North America Bus Market Size and Trends
The North America bus market size was exhibited at USD 7.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 21.25 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.9% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
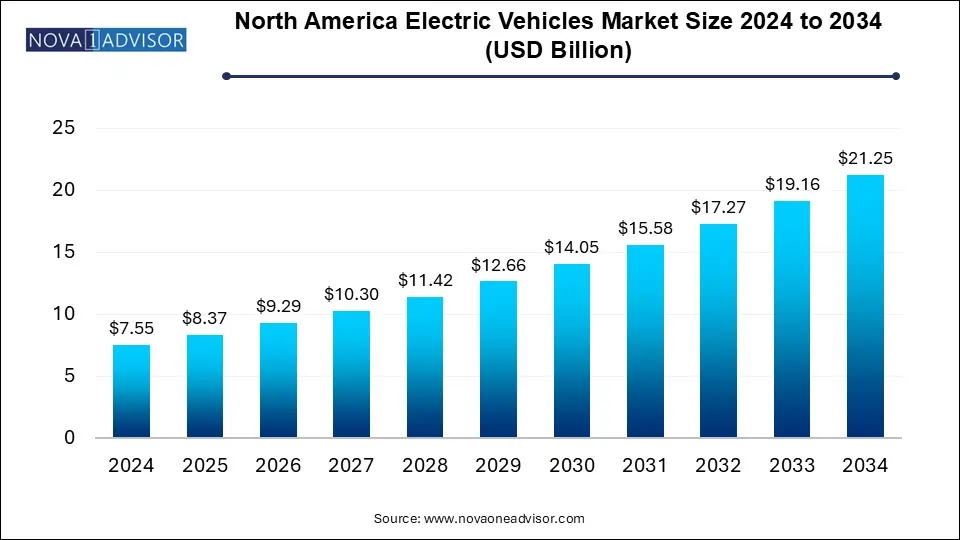
North America Bus Market Key Takeaways:
- The single deck segment accounted for the largest market share of over 92% in 2024 and is expected to exhibit the fastest growth rate over the forecast.
- The diesel segment accounted for the largest market share of more than 74% in 2024.
- The electric and hybrid segment is anticipated to register the highest growth over the forecast period.
- The 31 - 50 seats segment accounted for the largest market share of more than 50% in 2024 and is expected to exhibit the fastest growth rate from 2025 to 2034.
- The more than 50-seat segment is anticipated to register considerable growth over the forecast period.
- The school segment accounted for the largest market share of over 80.0% of the overall market in 2024.
Market Overview
The North America bus market plays a vital role in the continent’s transportation network, encompassing public transit, intercity travel, school commutes, and long-distance tourism. Buses continue to serve as the backbone of accessible and affordable mass mobility solutions, connecting urban, suburban, and rural communities. Despite increasing competition from rideshare services and personal vehicles, the bus market is witnessing renewed interest due to environmental mandates, urban congestion, and the electrification of fleet infrastructure.
In recent years, the demand for clean, sustainable, and technologically advanced buses has risen significantly. Public transit agencies across the United States, Canada, and Mexico are transitioning from conventional diesel fleets to electric and hybrid buses. Moreover, the rise in infrastructure investments—backed by policies such as the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act—has created a favorable environment for fleet renewal and expansion.
School buses represent a substantial share of the market, particularly in the U.S., where nearly half a million yellow school buses operate daily. Innovations in safety, digital fleet tracking, and alternative fuel types are reshaping how these buses are manufactured and deployed. Meanwhile, the coach and intercity segment is recovering from pandemic-related slowdowns, as tourism and cross-border travel rebound.
The North American bus market is increasingly shaped by the push for sustainability, safety regulation upgrades, and growing demand for low-floor, high-capacity models suited for urban congestion. As the transportation landscape shifts toward integrated mobility solutions, buses are expected to remain critical to equitable, cost-effective travel across the region.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Electrification of Public Transit Fleets: Municipalities are aggressively adopting battery electric buses to reduce carbon emissions and meet climate goals.
-
School Bus Electrification Programs: Federal and state grants in the U.S. and Canada are accelerating the transition to zero-emission school buses.
-
Technology Integration in Fleet Operations: GPS tracking, real-time diagnostics, and telematics are improving safety, fuel efficiency, and scheduling.
-
Growth of Demand-Responsive Transit (DRT): Flexible bus services are being piloted to serve low-density or underserved regions.
-
Rise of Double Deck Buses in Urban Corridors: High-capacity double deckers are gaining traction in cities with high passenger loads and constrained road space.
-
Expansion of Cross-Border Bus Travel: Increased demand for affordable intercity routes between the U.S., Mexico, and Canada is driving fleet upgrades.
-
Private Sector Investment in Clean Buses: Tech and logistics firms are investing in electric shuttle and commuter buses for employee transportation.
Report Scope of North America Bus Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 8.37 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 21.25 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 10.9% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Fuel Type, Seat Capacity, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America |
| Key Companies Profiled |
AB Volvo; Anhui Ankai Automobile Co., Ltd.; Blue Bird Corporation; BYD Company Limited; Daimler AG (Mercedes-Benz Group AG); Iveco SpA; Man Se; NAVISTAR (Traton Group); NFI Group; Proterra Inc. |
Market Driver: Push for Sustainable Public Transportation
The most significant driver for the North America bus market is the regional shift toward low-emission and zero-emission transportation systems. With climate change and air quality becoming urgent priorities, governments at federal, state, and municipal levels are rolling out aggressive targets for electrifying public and school bus fleets.
In the U.S., the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has launched the Clean School Bus Program, a $5 billion initiative to fund the replacement of diesel buses with electric or low-emission alternatives. Meanwhile, major cities like Los Angeles, New York, and Toronto have pledged to electrify their entire public transit fleets by 2040 or sooner. Canada’s Infrastructure Bank has allocated funding specifically for electric bus procurement and related charging infrastructure.
These sustainability goals are not merely aspirational—they come with real financial backing, spurring procurement contracts and R&D investment across OEMs and infrastructure players. Consequently, both public and private transit providers are aggressively modernizing their fleets, ensuring a robust pipeline of demand for electric, hybrid, and other clean-energy buses.
Market Restraint: High Upfront Costs of Electric Buses
A key restraint in the North America bus market is the high initial capital investment required for electric and hybrid buses compared to conventional diesel models. While electric buses offer long-term savings in fuel and maintenance, their purchase price can be two to three times higher. For instance, a typical diesel bus may cost around $500,000, while an electric equivalent can exceed $900,000.
These costs are further compounded by the need to install charging infrastructure, retrain maintenance staff, and upgrade depots to handle electric fleets. Smaller transit agencies, school districts, and private fleet operators may lack the capital or access to financing to support such transitions, even with available subsidies.
Although various government grants, tax incentives, and financing models aim to offset these challenges, the high cost barrier remains a bottleneck to mass adoption. Manufacturers are attempting to mitigate this with leasing programs and total-cost-of-ownership (TCO) calculators, but the up-front price disparity continues to slow market penetration, especially in lower-income or
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Transit-Oriented Development and Urban Mobility
A significant opportunity in the North American bus market lies in the integration of bus systems with transit-oriented development (TOD) and multimodal urban mobility strategies. As cities seek to reduce dependence on private vehicles and alleviate congestion, investments in high-frequency bus corridors, Bus Rapid Transit (BRT), and first-last mile solutions are on the rise.
Buses, due to their flexibility and relatively lower infrastructure costs compared to rail, are central to these strategies. Cities like Boston, Los Angeles, and Ottawa are expanding dedicated bus lanes, prioritization signals, and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms that enhance user convenience. Similarly, smaller cities are exploring microtransit and on-demand bus services to optimize coverage.
As urban populations grow and sustainability targets intensify, the demand for scalable, flexible, and digitally integrated bus systems will increase. This creates opportunities not only for OEMs but also for software providers, infrastructure firms, and energy suppliers to contribute to a more connected public transport ecosystem.
North America Bus Market By Type Insights
Single deck buses dominate the North American bus market, accounting for the majority of units deployed in public transit, school, and coach applications. These buses are valued for their simplicity, ease of maintenance, and adaptability across urban, suburban, and rural environments. In school transportation, single deck buses are the de facto standard, offering safety, compliance with regulations, and proven performance. In urban areas, low-floor single deck models provide accessibility for disabled and elderly passengers, meeting ADA and similar standards. The flexibility of seating configurations and ease of integration with electric drivetrains further support their continued dominance.
However, double deck buses are gaining traction in densely populated urban corridors and high-volume intercity routes. Cities like Toronto and San Francisco have adopted double deckers to improve capacity without increasing road footprint. In the coach segment, these buses offer premium experiences with panoramic upper decks and more passenger amenities. Transit agencies are also exploring double deck electric models for BRT routes, combining capacity with sustainability. Although still a niche segment, increasing urban density and operational cost optimization are accelerating the growth of double deck deployments.
North America Bus Market By Fuel Type Insights
Diesel-powered buses currently dominate the North American market, thanks to a well-established supply chain, widespread refueling infrastructure, and lower upfront costs. Diesel remains the default choice for long-distance coaches and rural transit routes, where electric charging networks may be limited. Furthermore, many fleets have invested in clean-diesel technologies that meet modern emissions standards, enabling them to extend vehicle life while maintaining compliance.
In contrast, electric and hybrid buses are the fastest-growing fuel type, driven by emission reduction mandates and operational savings. Electric buses are particularly suited for fixed urban routes with predictable distances and centralized depots. Major cities have committed to full electric transitions, creating consistent demand for battery electric models. Hybrid buses also serve as a transitional technology, offering fuel savings and reduced emissions without the infrastructure needs of full electrification. OEMs like New Flyer, BYD, and Proterra are capitalizing on this demand by expanding their electric bus portfolios and forming partnerships for charging solutions.
North America Bus Market By Seat Capacity Insights
The 31–50 seat capacity segment dominated the market due to its versatility in both urban transit and school bus applications. Buses in this range balance capacity, maneuverability, and cost efficiency. In school applications, mid-sized buses are ideal for suburban routes, while in transit, this segment supports medium-density urban corridors. Manufacturers have optimized designs in this category for safety, accessibility, and fuel economy.
However, buses with more than 50 seats are growing rapidly, particularly in intercity and coach segments. Long-distance operators like Greyhound and Megabus are deploying high-capacity coaches to optimize cost-per-passenger metrics. Additionally, transit agencies are adopting articulated buses and double deckers for BRT systems and event transportation. The shift toward mass transit in congested urban centers is expected to further boost this segment, especially as electric powertrains improve range and performance for larger vehicles.
North America Bus Market By Application Insights
Transit buses continue to lead the North America bus market in terms of volume and value. Urban bus networks are expanding in response to sustainability goals, reduced fare programs, and growing urban populations. Fixed-route transit buses account for a large portion of municipal procurement and are increasingly being electrified. Partnerships between transit agencies and federal programs, such as the U.S. Federal Transit Administration’s Low-No Emissions Program, support this dominance.
School buses, especially electric variants, are the fastest growing application segment. The U.S. and Canada operate the world’s largest school bus fleets, and recent funding initiatives are focused heavily on replacing diesel units with electric models. For example, the EPA’s Clean School Bus Program awarded over $900 million in 2023 to fund 2,400 electric school buses across all 50 states. With safety, noise reduction, and environmental benefits, electric school buses are rapidly transforming this once-static segment into a high-growth opportunity.
Country Insights
United States
The U.S. represents the largest market for buses in North America, with a broad ecosystem spanning public transit, intercity travel, and the world’s largest school transportation system. Government grants and regulations such as Buy America provisions and EPA emissions standards strongly influence purchasing behavior. The country is leading the charge in electric bus deployments, with hundreds of transit agencies and school districts transitioning their fleets. OEMs like Blue Bird, Gillig, and Proterra are at the forefront of domestic innovation.
Canada
Canada is investing heavily in electric transit through the Canada Infrastructure Bank and municipal programs. Cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal are at the forefront of deploying battery electric and hybrid buses. Canadian manufacturers such as New Flyer and Lion Electric are expanding their production capabilities to meet domestic and export demand. Federal zero-emission mandates and climate goals continue to shape procurement strategies nationwide.
Mexico
Mexico’s bus market is largely oriented toward diesel and CNG models, particularly in intercity and charter services. However, government efforts to reduce urban pollution have led to pilot deployments of electric buses in Mexico City and Guadalajara. International firms like BYD and Yutong are collaborating with Mexican operators and municipalities to expand electric offerings. While electrification is slower compared to the U.S. and Canada, policy alignment under USMCA and private investment is beginning to accelerate change.
Some of the prominent players in the North America bus market include:
- AB Volvo
- Anhui Ankai Automobile Co., Ltd.
- Blue Bird Corporation
- BYD Company Limited
- Daimler AG (Mercedes-Benz Group AG)
- IVECO SpA
- Man Se
- NAVISTAR (Traton Group)
- NFI Group
- Proterra Inc.
North America Bus Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Blue Bird Corporation delivered its 10,000th electric school bus to a California school district, marking a milestone in fleet electrification.
-
February 2025: New Flyer received a $120 million contract from Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) for 200 zero-emission buses with extended-range batteries.
-
January 2025: Lion Electric announced the opening of its U.S. battery manufacturing facility in Illinois to reduce supply chain dependencies for electric school buses.
-
December 2024: Proterra launched its next-generation ZX6 electric bus platform with modular battery configurations and enhanced range capabilities.
-
October 2024: The Mexican Ministry of Environment partnered with BYD to deploy 150 electric buses in Mexico City’s Metrobus system by mid-2025.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the North America bus market
By Type
By Fuel Type
- Diesel
- Electric and Hybrid
- Other Fuel Type
By Seat Capacity
- 15-30 Seats
- 31-50 Seats
- More Than 50 Seats
By Application
- Transit
- School
- Coach
- Others
By Country

