North America Polyolefin And Engineering Plastic Compounding Market Size and Trends
The North America polyolefin and engineering plastic compounding market size was exhibited at USD 13.40 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 25.87 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
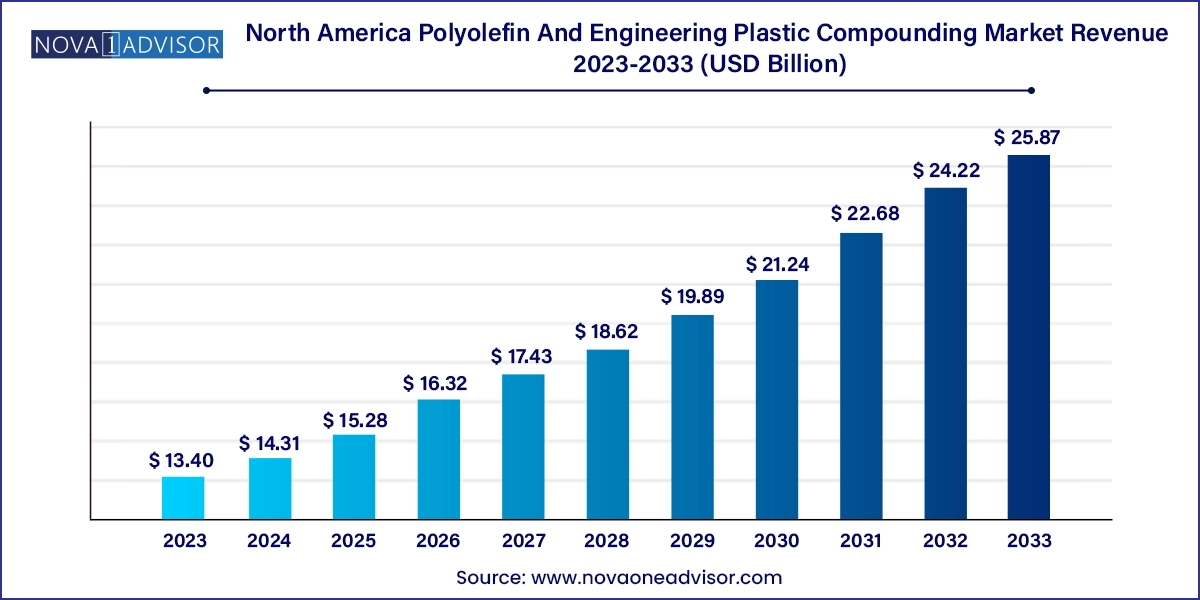
North America Polyolefin And Engineering Plastic Compounding Market Key Takeaways:
- In terms of product revenue, the polyolefin segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 59.0% in 2023.
- The engineering plastic segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 6.3% from 2024 to 2033.
- In terms of application, the automotive & transportation segment led the market in 2023 with share of 25.8%.
- The packaging segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The North America polyolefin and engineering plastic compounding market stands as a cornerstone of the region’s advanced manufacturing landscape. This industry plays a vital role in transforming raw polymers into high-performance materials with tailored mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. From automotive parts and electrical components to appliances and packaging, compounded plastics serve a wide range of industries. The compounding process involves the blending of base resins—primarily polyolefins and engineering plastics with additives, fillers, reinforcements, and colorants to achieve desired end-use characteristics.
Driven by the region’s focus on lightweighting, durability, and sustainability, compounded plastics are replacing traditional materials such as metals and glass. Engineering plastics like polyamide, polycarbonate, and ABS are crucial for producing parts that demand strength and heat resistance, particularly in automotive and electronics sectors. Simultaneously, polyolefins such as polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) dominate packaging and consumer applications due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
In North America, the U.S. leads the market due to its highly developed industrial base, followed by Canada and Mexico, which benefit from growing automotive manufacturing clusters and export-oriented industrial setups. Environmental regulations, technological innovation, and the integration of recycled content are reshaping the compounding landscape. The demand for specialty formulations—such as flame-retardant, UV-stabilized, or bio-based compounds is also witnessing a marked rise, reinforcing the strategic importance of compounding in the future of North American manufacturing.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Lightweight Materials in Automotive Manufacturing: OEMs are increasingly using compounded plastics to reduce vehicle weight and meet emission regulations, with applications in dashboards, bumpers, and engine components.
-
Increased Adoption of Electrification and E-Mobility: Engineering plastics are becoming indispensable in EV battery components, housings, and high-voltage connectors due to their insulation and thermal management capabilities.
-
Surge in Smart Consumer Appliances: With demand rising for energy-efficient and aesthetically pleasing appliances, compounded ABS and PC materials with glossy finishes and durability are in high demand.
-
Growth of Sustainable and Recycled Compounds: Regulatory mandates and corporate ESG goals are fueling innovations in recycled PP and PCR (post-consumer recycled) engineering plastics.
-
Integration of Additive Manufacturing and Custom Formulations: Companies are exploring compounded plastic filaments and powders for 3D printing, especially in prototyping and low-volume part production.
-
Use of Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Compounds in Medical Devices: Though niche, this trend is emerging in the wake of post-pandemic healthcare innovations and regulations.
-
Cross-border Production Optimization: Mexico is becoming a compounding hub due to lower operational costs, NAFTA/USMCA advantages, and rising investment in nearshoring strategies by U.S. and Canadian firms.
Report Scope of North America Polyolefin And Engineering Plastic Compounding Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 14.31 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 25.87 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 6.8% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S., Canada, Mexico |
| Key Companies Profiled |
BASF SE; LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V.; Dow Inc.; DuPont; SABIC; RTP Company; S&E Specialty Polymers LLC (Aurora Plastics); Asahi Kasei Corporation; Covestro AG; Washington Penn; Ascend Performance Materials; Kuraray Co. Ltd.; Teijin Limited; Evonik Industries AG; 3M |
A primary driver of the North American polyolefin and engineering plastic compounding market is the increasing emphasis on lightweight materials in the automotive industry. As automakers strive to reduce vehicle weight to comply with stringent fuel efficiency and emission norms, there has been a notable transition from metals to plastic compounds that offer equal or superior performance.
Compounded polypropylene, polyamide, and thermoplastic polyester are being widely adopted for under-the-hood applications, structural panels, interior trims, and electric vehicle battery modules. These materials reduce overall vehicle mass, improve fuel economy, and enhance thermal and chemical resistance. Notably, General Motors and Ford have both expanded the use of glass fiber-reinforced polyamides and polycarbonate blends in their EV and hybrid vehicle lines, showcasing how compounded plastics are becoming foundational to future mobility platforms. The shift is also bolstered by their design flexibility, recyclability, and ease of integration with automated manufacturing systems like injection molding.
Key Market Restraint: Volatility in Raw Material Prices and Supply Chain Disruptions
One significant restraint faced by the market is the instability in raw material prices and disruptions in the supply chain, especially post-pandemic. Most polyolefins are derived from petrochemical feedstocks, making their pricing sensitive to global oil prices and geopolitical dynamics. This volatility impacts the cost of base resins like PP and PE, making it difficult for compounders to offer stable pricing to downstream industries.
Moreover, supply chain challenges—such as container shortages, port congestion, and regional production outages have led to inconsistent availability of specialty additives and fillers required for customized compounding. Engineering plastics like polyamide and fluoropolymers often depend on globally distributed suppliers, making the North American market vulnerable to trade restrictions, tariffs, or manufacturing bottlenecks in other regions. As a result, many small and mid-size compounding companies are compelled to hold higher inventory levels, increasing operational costs and limiting responsiveness to market demand.
Key Market Opportunity: Expansion of Recycled and Bio-based Compounds
An emerging and lucrative opportunity in the North American market is the expansion of recycled and bio-based plastic compounding. With growing environmental awareness and stringent recycling regulations, compounders are innovating ways to integrate post-industrial and post-consumer recycled materials into high-performance compounds.
Recycled PP and PE are already being used in automotive interiors, packaging crates, and consumer products. Engineering plastics like polycarbonate and ABS are now available in PCR grades with nearly equivalent performance metrics. Companies like SABIC and Avient have introduced bio-based compounds for packaging and electronics applications, further expanding the sustainability profile of their offerings.
This trend is particularly advantageous for manufacturers seeking LEED certifications or carbon footprint reductions, making sustainable compounding a differentiator in competitive bids. The integration of chemical recycling technologies and closed-loop partnerships with OEMs is also expected to boost the uptake of circular polymers in compounded forms.
North America Polyolefin And Engineering Plastic Compounding Market By Product Insights
Polyolefins dominate the product segment, primarily due to their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and widespread use across multiple sectors. Within this category, polypropylene (PP) holds a leading position, especially in automotive interiors, food packaging, and consumer goods. Its balance of stiffness, processability, and recyclability makes it ideal for mass-market applications. Polyethylene (PE) is another cornerstone, used extensively in packaging films, agricultural films, and piping systems. Thermoplastic polyolefins (TPOs), known for their impact resistance and weatherability, are increasingly applied in automotive bumpers and roofing membranes.
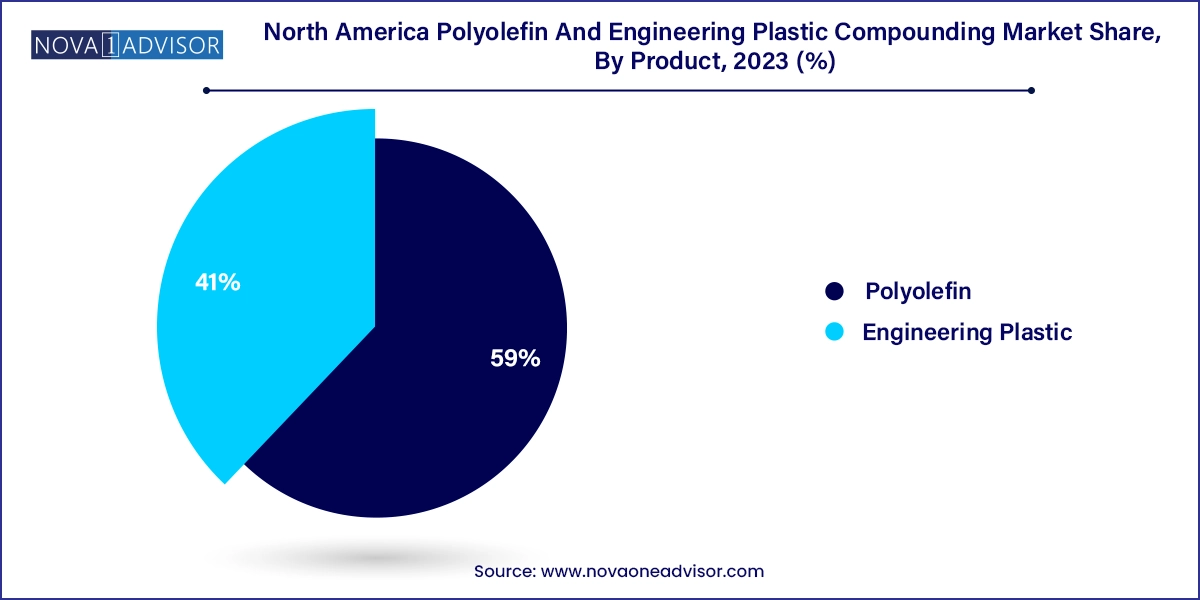
Conversely, engineering plastics are the fastest-growing product segment, driven by their superior mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability. Polyamide (PA) and polycarbonate (PC) are particularly in demand within the automotive and electronics industries. Polyamide compounds reinforced with glass fibers are used in engine covers and transmission components, while PC blends are favored in lighting systems and electrical housings. The growth of electric vehicles, along with the miniaturization of electronic devices, is accelerating the use of flame-retardant and thermally conductive engineering plastic compounds across North America.
North America Polyolefin And Engineering Plastic Compounding Market By Application Insights
The automotive and transportation segment is the dominant application area, accounting for the largest share of polyolefin and engineering plastic compounds. Lightweighting imperatives have led to the replacement of metallic parts with engineered plastic components that offer comparable strength and thermal performance. In addition to structural parts, these compounds are now used in battery enclosures, sensors, and underbody shields in electric vehicles. Companies such as Tesla and Ford have increased their use of TPOs, ABS, and nylon-based compounds in both interior and exterior modules.
Meanwhile, electrical and electronics represent the fastest-growing application segment, supported by the rapid proliferation of consumer electronics, home automation devices, and renewable energy systems. Engineering plastic compounds such as PC/ABS blends, thermoplastic polyesters, and fluoropolymers are widely used in circuit boards, switchgear, and photovoltaic connectors. As 5G deployment and smart grid upgrades accelerate across North America, demand for thermally stable, electrically insulating plastic compounds is expected to surge, creating robust opportunities for specialty compounders.
Country Insights
United States
The United States dominates the North American compounding market, supported by a strong industrial ecosystem, R&D infrastructure, and high-value manufacturing. U.S.-based compounders benefit from access to abundant petrochemical feedstocks, robust demand from the automotive and aerospace industries, and proximity to global technology hubs. Leading companies have established compounding facilities in states such as Texas, Michigan, and Ohio, catering to automotive OEMs, electronics giants, and packaging converters.
With the Biden administration pushing for clean energy, EV infrastructure, and reshoring of critical manufacturing, engineering plastic compounders in the U.S. are experiencing an uptick in demand. Recycled content mandates and consumer preference for sustainable products have also prompted a shift toward bio-based and circular polymer compounding. Advanced compounding technologies like twin-screw extrusion, reactive compounding, and nano-filler integration are widely employed across the country.
Canada
Canada’s compounding market is smaller but strategically aligned with sustainability trends. Canadian manufacturers prioritize recyclable and biodegradable compounds, particularly in packaging and building materials. With growing investments in green construction and electric vehicles, engineering plastics such as PVC, polyamide, and polyacetal are gaining traction. Regions like Ontario and Quebec are home to several midsize compounders serving local and cross-border markets.
Furthermore, Canada’s research institutions and government-funded innovation hubs are collaborating with private sector firms to develop low-carbon and flame-retardant compounds. The country’s strict environmental regulations and clean energy initiatives make it an ideal testing ground for advanced compounding materials, especially in construction, energy, and electronics sectors.
Mexico
Mexico is emerging as a high-growth compounding market, propelled by its expanding automotive production base and cost-efficient manufacturing environment. OEMs like Nissan, VW, and GM have major production units in Mexico, creating strong demand for locally sourced plastic compounds. Polypropylene compounds for bumpers, dashboards, and HVAC systems are particularly in demand. The availability of skilled labor and trade agreements under USMCA further support Mexico’s positioning as a compounding hub for export.
In addition, global compounders are investing in Mexican facilities to serve not just North America but also Latin American and European customers. Regions such as Monterrey and Guanajuato are seeing the establishment of extrusion lines and quality control labs, reinforcing Mexico’s potential in the plastic compounding value chain.
North America Polyolefin And Engineering Plastic Compounding Market Recent Developments
-
In March 2025, LyondellBasell announced a new polyolefin compounding facility in Texas to serve the growing demand for automotive and packaging applications in the U.S. and Mexico.
-
SABIC introduced a line of PCR-based polycarbonate compounds in February 2025, developed at their Canada R&D center, targeting sustainable electronics and mobility solutions.
-
In January 2025, RTP Company launched a new flame-retardant nylon 6/6 compound designed for electric vehicle applications, with production scaled across U.S. and Mexico plants.
-
Celanese Corporation in December 2024 expanded its thermoplastic polyester compounding capacity in Kentucky, driven by demand from the North American appliance and industrial tools sector.
Some of the prominent players in the North America polyolefin and engineering plastic compounding market include:
- BASF SE
- LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V.
- Dow, Inc.
- DuPont
- SABIC
- RTP Company
- S&E Specialty Polymers, LLC (Aurora Plastics)
- Asahi Kasei Corporation
- Covestro AG
- Washington Penn
- Ascend Performance Materials
- KURARAY CO., LTD.
- TEIJIN LIMITED
- Evonik Industries AG
- 3M
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the North America polyolefin and engineering plastic compounding market
Product
-
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
- Thermoplastic Polyolefins (TPOs)
- Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
- Other polyolefins
-
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
- Polyamide
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Thermoplastic Polyester
- Polyacetal
- Fluoropolymer
- Other engineering plastics
Application
- Automotive & Transportation
- Consumer Appliances
- Electrical & Electronics
- Building & Construction
- Industrial & Machinery
- Packaging
- Other applications
Country


