Point Of Care Diagnostics Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
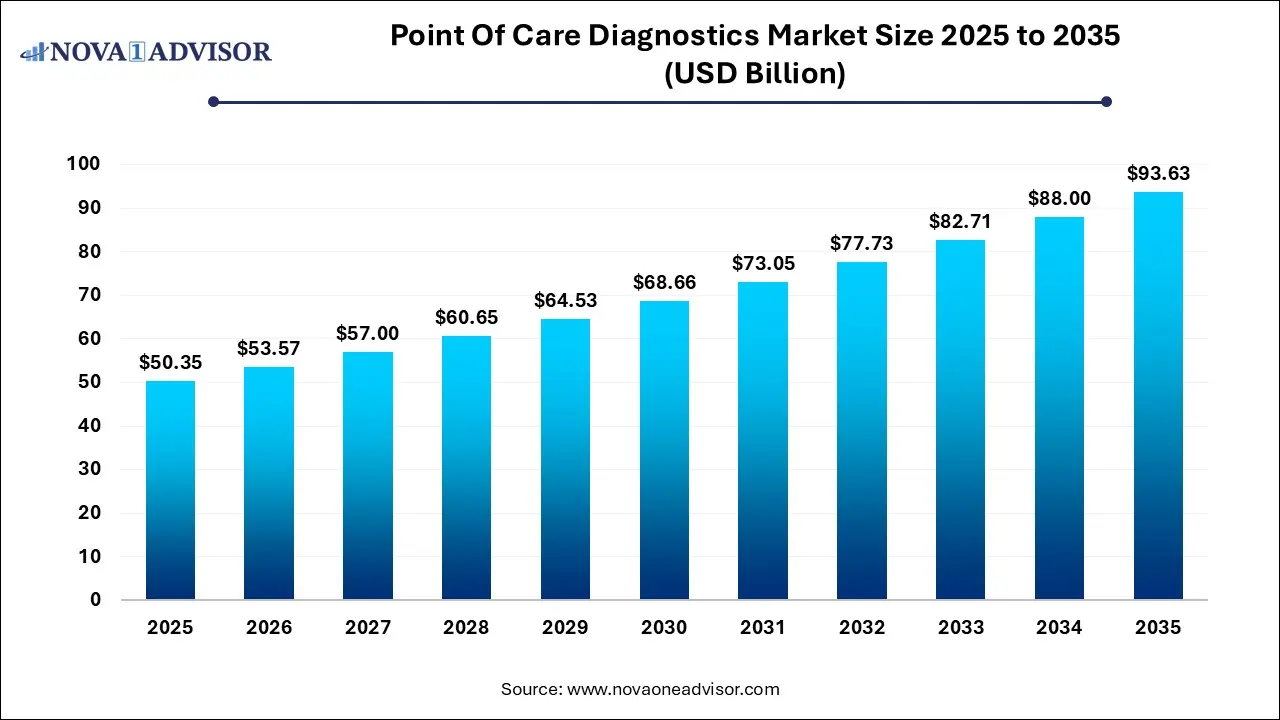
The global point-of-care diagnostics market size was exhibited at USD 50.35 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 93.63 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period of 2026 to 2035.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market and accounted for a 44.0% share in 2025.
- Infectious disease led the market and accounted for 27.11% of global revenue share in 2025.
- The clinic end-use segment led the market and accounted for the highest revenue share in 2025.
Market Overview
The Point of Care (POC) Diagnostics Market has become a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery, offering rapid, reliable, and actionable results at or near the site of patient care. These diagnostics reduce the need for centralized laboratory testing by providing results within minutes or hours, thereby accelerating clinical decision-making, improving patient outcomes, and reducing the burden on overstretched healthcare infrastructures.
The evolution of POC diagnostics has been propelled by technological innovations in biosensors, microfluidics, nanotechnology, and portable device design. Initially focused on glucose testing for diabetic patients, the market has expanded to encompass a broad spectrum of clinical areas including infectious diseases (e.g., HIV, COVID-19, RSV), chronic conditions (e.g., cardiac markers, thyroid issues), and even cancer diagnostics. The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically underscored the value of POC testing, driving demand for rapid antigen and molecular tests worldwide and catalyzing investment into mobile and decentralized diagnostic solutions.
From rural clinics in low-resource regions to high-tech hospitals in developed economies, POC diagnostics are now integral in delivering accessible, personalized, and time-sensitive care. As healthcare systems transition towards value-based care and patient-centric models, the relevance of POC diagnostics continues to grow.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Miniaturization and Portability of Devices: Technological advancement has led to compact, handheld, or wearable POC devices that are user-friendly and require minimal training.
-
Integration with Digital Health Platforms: Devices increasingly incorporate Bluetooth or IoT capabilities to sync test data with electronic health records (EHRs), facilitating telehealth and remote monitoring.
-
Increased Focus on Home-based Testing: Demand for self-testing kits has grown, especially in chronic disease management, fertility, and infectious disease diagnosis.
-
Multiplex Testing Platforms: Devices capable of detecting multiple biomarkers simultaneously are gaining traction, particularly in emergency care and infectious disease settings.
-
Rising Demand in Emerging Economies: Expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising disease awareness in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are fueling POC diagnostic adoption.
-
AI-driven Diagnostics: Machine learning is being embedded into POC platforms for automated interpretation, enhancing accuracy and scalability.
-
Public-Private Partnerships: Governments are increasingly collaborating with diagnostic firms to improve POC access, especially in epidemic-prone and rural regions.
Point Of Care Diagnostics Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 53.57 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 93.63 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 6.4% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Qiagen; Danaher Corporation; Becton Dickinson (BD); bioMérieux; Abbott; Siemens Healthcare GmbH; Werfen; Nova Biomedical; Trividia Health, Inc.; QuidelOrtho Corporation; Trinity Biotech; Sekisui Diagnostics; Orasure Technologies, Inc.; Spectral Medical, Inc.; EKF Diagnostics Holdings Plc.; Anbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; AccuBioTech Co., Ltd.; ALPHA LABORATORIES. |
Key Market Driver: Demand for Rapid Diagnostic Solutions in Infectious Disease Management
One of the most powerful drivers for the point of care diagnostics market is the urgent need for timely diagnosis in infectious diseases, particularly during outbreaks. The global health crises posed by COVID-19, Ebola, Zika, and Tuberculosis have highlighted the limitations of centralized lab-based systems. In such situations, every minute matters POC diagnostics enable rapid screening and isolation protocols, helping contain disease spread. For example, Abbott’s ID NOW™ COVID-19 test, which delivers results in under 15 minutes, was widely adopted during the pandemic, especially in airport screening, emergency rooms, and drive-through testing centers. Similarly, Cepheid’s GeneXpert platform enabled remote TB detection in sub-Saharan Africa, revolutionizing access to molecular diagnostics. The ability to make diagnostic data available instantly is a game-changer in both high-acuity and primary care settings.
Key Market Restraint: Variability in Accuracy Compared to Central Lab Testing
Despite their convenience, one of the significant limitations of POC diagnostics lies in their variability in sensitivity and specificity, particularly in complex disease profiles. While central laboratories benefit from sophisticated equipment and rigorous quality control protocols, POC devices especially over-the-counter and at-home kits can yield false positives or negatives due to user error, improper storage, or limited assay robustness. For example, during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, many rapid antigen tests demonstrated inconsistent performance compared to PCR testing, leading to misdiagnoses and delayed interventions. This inconsistency affects physician confidence in POC results and can restrict adoption in certain clinical scenarios, particularly in oncology and autoimmune disease diagnostics where accuracy is paramount.
An exciting frontier for the POC diagnostics market lies in the convergence of diagnostics with mobile health (mHealth) and wearable technologies. Increasingly, tech companies are entering the healthcare space to develop smart diagnostic tools that are portable, connected, and continuous. For example, Apple’s collaboration with Johnson & Johnson on the Heartline study explores whether wearable ECG monitors can detect atrial fibrillation more effectively. Similarly, Cue Health's molecular diagnostic device integrates with a smartphone to deliver results for respiratory infections and COVID-19. As consumers demand more control over their health, this integration of POC diagnostics with real-time health tracking platforms opens new doors for preventive care, remote patient monitoring, and chronic disease management.
Segments Insights:
By Product
Glucose testing dominated the point of care diagnostics market in 2025, due to its longstanding use, high disease burden, and widespread accessibility. Diabetes affects over 530 million people globally, and glucose testing devices have become the most common form of self-administered diagnostic technology. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) like Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre and Dexcom’s G7 are revolutionizing diabetic care by providing near real-time readings and alerts. These devices enhance glycemic control, reduce complications, and are now even being integrated with insulin pumps for automated dosing. The segment continues to grow due to new entrants, expanded insurance coverage, and user-friendly product innovations.
Infectious disease testing is anticipated to be the fastest-growing product segment, propelled by increasing incidence rates of communicable diseases, especially in developing regions. Subsegments such as COVID-19 POC, HIV POC, and Influenza POC have seen exceptional growth. The pandemic brought a surge in demand for rapid antigen tests, driving massive investments in diagnostic manufacturing. Companies like Abbott, BD, and Roche responded with scalable testing platforms. Beyond COVID-19, the growing concern over antibiotic resistance and re-emergence of diseases like TB and RSV is fueling innovation in multi-pathogen detection panels and molecular diagnostics in POC settings.
By End-Use
Hospitals held the largest share of the POC diagnostics market, given their critical role in acute care delivery, surgical procedures, and emergency interventions. In hospitals, rapid test results can alter treatment pathways immediately—this is especially important for sepsis diagnosis, cardiac marker evaluation (e.g., troponin), and coagulation monitoring. Additionally, hospitals house POC devices across departments such as ICU, ER, and maternity care, where time-sensitive decisions are crucial. Platforms like Abbott’s i-STAT and Roche’s cobas Liat are commonly used in hospitals to streamline testing without sending samples to central labs.
Home settings are expected to be the fastest-growing end-use segment. The combination of aging populations, chronic disease burden, and rising healthcare consumerism is pushing diagnostics closer to the patient. The shift toward home-based care was further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, with millions adopting self-test kits for infectious diseases. Additionally, telehealth services often recommend at-home POC testing to confirm diagnoses remotely. From ovulation and fertility kits to urinalysis strips and cancer biomarker tests, a growing product portfolio is available for consumer use. Companies like LetsGetChecked and Everlywell have also introduced subscription-based diagnostic services, turning the home into a mini-clinic for routine health monitoring.
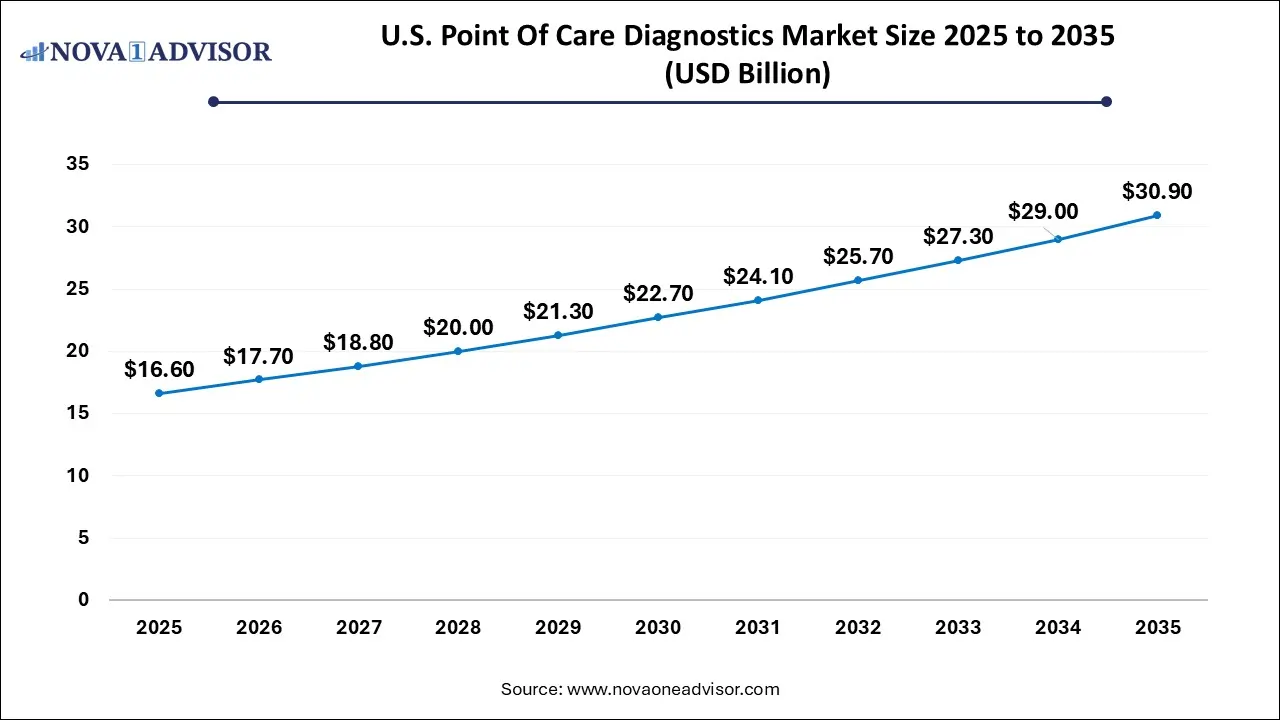
U.S. Point Of Care Diagnostics Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
The U.S. point-of-care diagnostics market size is calculated at USD 16.6 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach nearly USD 30.9 billion in 2035, accelerating at a strong CAGR of 5.81% between 2026 and 2035.
By Regional Insights
North America emerged as the leading regional market in 2025, owing to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high adoption of new technologies, and strong presence of key market players. The United States alone accounts for a significant share of the global market, bolstered by supportive regulatory frameworks and reimbursement policies. The FDA has accelerated the clearance of several innovative POC diagnostics through Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) and Breakthrough Device Programs. Moreover, government initiatives like the RADx program (Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics) have poured billions into scaling diagnostic access during health crises. Hospitals, retail clinics, and pharmacies in the U.S. actively offer POC tests, particularly for glucose, cardiac markers, STDs, and COVID-19.
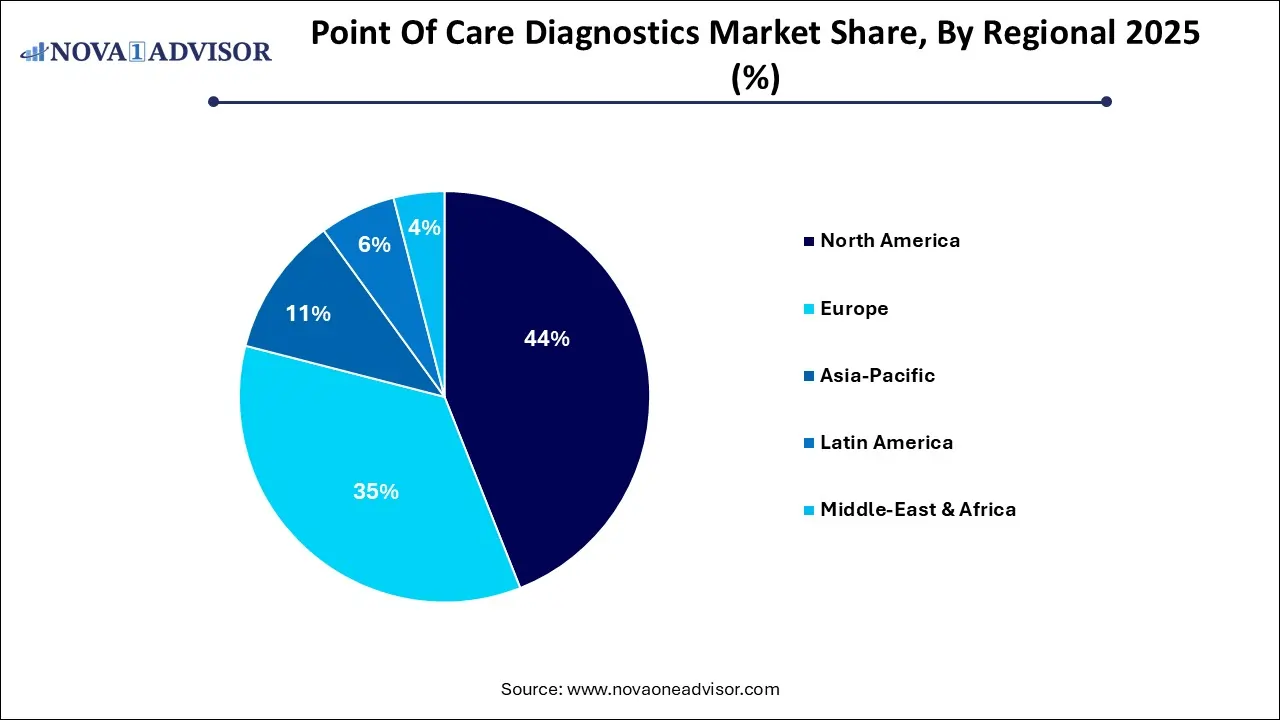
Asia-Pacific is forecasted to be the fastest-growing region in the coming years. Factors such as rising healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of disease prevention, and high prevalence of infectious diseases are driving market expansion. Countries like India and China are focusing on rural healthcare outreach programs, integrating portable diagnostic units into primary health centers. Moreover, domestic companies such as Mylab (India) and Wondfo (China) are launching low-cost, easy-to-use POC kits tailored for local needs. Japan and South Korea are also contributing to growth through innovations in mobile diagnostics and aging population-focused POC products. With a large population base and expanding middle class, Asia-Pacific represents a fertile ground for both global and local diagnostic players.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – Abbott Laboratories launched its new version of FreeStyle Libre 4, a continuous glucose monitor with enhanced integration into smartphones and automated insulin delivery systems.
-
February 2025 – Roche Diagnostics introduced a new POC influenza and RSV combo test using its cobas Liat system, aimed at tackling seasonal respiratory disease surges in Europe and the U.S.
-
January 2025 – BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) announced the global expansion of its BD Veritor Plus platform for rapid COVID-19 and flu combo testing in pharmacies and outpatient settings.
-
December 2024 – Siemens Healthineers partnered with India’s MedGenome to expand access to its cardiac POC diagnostic tools in South Asia, especially targeting rural hospitals.
-
November 2024 – Cue Health received FDA De Novo authorization for its molecular COVID-19 test, making it one of the first molecular POC tests to receive full clearance outside of EUA.
Some of the prominent players in the point-of-care diagnostics market include:
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Qiagen
- Danaher Corporation
- Becton Dickinson (BD)
- bioMérieux
- Abbott
- Siemens Healthcare GmbH
- Werfen
- Nova Biomedical
- Trividia Health, Inc.
- QuidelOrtho Corporation
- Trinity Biotech
- Sekisui Diagnostics
- Orasure Technologies, Inc.
- Spectral Medical, Inc.
- EKF Diagnostics Holdings plc.
- Anbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
- AccuBioTech Co., Ltd
- ALPHA LABORATORIES.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global point of care diagnostics market.
Product
- Glucose Testing
- Hb1Ac Testing
- Coagulation Testing
- Fertility/Pregnancy
- Infectious Disease
-
- HIV POC
- Clostridium Difficile POC
- HBV POC
- Pneumonia or Streptococcus Associated Infections
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) POC
- HPV POC
- Influenza/Flu POC
- HCV POC
- MRSA POC
- TB and Drug-resistant TB POC
- HSV POC
- COVID-19
- Other Infectious Diseases
- Cardiac Markers
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- Hematology
- Primary Care Systems
- Decentralized Clinical Chemistry
- Feces
- Lipid Testing
- Cancer Marker
- Blood Gas/Electrolytes
- Ambulatory Chemistry
- Drug of Abuse (DOA) Testing
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Urinalysis/Nephrology
End-use
- Clinics
- Hospitals
- Home
- Assisted Living Healthcare Facilities
- Laboratory
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



