Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market Size and Growth
The personalized medicine biomarkers market size was exhibited at USD 21.95 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 79.26 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 13.7% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
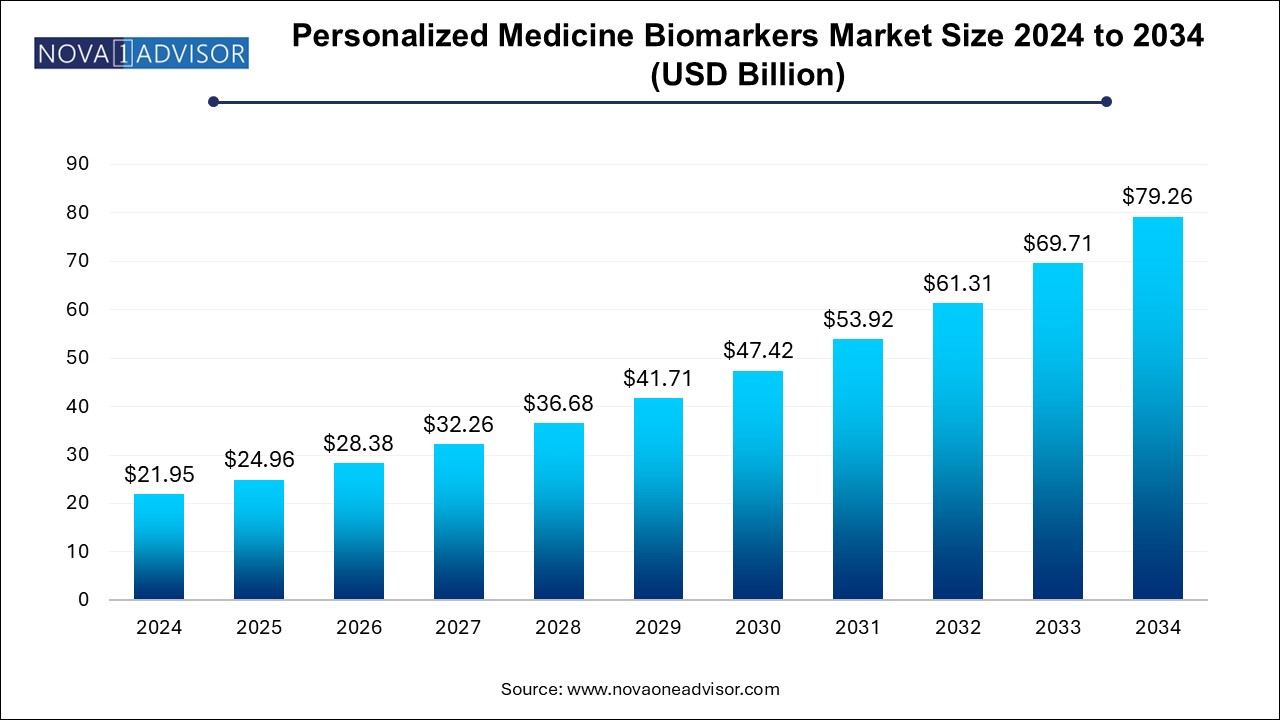
Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market Key Takeaways:
- The North America personalized medicine biomarkers market dominated the global market and accounted for 52.0% of revenue share in 2024
- The treatment selection segment dominated the market with the largest market share of 50.2% in 2024.
- Early detection/screening is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 15.8% over the forecast period.
- Oncology dominated the market with the largest share of 36.0% in 2024, driven by the increasing prevalence of cancer worldwide.
- The diabetes segment is the fastest-growing segment and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.4% over the forecast period.
U.S. Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market Size and Growth 2024 to 2034
The U.S. Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market size is exhibited at USD 9.68 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 40.90 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15.5% from 2024 to 2034.
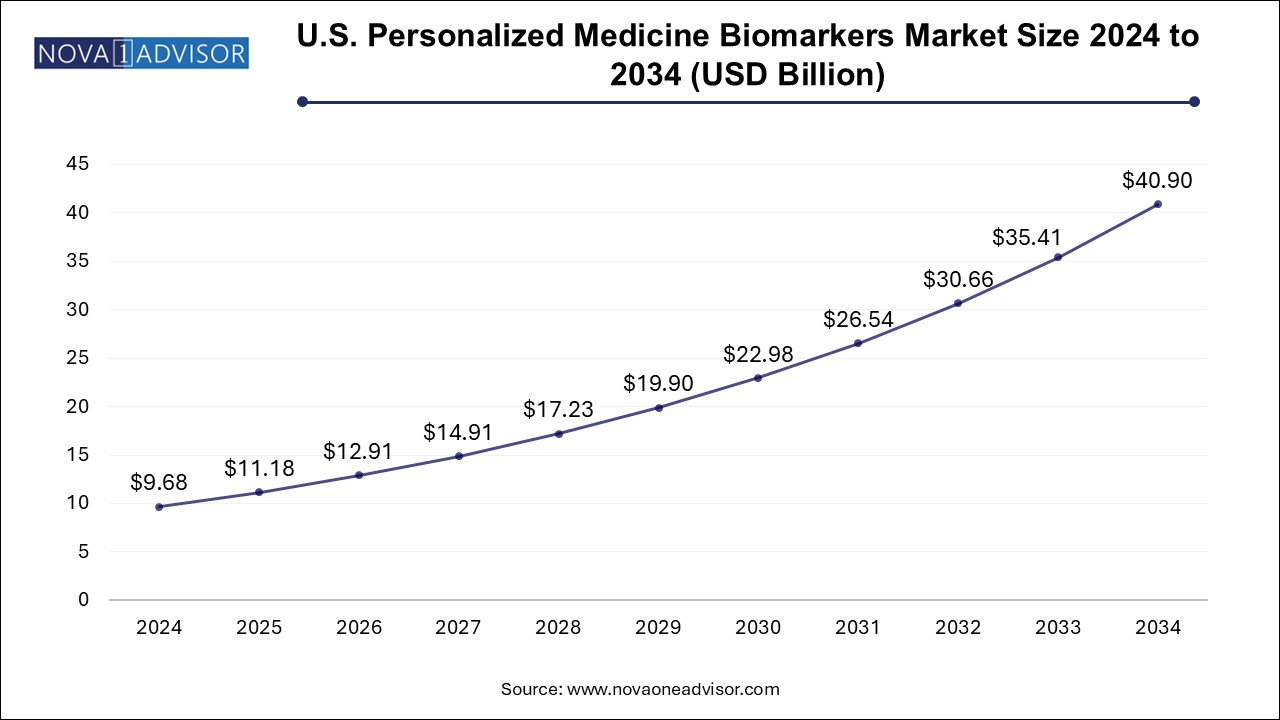
North America is the largest regional market, owing to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high per capita health spending, and strong government initiatives supporting precision medicine. The U.S. Precision Medicine Initiative and the Cancer Moonshot program have fueled R&D in biomarker science. Major biotech hubs, the presence of leading players like Thermo Fisher Scientific and Illumina, and extensive biobanking networks further consolidate the region’s dominance. Furthermore, the FDA’s supportive regulatory pathway for companion diagnostics accelerates clinical deployment of biomarker-based therapies.
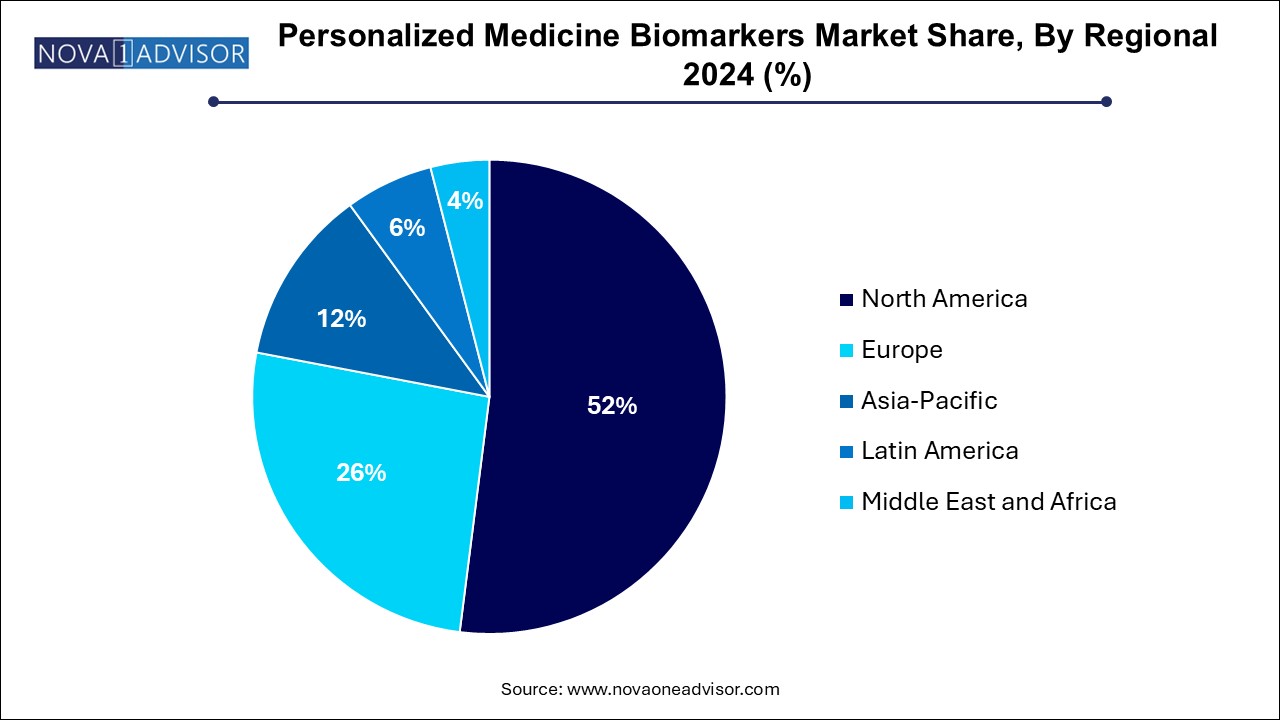
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, spurred by rising healthcare investments, growing prevalence of chronic diseases, and expanding genomic capabilities. China’s “Healthy China 2030” plan includes personalized medicine components, while India’s Department of Biotechnology is funding precision healthcare startups. Japan, already a leader in genetic research, has implemented reimbursement models for advanced diagnostics. The increase in clinical trials, public-private partnerships, and genomic literacy is laying the foundation for explosive growth in this region.
Market Overview
The Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market is undergoing a transformative phase, catalyzed by advancements in molecular biology, genomics, and digital health infrastructure. Personalized medicine aims to tailor treatment strategies based on the unique genetic, biochemical, and physiological profile of individual patients. Biomarkers biological molecules that signify normal or abnormal processes or pharmacologic responses play a pivotal role in this paradigm shift. They enable more accurate diagnosis, early disease detection, stratified therapy, and continuous monitoring of treatment efficacy and progression.
Biomarkers have revolutionized disease management across diverse indications, particularly in oncology, cardiology, neurology, and autoimmune disorders. Their application in drug discovery and development is streamlining clinical trials and minimizing risks, ultimately reducing costs and improving therapeutic outcomes. For instance, the success of Herceptin in HER2-positive breast cancer exemplifies how biomarker-driven therapy can be life-saving. As healthcare systems globally push toward value-based care, the demand for biomarker-based personalized solutions is intensifying, with implications across diagnostic labs, pharmaceutical R&D, and clinical practices.
Moreover, the rising prevalence of chronic and lifestyle diseases, combined with the aging population and heightened awareness among healthcare providers, has created a fertile ground for the expansion of this market. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA and EMA are actively endorsing biomarker integration through accelerated approval pathways and companion diagnostics frameworks. The increasing investment from biopharma giants and the advent of omics technologies (genomics, proteomics, metabolomics) are further shaping a robust ecosystem for personalized biomarker applications.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of Liquid Biopsy Technologies: Non-invasive sampling techniques using circulating biomarkers (CTCs, cfDNA, EVs) are becoming mainstream in cancer detection and monitoring.
-
Integration of Multi-Omics Approaches: Combining genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics data enhances the predictive power and specificity of biomarkers.
-
AI-Driven Biomarker Discovery: Machine learning and AI tools are expediting the identification and validation of novel biomarkers by mining large-scale datasets.
-
Growth of Companion Diagnostics: Co-development of diagnostic tests with therapeutics ensures optimal patient selection and improves drug efficacy and safety.
-
Increasing Role of Real-World Evidence (RWE): Data from clinical practice is being used to validate biomarkers, particularly in chronic diseases and rare disorders.
-
Focus on Early Detection and Preventive Healthcare: Biomarkers are increasingly used in asymptomatic populations to catch diseases in pre-clinical stages.
-
Global Expansion of Genomic Testing Facilities: Developing countries are investing in genomic labs and biobanks, expanding access to personalized medicine.
Report Scope of Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 24.96 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 79.26 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 |
CAGR of 13.7% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Application, Indication, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Laboratory Corporation of America Holding; Quest Diagnostics Incorporated; Agilent Technologies, Inc.; Genome Medical, Inc.; Coriell Life Sciences; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; NeoGenomics Laboratories; FOUNDATION MEDICINE, INC.; Illumina, Inc.; Guardant Health. |
Market Driver: Advancement in Genomic Technologies
One of the most influential drivers of the personalized medicine biomarkers market is the rapid advancement of genomic technologies. The cost of genome sequencing has plummeted, from nearly $100 million in 2001 to less than $1,000 today. Technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), CRISPR-Cas9 for gene editing, and transcriptomics have dramatically increased the capability to discover, validate, and utilize biomarkers. These tools facilitate the precise characterization of diseases at the molecular level, enabling tailored therapy plans and improved prognostic capabilities. For instance, genomic profiling of tumors is now routine in many oncology practices, guiding the use of targeted therapies like EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer.
Market Restraint: Lack of Standardization and Regulatory Hurdles
Despite robust innovation, the lack of standardization and complex regulatory frameworks present considerable obstacles. Biomarkers vary significantly in quality, reproducibility, and clinical utility across labs and populations. The absence of universally accepted validation protocols can delay regulatory approvals and commercial adoption. Additionally, reimbursement challenges and the fragmented nature of healthcare systems—particularly in low- and middle-income countries—restrict the integration of personalized diagnostics. The inconsistent policies among agencies like the FDA, EMA, and regional authorities can also complicate global market entry strategies for biomarker-based products.
Market Opportunity: Expansion in Non-Oncology Indications
While oncology remains the flagship domain, the extension of personalized biomarkers into non-oncology indications offers a massive untapped opportunity. Cardiology, neurology, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases are now witnessing growing research in biomarker-led interventions. For example, the use of cardiac biomarkers like high-sensitivity troponin in heart failure prognosis is becoming mainstream. In neurology, biomarkers like tau protein and beta-amyloid are vital for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and monitoring. The continued expansion of clinical trials, government funding for chronic disease management, and patient-centric drug development frameworks will likely open new frontiers in these therapeutic areas.
Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market By Application Insights
Treatment selection dominates the application segment, owing to its integral role in optimizing therapeutic outcomes. Physicians are increasingly relying on biomarker insights to choose the most effective drugs while minimizing adverse reactions. In oncology, for instance, biomarkers like PD-L1 expression guide immunotherapy decisions, while KRAS mutations affect chemotherapy choice in colorectal cancer. Treatment personalization not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces costs associated with ineffective therapies.
Early detection/screening is the fastest-growing application, driven by the push toward preventive medicine and public health initiatives. Biomarkers are being used to identify diseases at a subclinical stage, allowing for timely intervention. For instance, in breast cancer, liquid biopsies detecting circulating tumor DNA have shown promise in identifying recurrence risk even before imaging findings. In cardiovascular medicine, biomarkers like NT-proBNP help identify asymptomatic individuals at risk for heart failure. These applications are particularly vital in aging populations where proactive disease management improves quality of life and healthcare sustainability.
Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market By Indication Insights
Oncology remains the largest indication, given the sheer volume of research, funding, and approvals linked to cancer biomarker applications. Within oncology, breast cancer dominates due to the widespread use of markers like HER2, BRCA1/2, and Ki-67. The availability of targeted therapies has necessitated the use of these markers, integrating them into national and global treatment guidelines. In addition, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is becoming a key tool in minimal residual disease detection and therapy response monitoring.
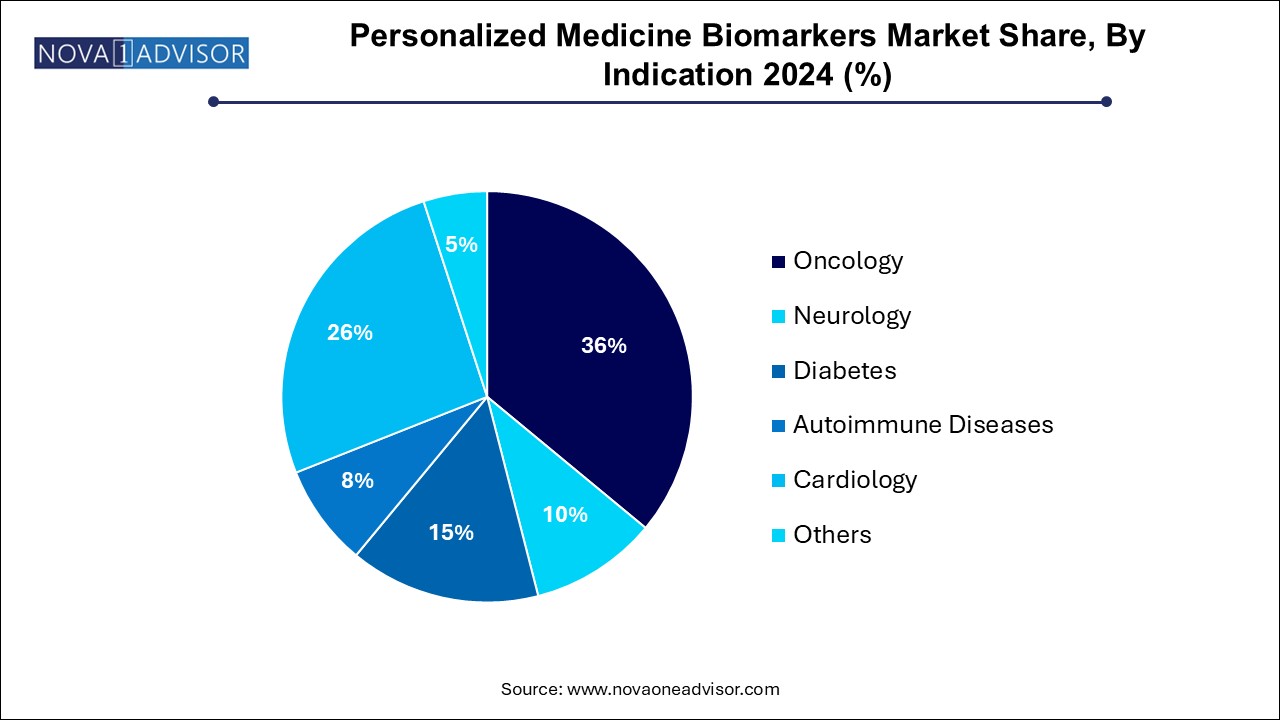
Neurology is emerging as the fastest-growing indication, with a rising burden of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid (e.g., amyloid-beta, tau) and blood-based tests are increasingly used for early diagnosis and disease monitoring. The development of neuro-biomarker panels and blood tests for cognitive decline are making strides, especially with FDA-approved diagnostics entering the market, such as those by C2N Diagnostics.
Some of the prominent players in the personalized medicine biomarkers market include:
Personalized Medicine Biomarkers Market Recent Developments
-
Roche Diagnostics (January 2025): Launched a next-gen panel of liquid biopsy tests under its AVENIO brand, targeting cfDNA applications in colorectal and lung cancers.
-
Illumina Inc. (March 2025): Partnered with AstraZeneca to co-develop NGS-based companion diagnostics focused on rare biomarkers in oncology and neurology.
-
Guardant Health (February 2025): Received FDA breakthrough designation for a cfDNA-based blood test for minimal residual disease (MRD) detection in early-stage colon cancer.
-
Bio-Techne (December 2024): Expanded its neurodegenerative disease biomarker portfolio with new assays for tau and amyloid in blood and CSF samples.
-
Exact Sciences (November 2024): Announced results from a pivotal study showing over 90% accuracy of their multi-cancer detection test based on cfDNA methylation markers.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the personalized medicine biomarkers market
By Application
- Early Detection/Screening
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Selection
- Monitoring
By Indication
-
-
- Breast Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Colon Cancer
- Others
-
- By Circulating Biomarkers
-
-
- Circulating Tumor Cells(CTCs)
- Circulating Cell-free DNA(cfDNA)
- Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
- Other Circulating Biomarkers
- Neurology
- Diabetes
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Cardiology
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)




