North America Durable Medical Equipment Market Size and Research
The North America durable medical equipment market size was exhibited at USD 81.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 144.64 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
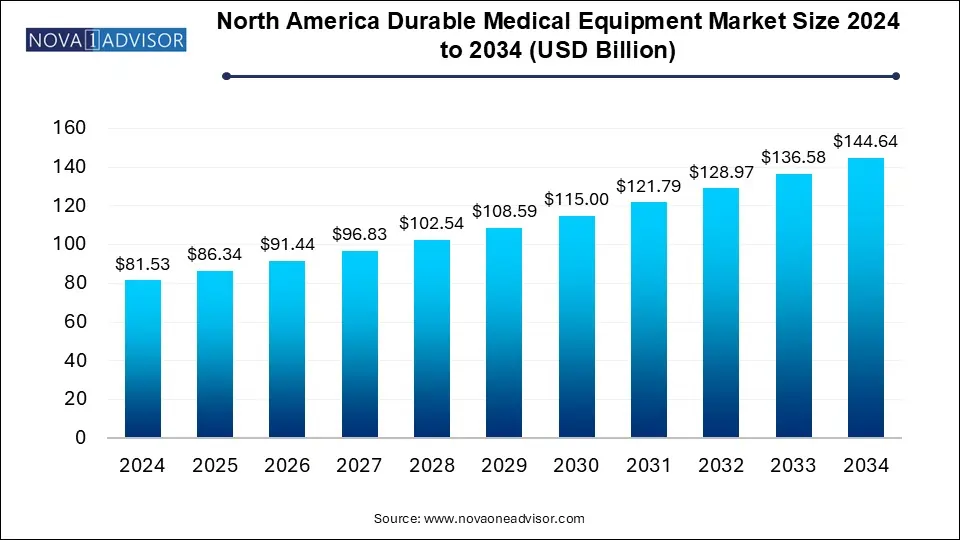
North America Durable Medical Equipment Market Key Takeaways:
- The monitoring and therapeutic devices held the largest market share of 89.4% in 2024.
- The bathroom safety devices and medical furniture segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of over 6.8% during the forecast period.
- Hospitals led the end-use segment with 35.0% in 2024 on account of the rising number of patient admission due to the increasing chronic diseases and healthcare needs.
- Home healthcare is expected to witness the highest growth rate of 6.4% over the forecast period.
- The U.S. accounted highest market share of 82.2% in 2024.
Market Overview
The North America durable medical equipment (DME) market plays a foundational role in supporting long-term care, chronic disease management, and patient recovery across a variety of healthcare settings. Durable medical equipment refers to devices that are used repeatedly and designed for long-term medical assistance, such as wheelchairs, hospital beds, oxygen concentrators, blood glucose monitors, and more. These products are pivotal in enabling aging populations, disabled individuals, and patients recovering from surgeries or chronic illnesses to maintain mobility, independence, and health monitoring at home or in institutional environments.
The U.S. and Canada are the key contributors to this market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high chronic disease prevalence, favorable reimbursement policies (e.g., Medicare Part B), and growing emphasis on home-based care models. Furthermore, the market is expanding as a result of increased awareness of assistive technologies, technological integration (smart DME), and rising health expenditure.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, demand for respiratory devices such as oxygen concentrators, CPAP machines, and nebulizers surged due to complications associated with viral respiratory illnesses. This heightened awareness has had a lasting impact, positioning DME as a critical part of emergency preparedness and chronic care pathways. Additionally, the trend toward early hospital discharges and aging in place has led to greater reliance on home healthcare solutions, boosting the need for durable equipment in domestic settings.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Home Healthcare Expansion Driving Equipment Demand: Increasing preference for in-home care is resulting in higher demand for mobility aids, respiratory support, and monitoring devices.
-
Integration of Smart Technologies in DME: CPAP machines, blood glucose monitors, and infusion pumps are now embedded with Bluetooth, data analytics, and remote reporting capabilities.
-
Customized Mobility Solutions for Elderly Patients: Manufacturers are developing ergonomically improved and adjustable devices tailored for individual comfort and usability.
-
Sustainability in Equipment Manufacturing: Companies are investing in eco-friendly materials, recyclable components, and energy-efficient production practices.
-
DME Subscription and Rental Models Gaining Traction: Hospitals, nursing homes, and even individuals are increasingly opting for leasing DME to reduce upfront costs and maintenance burdens.
Report Scope of North America Durable Medical Equipment Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 86.34 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 144.64 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 5.9% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Invacare Corp.; Sunrise Medical; Arjo; Medline Industries, Inc.; GF Healthcare Products, Inc.; Carex Health Brands, Inc.; Cardinal Health; Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare; NOVA Medical Products; Kaye Products, Inc. |
Key Market Driver: Aging Population and Chronic Disease Burden
The most compelling driver of the North America DME market is the region's rapidly aging population combined with the high burden of chronic illnesses. In the United States alone, over 54 million individuals are aged 65 or older—a demographic that is expected to nearly double by 2040. This aging cohort is significantly more likely to experience mobility issues, cardiovascular disease, respiratory disorders, and musculoskeletal degeneration, which necessitate long-term use of supportive medical equipment.
Moreover, chronic diseases such as diabetes, COPD, and arthritis demand continuous monitoring and therapy, often administered at home. For instance, blood glucose monitors and CPAP devices are increasingly used by aging adults as part of regular care routines. DME enables improved quality of life and independence, which aligns with seniors’ preference to age in place rather than move into institutional settings. Consequently, healthcare systems, insurers, and families alike are investing in DME as a long-term care strategy.
Key Market Restraint: Reimbursement and Cost Constraints
One of the major restraints for market expansion is the variability and complexity of reimbursement policies, particularly for at-home equipment. While Medicare Part B covers many types of DME, the reimbursement rates are often below market prices, leading to cost pressures for suppliers and limiting choices for consumers. Competitive bidding programs for DME suppliers have further narrowed the list of eligible vendors, sometimes leading to supply disruptions or delays.
Additionally, upfront costs for certain advanced DME products such as motorized wheelchairs or high-capacity oxygen concentrators can be prohibitive for patients without comprehensive insurance or supplemental coverage. Even when reimbursed, patients may have to cover co-pays, deductibles, or rental fees. These financial hurdles restrict access for vulnerable populations, particularly in low-income or rural communities, and may push healthcare providers to select lower-cost, lower-quality equipment.
Key Market Opportunity: Expansion of Home-Based Monitoring and Remote Therapy
An emerging opportunity in the North American DME market is the integration of digital health and telemedicine into durable medical equipment. Devices such as CPAP machines, infusion pumps, and glucose monitors are increasingly embedded with sensors, Bluetooth, and cloud connectivity to enable remote monitoring and real-time data sharing with healthcare providers. This functionality improves patient adherence, reduces emergency visits, and facilitates proactive interventions.
For example, a CPAP device with cloud connectivity can send sleep and respiratory metrics directly to a clinician, who can adjust treatment remotely or prompt a patient for check-ins. Similarly, blood sugar monitors can now send alerts for hypoglycemic episodes to both the patient and care team. This level of connectivity not only enhances care outcomes but also aligns with reimbursement models emphasizing preventive care and value-based outcomes. As home-based care becomes a dominant model, DME equipped with smart features will gain substantial traction.
North America Durable Medical Equipment Market By Product Insights
Monitoring and therapeutic devices dominate the North American DME market, representing a substantial portion of overall demand due to their essential role in managing chronic conditions and post-operative recovery. Devices like oxygen concentrators, CPAP machines, blood sugar monitors, infusion pumps, and nebulizers are central to home-based care plans for individuals with respiratory illnesses, sleep apnea, diabetes, and other long-term health needs. For instance, the rising incidence of obstructive sleep apnea has directly boosted sales of CPAP machines and associated accessories. These products are not only prescribed more frequently but are also increasingly equipped with connectivity features that facilitate compliance tracking and outcomes reporting.
Personal mobility devices, particularly wheelchairs and walkers, are the fastest-growing segment, driven by the aging population and the increasing prevalence of musculoskeletal and neurological disorders. Manual and powered wheelchairs, rollators, and adjustable walkers are essential for enabling elderly and disabled individuals to maintain independence, avoid falls, and participate in daily activities. Technological innovation—such as voice-activated wheelchairs, stair-climbing models, and lightweight foldable designs—is enhancing user convenience and driving adoption in home, rehab, and institutional settings. The growing availability of these devices through direct-to-consumer and online channels further supports segment growth.
North America Durable Medical Equipment Market By End-use Insights
Home healthcare remains the dominant end-use segment, reflecting the broader healthcare shift toward outpatient and at-home management models. As hospitals prioritize reducing readmissions and as patients seek comfort and autonomy, the demand for DME in home settings has accelerated. Devices like oxygen support systems, hospital beds, and blood pressure monitors are now routinely used in private residences, assisted by the growth of home health agencies and caregiver networks. Additionally, insurers and public programs increasingly promote home-based care as a cost-effective alternative to prolonged hospitalization or skilled nursing stays.
Hospitals and institutional settings represent a growing end-use segment, especially for advanced therapeutic equipment and transitional care tools. Hospitals procure large volumes of monitoring devices and therapy tools for use in acute care, surgery recovery, and intensive rehabilitation. Moreover, the post-acute care model—where patients transition from hospital beds to intermediate care supported by DME—has increased hospitals’ role in prescribing and renting these devices. As value-based care becomes more embedded in hospital operations, DME will be critical to improving discharge readiness and long-term outcomes.
Country-Level Analysis: United States and Canada
In the United States, the DME market is propelled by a mature healthcare ecosystem, high chronic disease incidence, and expansive public health insurance coverage. Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers all contribute to demand across various categories, with reimbursement frameworks dictating the types and volumes of DME that are accessible to patients. The U.S. also benefits from a robust pipeline of medical device manufacturers, innovative startups, and strong regulatory pathways for new DME introductions. However, reimbursement complexity and supplier consolidation under Medicare’s competitive bidding remain points of contention and inefficiency.
In Canada, the market is shaped by its publicly funded universal healthcare system. DME procurement is typically handled at the provincial level, with varying degrees of coverage based on region and income level. While access is generally strong, wait times and regional disparities can limit timely availability of certain high-demand items. The Canadian market is also influenced by the aging population and increased investment in community-based care programs. As provinces expand remote care infrastructure, smart DME adoption is likely to accelerate.
Some of the prominent players in the North America durable medical equipment market include:
Recent Developments
-
ResMed (March 2025) launched its latest CPAP platform featuring AI-driven sleep pattern recognition and cloud-based compliance monitoring, aimed at enhancing sleep apnea treatment adherence at home.
-
Invacare Corporation (February 2025) introduced a lightweight power wheelchair with modular design, specifically engineered for independent seniors seeking travel-friendly mobility solutions.
-
Medline Industries (January 2025) expanded its North American distribution network for home care products, including mattress systems and transfer aids, amid surging demand from post-acute care agencies.
-
Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare (December 2024) announced a partnership with a major Canadian home healthcare agency to deploy IoT-connected nebulizers and suction devices for remote respiratory therapy.
-
Cardinal Health (November 2024) unveiled a digital dashboard for DME providers and hospital discharge planners to coordinate equipment orders, track utilization, and manage inventory in real-time.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2024 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the North America durable medical equipment market
By Product
- Personal Mobility Devices
-
- Wheelchairs
- Scooters
- Walker and Rollators
- Canes and Crutches
- Door Openers
- Other Devices
- Bathroom Safety Devices And Medical Furniture
-
- Commodes And Toilets
- Mattress & Bedding Devices
- Monitoring And Therapeutic Devices
-
- Blood Sugar Monitors
- Continuous Passive Motion (CPM)
- Infusion Pumps
- Nebulizers
- Oxygen Equipment
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
- Suction Pumps
- Traction Equipment
- Others Equipment
By End-use
- Hospitals
- Nursing Homes
- Home Healthcare
- Other End-user
By Regional

