Neurological Biomarkers Market Size and Trends
The neurological biomarkers market size was exhibited at USD 9.45 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 31.82 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.91% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
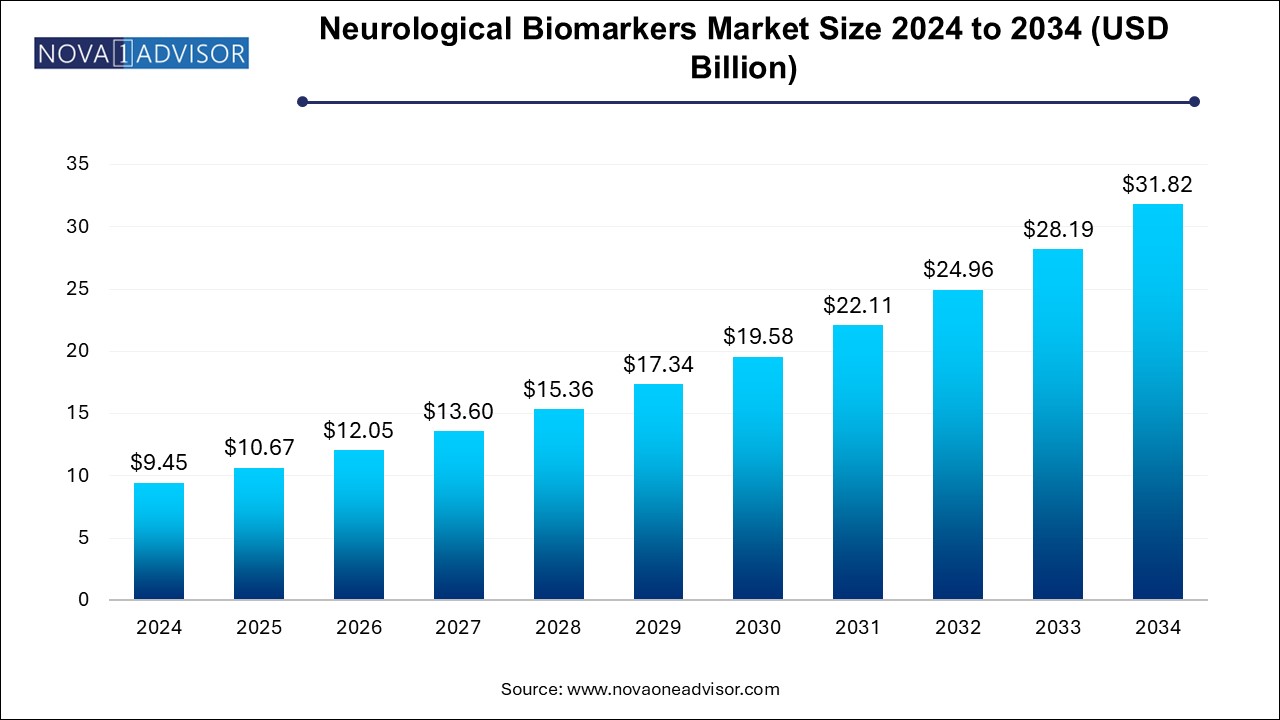
Neurological Biomarkers Market Key Takeaways:
- Proteomic biomarkers accounted for largest share of 30.49% of the neurological biomarkers market in 2024.
- Alzheimer’s disease accounted for the largest market share in 2024 and is expected to remain dominant during the forecast period
- The Parkinson’s disease segment is expected to expand at a substantial CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- Research organizations and other end-use areas accounted for a dominant market share 45.0% in 2024.
- Hospital & hospital laboratories segment, meanwhile, is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR through 2034.
- North America accounted for a significant revenue share in 2024 and is expected to witness strong growth from 2025 to 2034.
- Asia Pacific is meanwhile expected to advance at the highest CAGR through 2034.
Market Overview
The Neurological Biomarkers Market represents a pivotal frontier in the evolution of neurological disease diagnosis, monitoring, and therapeutic development. Neurological biomarkers are measurable indicators found in blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), or imaging scans that signify the presence or progression of neurological disorders. They play an essential role in conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), offering clinicians insights into disease onset, prognosis, and response to treatment.
As neurological disorders surge globally driven by an aging population, environmental stressors, and genetic predispositions traditional diagnostic approaches like neuroimaging and behavioral assessments are increasingly seen as inadequate for early detection. In contrast, biomarkers enable precision neurology, allowing for early and non-invasive detection of neurological changes even before symptoms become evident. For example, the use of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers like tau proteins and beta-amyloid peptides is now widespread in Alzheimer’s research and clinical trials.
Further propelling the market is the convergence of biotechnology, genomics, and AI-driven analytics, which are enabling the discovery and validation of novel biomarkers. Pharmaceutical and diagnostics companies are ramping up investments into biomarker-based companion diagnostics, particularly as regulatory agencies like the FDA increasingly endorse biomarker-guided trials. With neurological disorders emerging as one of the costliest and most disabling conditions globally, the demand for accurate, cost-effective, and early-stage diagnostics is projected to intensify, ensuring sustained growth of the neurological biomarkers market.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Early-Stage Diagnosis: Growing emphasis on identifying neurodegenerative diseases at pre-symptomatic stages using fluid biomarkers and imaging-based markers.
-
Integration of Multi-omics Approaches: Combining genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to capture a more comprehensive biological picture of neurological disease progression.
-
Rise in Biomarker-Based Clinical Trials: Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly using biomarkers as surrogate endpoints in clinical trials for neurodegenerative drugs.
-
Advancement in Imaging Technologies: The use of PET and MRI imaging biomarkers is improving diagnosis and monitoring of brain disorders in both research and clinical settings.
-
Digital Biomarkers Gaining Traction: Smartphone apps and wearable devices are being utilized to track cognitive changes and motor symptoms as potential real-world biomarkers.
-
Collaborations for Biomarker Discovery: Increased partnerships between academic institutions, biopharma, and diagnostics companies to validate and commercialize new neurological biomarkers.
-
Global Initiatives for Brain Health: Public health programs like the EU’s Human Brain Project and the U.S. BRAIN Initiative are generating extensive data for biomarker research.
-
AI and Machine Learning in Biomarker Analytics: Use of AI algorithms to process vast datasets and identify meaningful biomarker patterns that correlate with disease states.
Report Scope of Neurological Biomarkers Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 10.67 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 31.82 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 12.91% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Application, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Merck & Co., Inc.; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Alseres Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; DiaGenic ASA; Banyan Biomarkers, Inc.; Rules-Based Medicine; Quanterix |
Market Driver
Rising Prevalence of Neurological Disorders
A compelling driver for the neurological biomarkers market is the rising global prevalence of neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), neurological disorders are the second leading cause of death and the leading cause of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) globally. Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease affect over 55 million people worldwide and are expected to triple by 2050. Similarly, Parkinson’s disease is one of the fastest-growing neurological disorders, particularly in aging populations.
These figures highlight the dire need for effective early detection and monitoring tools. Biomarkers have demonstrated substantial promise in transforming the neurological disease landscape from preclinical detection to real-time therapeutic monitoring. For example, neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels in blood have shown effectiveness in identifying neuronal damage across multiple conditions. As public health priorities shift toward early intervention and disease-modifying strategies, neurological biomarkers stand to play an increasingly central role, driving market expansion.
Market Restraint
Challenges in Standardization and Validation
One of the most significant challenges impeding the growth of the neurological biomarkers market is the lack of standardization in biomarker validation protocols and assay reproducibility. The biological complexity of the central nervous system (CNS), combined with inter-individual variability and comorbidities, complicates biomarker development. A biomarker that performs well in a small academic study may not replicate in larger, heterogeneous populations.
Moreover, obtaining consistent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples for biomarkers like tau or beta-amyloid remains invasive and impractical in routine clinical settings. Blood-based biomarkers are a promising alternative but often face sensitivity and specificity issues. Regulatory hurdles also persist, as approval for neurological biomarkers involves demonstrating clear clinical utility, which requires large-scale longitudinal studies. These scientific, technical, and regulatory uncertainties may delay product commercialization, particularly for smaller firms with limited R&D budgets.
Market Opportunity
Emergence of Blood-Based Biomarkers
A game-changing opportunity in the neurological biomarkers market is the emergence of blood-based biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Historically, biomarker detection relied heavily on CSF collection or neuroimaging, both of which are expensive and invasive. Recent advances in ultra-sensitive assay technologies, such as Single Molecule Array (Simoa), have made it possible to detect key biomarkers like NfL, p-tau, and beta-amyloid in blood with high accuracy.
For example, in 2023, several studies demonstrated that blood-based p-tau181 levels could reliably distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from other dementias and correlate with disease severity. The adoption of these non-invasive assays in primary care settings could transform early diagnosis and expand testing access in resource-limited regions. Pharmaceutical firms also benefit, as such biomarkers allow for more inclusive and efficient clinical trial recruitment. As validation improves, these innovations may bridge the gap between academic discoveries and widespread clinical application, opening new revenue streams.
Neurological Biomarkers Market By Type Insights
Proteomic biomarkers dominate the market, owing to their pivotal role in identifying protein alterations associated with neurological diseases. Proteins such as tau, amyloid-beta, neurofilament light chain (NfL), and alpha-synuclein are well-established in the study of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other disorders. These proteins reflect disease mechanisms like amyloid plaque formation, neuronal injury, and synaptic dysfunction. With technological advances in mass spectrometry and immunoassay platforms, the sensitivity and reproducibility of proteomic biomarkers have significantly improved, reinforcing their dominance in both research and diagnostics.
Metabolomic biomarkers are the fastest-growing segment, driven by their ability to provide a holistic understanding of disease metabolism and cellular health. Metabolites reflect the biochemical state of cells and can capture early-stage disease signatures often missed by genomics or proteomics alone. For example, alterations in lipid and amino acid metabolism have been associated with early Alzheimer’s progression. Moreover, metabolomics allows the discovery of markers related to environmental exposures, diet, and drug response. As the field embraces systems biology, metabolomics is expected to witness rapid adoption in both research and precision medicine contexts.
Neurological Biomarkers Market By Application Insights
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the leading application segment, as it is the most prevalent and researched neurodegenerative disorder globally. The availability of validated CSF biomarkers (e.g., amyloid-beta42, total tau, and phosphorylated tau) has made AD the cornerstone of neurological biomarker development. These biomarkers support diagnosis, stratification of patients in clinical trials, and therapeutic response monitoring. With disease-modifying therapies like aducanumab gaining regulatory traction, biomarker-based companion diagnostics are becoming integral to treatment pathways. Investment by big pharma and research consortia into Alzheimer’s biomarker pipelines continues to sustain this segment’s leadership.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is emerging as a fast-growing application, driven by increasing awareness, diagnosis rates, and unmet clinical needs. Traditionally diagnosed through behavioral assessments, the search for objective biomarkers is gaining momentum. Studies investigating inflammatory markers, immune profiles, and gut-brain axis metabolites have shown potential in distinguishing ASD subtypes and predicting treatment response. Biomarker-based stratification could pave the way for personalized interventions in ASD, a highly heterogeneous condition. As research funding grows and neurodevelopmental disorder diagnostics evolve, ASD biomarkers are expected to attract more commercial interest.
Neurological Biomarkers Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals and hospital laboratories are the dominant end-users, as they serve as primary diagnostic centers for neurological conditions. These settings are equipped to handle complex diagnostic workflows involving imaging, CSF analysis, and biomarker panels. Neurologists rely on these facilities for confirming clinical suspicion, staging diseases, and managing treatment plans. With the increasing clinical validation of biomarkers, more hospitals are incorporating them into neurology departments and memory clinics. Advanced tertiary care centers often participate in biomarker-based clinical trials, further reinforcing their central role in the market.
Research organizations and academic institutions represent the fastest-growing end-use segment, due to their contribution to early biomarker discovery and validation. From basic research on disease mechanisms to translational studies involving animal models and clinical cohorts, these institutions are critical to the biomarker pipeline. Global initiatives such as the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) are driven by research consortia. As funding for neuroscience research accelerates and public-private collaborations expand, the role of academic and research organizations in shaping the future of neurological biomarkers will only grow.
Neurological Biomarkers Market By Regional Insights
North America, particularly the United States, leads the global neurological biomarkers market due to its robust healthcare infrastructure, high disease prevalence, and proactive research landscape. The region is home to several key players like Thermo Fisher Scientific, Quanterix, and Bio-Rad Laboratories. Federal funding through agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) supports extensive biomarker discovery programs, particularly in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Furthermore, the U.S. regulatory environment has been increasingly receptive to biomarker-guided therapeutic development. The FDA’s Biomarker Qualification Program encourages validation efforts, while Medicare and private insurers have started covering biomarker tests under specific conditions. With a well-established clinical trial ecosystem, large biobank repositories, and the presence of top neuroscience institutions, North America remains the nerve center of biomarker innovation.
Asia Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth in the neurological biomarkers market, underpinned by rising neurological disease burden, expanding research infrastructure, and growing investment in healthcare. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India are investing heavily in neuroscience research and building diagnostic capabilities. For instance, China’s Brain Project and Japan’s Brain/MINDS initiative are generating massive genomic and clinical datasets for biomarker exploration.
Additionally, the increasing elderly population in the region is leading to higher incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, driving clinical demand for early diagnosis tools. Emerging biotech firms in the region are developing localized biomarker panels that consider ethnic and genetic diversity. With growing academic-industry collaboration and favorable government policies, Asia Pacific is expected to be a major contributor to the market’s next phase of expansion.
Some of the prominent players in the Neurological Biomarkers Market include:
- Abbott
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- DiaGenic ASA
- Banyan Biomarkers, Inc.
- Quanterix
- Alseres Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Rules-Based Medicine
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – Quanterix Corporation unveiled an updated version of its Simoa® assay, capable of detecting multiple neurological biomarkers in blood simultaneously with improved accuracy.
-
February 2025 – Thermo Fisher Scientific announced a collaboration with the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation to develop blood-based biomarkers for early Alzheimer's detection.
-
January 2025 – Biogen Inc. partnered with UC San Diego to explore proteomic biomarkers associated with Parkinson’s disease progression.
-
November 2024 – Roche Diagnostics received CE marking for its Elecsys® pTau217 assay, enhancing its European presence in Alzheimer’s diagnostics.
-
October 2024 – Bio-Techne Corporation acquired ACD Bio to strengthen its imaging biomarker and spatial biology capabilities relevant to neurodegenerative disorders.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the neurological biomarkers market
By Type
- Genomic
- Proteomic
- Metabolomic
- Imaging
- Others
By Application
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Parkinson's Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Others
By End-use
- Hospital & Hospital Laboratories
- Independent clinical diagnostic centers
- Research Organizations and Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

