nasal mucosa as a conduit to systemic circulation, this route bypasses hepatic first-pass metabolism and enables rapid onset of therapeutic effects. This has made nasal delivery particularly attractive for treating acute and chronic conditions ranging from allergic rhinitis and migraines to breakthrough pain and even systemic diseases like Parkinson's.
Historically confined to decongestants and anti-allergy treatments, the scope of nasal delivery has expanded substantially with technological advancements in formulation science, delivery devices, and absorption enhancers. The market is being propelled by the increasing prevalence of respiratory diseases, CNS disorders, and a growing demand for pain management options that offer improved bioavailability and ease of use. Furthermore, intranasal vaccines and biologics have emerged as frontier segments, especially in the wake of global pandemics and the need for needle-free immunization alternatives.
This growing appeal of nasal drug delivery technologies is also influenced by the pharmaceutical industry's shifting focus toward patient-centric care. Innovations such as powder-based delivery systems, smart inhalers, and bioadhesive gels are driving higher drug efficacy and safety. The market is being shaped not only by clinical needs but also by preferences in consumer healthcare, particularly in over-the-counter (OTC) segments.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising adoption of nasal sprays for migraine and acute pain management
-
Expansion of nasal vaccines, especially for influenza and COVID-19 variants
-
Growing use of nasal delivery for CNS-active drugs (e.g., seizure rescue medications)
-
Increased demand for preservative-free and multi-dose nasal devices
-
Development of mucoadhesive nasal gels for improved retention and absorption
-
Progress in dry powder nasal formulations to enhance stability and portability
-
Adoption of smart nasal drug delivery devices integrating dose monitoring
-
Regulatory encouragement for needle-free delivery platforms, especially in pediatrics
Report Scope of The Nasal Drug Delivery Technology Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 78.39 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 150.93 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 7.55% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Dosage Form, Container Type, Therapeutic Application, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
GlaxoSmithKline PLC; AstraZeneca PLC; Pfizer, Inc.; OptiNose, Inc.; Becton, Dickinson and Company; Promius Pharma, LLC; Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd.; B.F. Ascher & Company, Inc.; PendoPharm, Inc.; Douglas Pharmaceuticals Ltd.; ENT Technologies Pty. Ltd.; NAVEH Pharma Ltd. |
Market Driver: Demand for Rapid-Action Therapeutics
A primary driver for the nasal drug delivery market is the growing demand for rapid-onset therapeutics, particularly in emergency or acute care settings. Nasal administration provides a direct pathway to systemic circulation through the highly vascularized nasal cavity, enabling faster drug absorption than oral routes. This is particularly beneficial in neurological emergencies such as epileptic seizures, where nasal midazolam has proven life-saving in out-of-hospital settings.
In pain management, intranasal fentanyl and ketorolac have seen increasing use for breakthrough pain due to their rapid action. For migraine attacks, drugs like sumatriptan nasal sprays offer relief in minutes, bypassing gastrointestinal absorption issues. These capabilities position nasal delivery as a preferred alternative in both chronic care and acute rescue scenarios.
Market Restraint: Limited Volume and Dose Precision Challenges
Despite its advantages, nasal drug delivery is limited by the small volume of medication that can be administered—typically between 25-200 microliters per nostril. This restricts its use to highly potent drugs and can pose challenges for consistency in dosing, particularly in drugs that require exact plasma concentration thresholds. Additionally, inter-patient variability in nasal mucosa absorption, mucociliary clearance, and nasal pathology (e.g., congestion) can affect the reliability of drug delivery.
Furthermore, improper use of devices by patients can lead to inadequate dosing or wastage. This necessitates better patient education, device innovation, and sometimes higher production costs to ensure consistent therapeutic outcomes. Manufacturers must invest in user-friendly designs and precision-engineered nozzles to overcome these inherent limitations.
Market Opportunity: Expansion into CNS and Hormonal Therapies
The expanding use of nasal delivery for central nervous system (CNS) and hormonal therapies presents a significant growth opportunity. The nasal cavity offers a direct route to the brain via the olfactory and trigeminal pathways, bypassing the blood-brain barrier. This is particularly promising for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where drug delivery to the brain is notoriously difficult.
Nasal delivery of peptide-based hormonal treatments, such as oxytocin, calcitonin, and desmopressin, is also gaining ground due to enhanced patient compliance and favorable absorption kinetics. This trend is being accelerated by technological innovations in absorption enhancers and mucoadhesive agents. Companies that successfully leverage these advances may unlock new therapeutic segments and strengthen their competitive edge.
Segments:
Nasal sprays dominated the nasal drug delivery market, largely due to their widespread application in treating allergic rhinitis, nasal congestion, and flu symptoms. Nasal sprays offer uniform distribution across the mucosal surface and are typically preferred for both OTC and prescription medications. Their compact form factor, ease of use, and fast onset of action make them highly desirable for both patients and clinicians. Innovations such as metered-dose pumps and preservative-free formulations have further enhanced the market share of nasal sprays.
Nasal powders are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, driven by their improved shelf stability and absence of preservatives. Powder formulations avoid microbial contamination issues associated with aqueous sprays and are better suited for heat-sensitive biologics. For example, dry powder naloxone has been used successfully in opioid overdose emergencies. Furthermore, powder-based vaccines and pain management drugs are in development stages, signaling strong future potential for this segment.
Nasal Drug Delivery Technology Market By Container Type Insights
Non-pressurized containers currently dominate the market due to their use in most nasal sprays and drops. These containers are simple to manufacture, cost-effective, and allow metered dosing, making them ideal for chronic use medications. Multi-dose and unit-dose designs with anti-microbial features are further supporting their adoption, especially in clinical and home-care settings.
Pressurized containers are gaining momentum in niche applications, particularly in nasal aerosol systems where uniform particle size distribution and deep nasal penetration are required. These are often used in sophisticated drug delivery platforms involving steroids or rescue medications. Innovations in propellant-free pressurized systems and eco-friendly materials are anticipated to expand the application scope of this segment.
Nasal Drug Delivery Technology Market By Distribution Channel Insights
Retail pharmacies lead the distribution channel segment, accounting for the largest share due to the accessibility of nasal sprays and drops over-the-counter. Chain pharmacies, independent drugstores, and supermarket pharmacies provide wide availability of prescription and non-prescription nasal medications. Seasonal spikes in allergy and flu-related products make this channel highly profitable.
Online pharmacies are rapidly expanding their market share due to increasing consumer preference for contactless delivery and digital health platforms. E-commerce giants and pharmacy-focused platforms offer home delivery, subscription models, and better price comparison, which appeal to tech-savvy and mobility-restricted patients alike.
Nasal Drug Delivery Technology Market By Therapeutic Application Insights
Nasal congestion and rhinitis dominate the therapeutic application segment, primarily due to the high global prevalence of seasonal allergies, common colds, and environmental pollutants. OTC nasal sprays containing antihistamines, decongestants, or corticosteroids remain the frontline treatment options. Their availability without a prescription and immediate relief factor contribute to sustained demand.
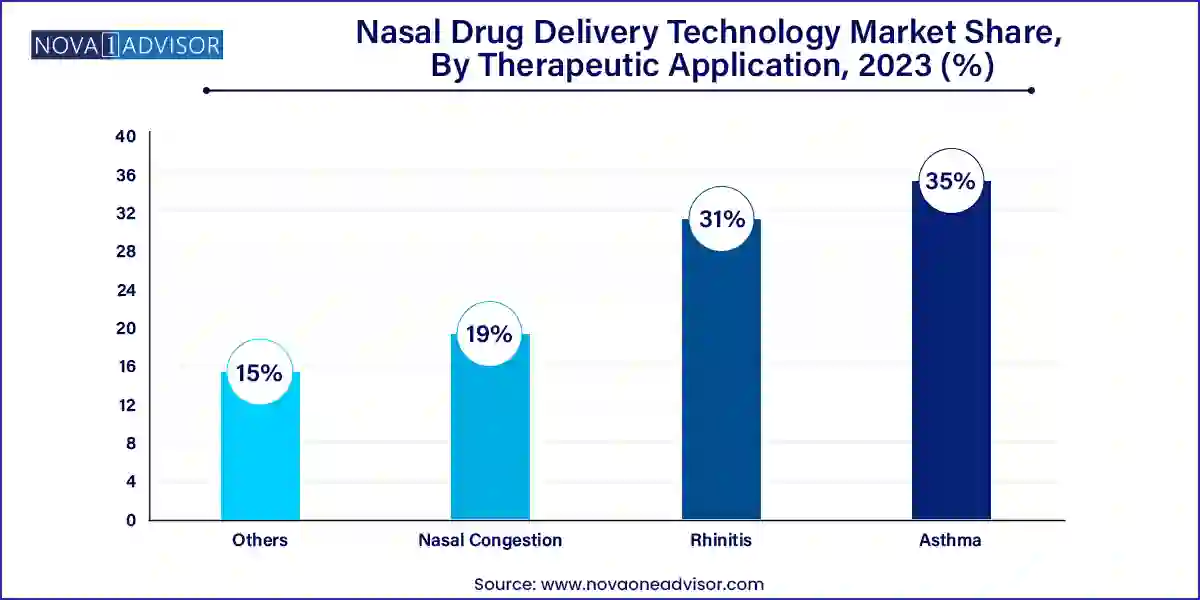
Asthma and other respiratory conditions are the fastest-growing applications, especially as adjunct therapies or alternatives to inhalation devices. Intranasal corticosteroids and beta-agonists are being researched for direct respiratory and systemic effects. Additionally, intranasal administration of monoclonal antibodies for respiratory viruses is a novel area of research gaining interest.
Nasal Drug Delivery Technology Market By Regional Insights
North America dominates the global nasal drug delivery technology market, with the U.S. leading in terms of innovation, regulatory approvals, and consumer adoption. High prevalence of respiratory conditions, allergies, and CNS disorders, coupled with a well-structured healthcare system and strong pharmaceutical R&D, supports market dominance. The region also boasts a favorable reimbursement framework and fast-track regulatory pathways like the FDA's 505(b)(2) NDA process, facilitating quicker commercialization of nasal drug products.

Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by increasing healthcare access, rising awareness about non-invasive therapies, and expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capacity. Countries such as China, India, and South Korea are investing heavily in biotechnology and drug delivery innovation. In addition, the growing burden of asthma and allergic diseases, particularly in urban populations, is stimulating demand for nasal drug products.
Some of the prominent players in the Nasal drug delivery technology market include:
- GlaxoSmithKline PLC
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Pfizer, Inc.
- OptiNose, Inc.
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Promius Pharma, LLC
- Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- B.F. Ascher & Company, Inc.
- PendoPharm, Inc.
- Douglas Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- ENT Technologies Pty. Ltd.
- NAVEH Pharma Ltd.
Recent Developments
-
In April 2025, Pfizer announced a strategic collaboration with a biotech firm to develop an intranasal COVID-19 booster using dry powder delivery technology.
-
In January 2025, Bausch Health launched a preservative-free fluticasone nasal spray in the U.S., expanding its allergy and respiratory portfolio.
-
In November 2024, Impel Pharmaceuticals received FDA approval for TRUDHESA, an innovative dihydroergotamine mesylate nasal spray for acute migraine.
-
In September 2024, Altamira Therapeutics began Phase 2 trials for its intranasal RNA-based therapy targeting viral infections.
-
In June 2024, Aptar Pharma launched a digital nasal spray delivery system with dose tracking and app integration for improved adherence.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global nasal drug delivery technology market.
Dosage Form
- Nasal Spray
- Nasal Drop
- Nasal Gel
- Nasal Powder
Container Type
- Pressurized Containers
- Non-pressurized Containers
Therapeutic Application
- Nasal Congestion
- Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Others
Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



