Pharmaceutical CDMO Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
The global pharmaceutical CDMO market size was estimated at USD 168.75 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 347.8 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
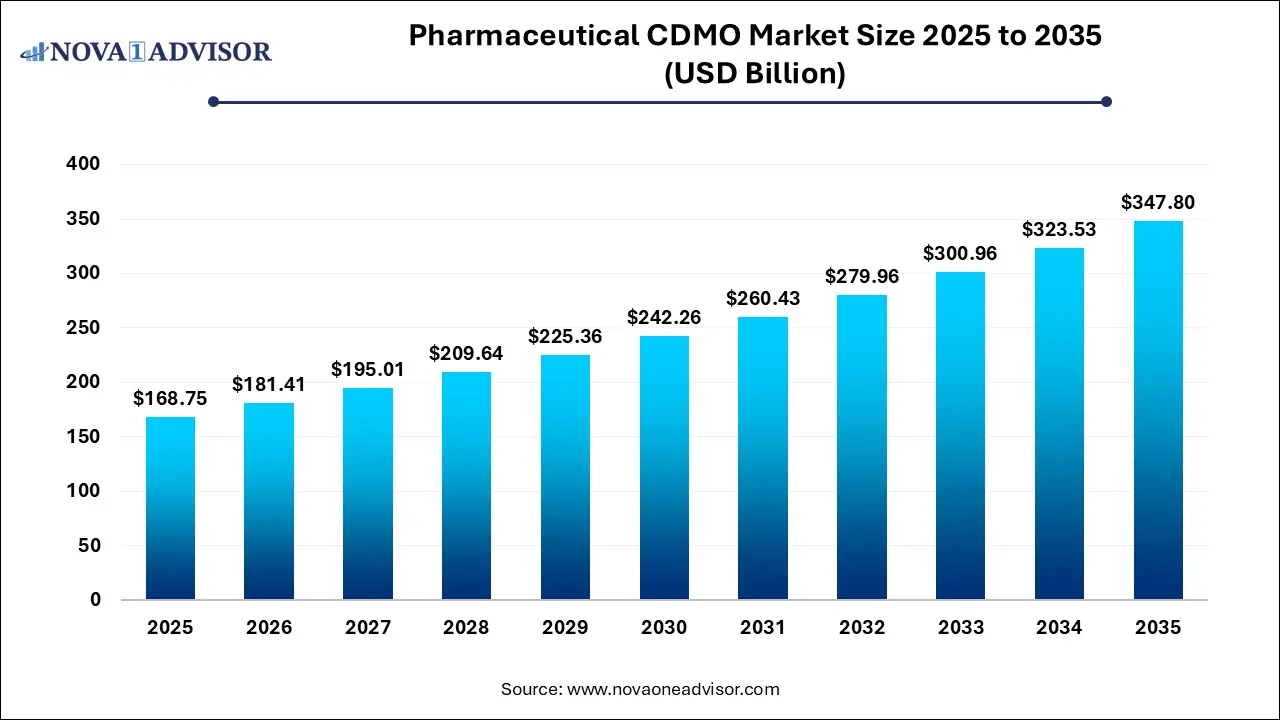
Key Takeaways:
- Based on application, the oncology segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 21.92% in 2025 and is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period.
- Based on product, the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 81.11% in 2025.
- In 2025, the drug product segment is anticipated to grow at a lucrative CAGR over the forecast period.
- Based on work-flow, The commercial segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 87.99% in 2025.
- The pharmaceutical CDMO market in the U.S. held the largest share in 2025.
- Asia Pacific held the market with the largest revenue share of 37.85% in 2025.
- The pharmaceutical CDMO market in Europe is expected to grow at the significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- The Germany pharmaceutical CDMO market held the largest share in 2025.
- The pharmaceutical CDMO market in the UK is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The pharmaceutical CDMO market in China held the largest share in 2025.
- The Japan pharmaceutical CDMO market is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The pharmaceutical CDMO market in India is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The pharmaceutical contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) market has become an essential component of the global pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical ecosystem. As drug developers increasingly focus on research, marketing, and patient access strategies, CDMOs have emerged as key partners that offer outsourced services for drug development, formulation, manufacturing, packaging, and regulatory compliance. This outsourcing model has gained immense traction due to the rising complexity of drug molecules, demand for faster time-to-market, and the capital-intensive nature of manufacturing infrastructure.
The market encompasses a wide range of services across both active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished drug products, serving pharmaceutical companies of all sizes. From small biotech startups seeking clinical-stage manufacturing to large pharma companies outsourcing commercial volumes, CDMOs have positioned themselves as agile, scalable, and technologically advanced service providers. The surge in demand for specialized drug forms such as highly potent APIs, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and complex oral or injectable formulations further enhances the strategic relevance of CDMOs.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical need for reliable outsourcing partners, with CDMOs playing pivotal roles in vaccine production, therapeutic scale-up, and supply chain continuity. This event has reinforced the importance of geographic diversification, technological capability, and regulatory compliance in selecting CDMO partners.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising adoption of continuous manufacturing technologies for improved yield and efficiency
-
Increased demand for highly potent APIs (HP-APIs) and ADCs, particularly in oncology
-
Expansion of biologics CDMO capacity to meet demand for monoclonal antibodies, cell & gene therapies
-
Surge in integrated CDMO models offering end-to-end services from clinical to commercial stages
-
Enhanced digitalization of manufacturing operations for traceability and quality assurance
-
Growth in demand for sterile injectable and parenteral dosage manufacturing
-
Strategic partnerships and M&A activity between CDMOs and pharma companies
-
Increased reshoring of pharmaceutical manufacturing in the U.S. and Europe
Pharmaceutical CDMO Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 181.41 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 347.80 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 7.5% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Workflow, Application, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Lonza; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Recipharm AB; Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (LabCorp); Catalent, Inc.; WuXi AppTec, Inc.; Samsung Biologics; Piramal Pharma Solutions; Siegfried Holding AG; CordenPharma International; Cambrex Corporation; Bushu Pharmaceuticals Ltd.; Nipro Corporation |
Key Market Driver: Rising Complexity in Drug Development and the Shift to Specialty Therapies
A key driver of the pharmaceutical CDMO market is the growing complexity of modern drug development, including the shift toward specialty, personalized, and high-potency therapies. Drugs in development today often involve complex APIs, intricate dosage forms, and require advanced formulation technologies. Manufacturing these products in-house demands significant capital investment, operational expertise, and regulatory compliance, all of which are non-core functions for many pharmaceutical firms.
CDMOs, with their focused expertise, scalable infrastructure, and regulatory track records, offer an attractive solution. Whether it’s micro-dosing for pediatric use, conjugation chemistry for ADCs, or aseptic fill-finish for biologics, CDMOs provide the capabilities that support a wide spectrum of drug modalities. This complexity-driven outsourcing is especially valuable to mid-sized and small pharmaceutical firms that may lack the technical or financial resources to build in-house capacity.
Key Market Restraint: Regulatory Compliance and Supply Chain Vulnerability
A significant restraint in the CDMO market is managing regulatory compliance across geographies and mitigating supply chain vulnerabilities. Pharmaceutical manufacturing is subject to stringent oversight by authorities such as the U.S. FDA, European EMA, and other national regulators. Ensuring adherence to current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP), validation protocols, and quality control can be challenging for CDMOs operating multiple global facilities.
Furthermore, CDMOs often source raw materials and intermediates globally, which exposes them to risks such as geopolitical conflicts, trade restrictions, and pandemic-related disruptions. The need to maintain regulatory compliance while managing complex logistics and material dependencies requires CDMOs to invest heavily in risk management, supplier audits, and inventory control. Smaller CDMOs, in particular, may struggle to implement the comprehensive systems required to maintain seamless compliance and delivery.
Key Market Opportunity: Expansion in Biologics and Personalized Medicine Manufacturing
The most compelling opportunity in the pharmaceutical CDMO market lies in the expansion of biologics and personalized medicine manufacturing capabilities. The shift from traditional small molecules to large molecule biologics, including monoclonal antibodies, cell and gene therapies, and nucleic acid-based treatments, is reshaping the pharmaceutical landscape. These therapies require entirely different manufacturing technologies and regulatory standards.
Many CDMOs are now investing in single-use bioreactors, aseptic processing lines, and gene therapy suites to support growing demand. Additionally, personalized medicine necessitates flexible, small-batch manufacturing and rapid turnaround capabilities, which CDMOs are uniquely positioned to offer. Biopharmaceutical firms increasingly rely on CDMO partners that can manage clinical trial supplies, scale-up, and commercial production under one umbrella, especially in niche areas such as CAR-T cell therapy or mRNA vaccines.
By Application Insights
Oncology leads the application segment, with the highest number of new drug approvals and clinical trials targeting cancer therapies. The increasing use of targeted small molecules and biologics, including HP-APIs and ADCs, necessitates specialized manufacturing that CDMOs are now equipped to provide. Oncology drugs also tend to have smaller batch sizes but require higher containment and complexity, favoring advanced CDMO engagement.
Infectious diseases and metabolic disorders are steady contributors, while neurological and autoimmune diseases are emerging as high-growth segments. These areas often involve novel delivery systems or therapeutic modalities such as gene therapies, requiring CDMOs to adapt rapidly. The growing focus on mental health, rare diseases, and gene editing technologies will continue to diversify application-driven demand.
By Product Insights
Oral solid dosage forms dominate the drug product segment, driven by their ease of administration, stability, and high patient compliance. CDMOs provide granulation, tablet compression, coating, and packaging services for a wide range of therapeutic areas, often integrating formulation development with commercial-scale production. This segment also benefits from established regulatory frameworks and high automation potential.
On the other hand, liquid dose and injectable formulations are growing rapidly, particularly due to the increasing demand for biologics and parenteral drugs. These formulations require aseptic environments and specialized filling technologies, making them more complex and capital-intensive. CDMOs with capabilities in sterile fill-finish, lyophilization, and vial/syringe production are becoming increasingly attractive, especially for biologics and vaccines.
By Work Flow Insights
Commercial manufacturing remains the dominant workflow, as many pharma companies outsource commercial volumes of mature or approved drugs to CDMOs to reduce internal burden and maintain cost-efficiency. This includes large-scale API synthesis, oral dose production, and packaging for global distribution.
However, clinical manufacturing is the fastest-growing segment, owing to the surge in early-stage R&D activity among biotech and mid-sized pharma firms. These companies often lack in-house capabilities and seek CDMOs for flexible, small-batch production under GMP conditions. CDMOs that also offer regulatory filing support, analytical method validation, and process scale-up services are particularly valued in this stage.
By Regional Insights
North America leads the global pharmaceutical CDMO market, largely due to the strong presence of major pharmaceutical companies, regulatory clarity, and high R&D investments. The U.S., in particular, has a robust network of CDMOs offering advanced manufacturing for small molecules and biologics. Companies like Catalent, Thermo Fisher, and Patheon dominate in this region. Moreover, government incentives to reshore critical drug production are driving fresh investments in local CDMO capacity.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with India and China emerging as global manufacturing powerhouses. Indian CDMOs excel in generic API production and have global regulatory approvals, while China is investing in high-tech biologics manufacturing facilities. The region benefits from low-cost labor, favorable tax regimes, and increasing domestic pharmaceutical demand. Moreover, Korean and Japanese CDMOs are expanding in cell therapy and high-value biologics.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Catalent announced a $250 million investment in its gene therapy manufacturing facility in Maryland, expanding viral vector and plasmid production.
-
January 2025: Lonza opened a new ADC suite in Switzerland, enhancing its high-potency conjugation capabilities.
-
December 2024: Samsung Biologics signed a $1 billion contract with a global pharma firm to provide biologics manufacturing and fill-finish services.
-
November 2024: Thermo Fisher Scientific completed the expansion of its biologics site in St. Louis, adding capacity for flexible GMP production.
-
September 2024: Recipharm acquired a mid-sized U.S.-based CDMO focused on sterile injectables and small-volume parenterals.
Key Pharmaceutical CDMO Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the pharmaceutical CDMO market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Lonza
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Recipharm AB
- Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (LabCorp)
- Catalent, Inc.
- WuXi AppTec, Inc.
- Samsung Biologics
- Piramal Pharma Solutions
- Siegfried Holding AG
- CordenPharma International
- Cambrex Corporation
- Bushu Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- Nipro Corporation
- Sequens
- EuroAPI
- Hovione
- Axplora
- Curia
- Dottikon
- Almac
- FIS - Fabbrica Italiana Sintetici S.p.A.
- Evonik
- Carbogen Amcis
- Farmhispania
- Uquifa
- AjiBio
- Pfizer Centre One
- Fareva
- Sterling
- Veranova
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Pharmaceutical CDMO market.
By Product
- API
- Type
- Traditional Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (Traditional API)
- Highly Potent Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (HP-API)
- Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC)
- Others
- Synthesis
- Drug
- Manufacturing
- Continuous manufacturing
- Batch manufacturing
- Drug Product
- Oral solid dose
- Semi-solid dose
- Liquid dose
- Others
By Workflow
By Application
- Oncology
- Small Molecules
- Biologics
- Infectious Diseases
- Neurological Disorders
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Metabolic Disorders
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Respiratory Diseases
- Ophthalmology
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Hormonal Disorders
- Hematological Disorders
- Others
By End-use
- Small Pharmaceutical Companies
- Medium Pharmaceutical Companies
- Large Pharmaceutical Companies
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

