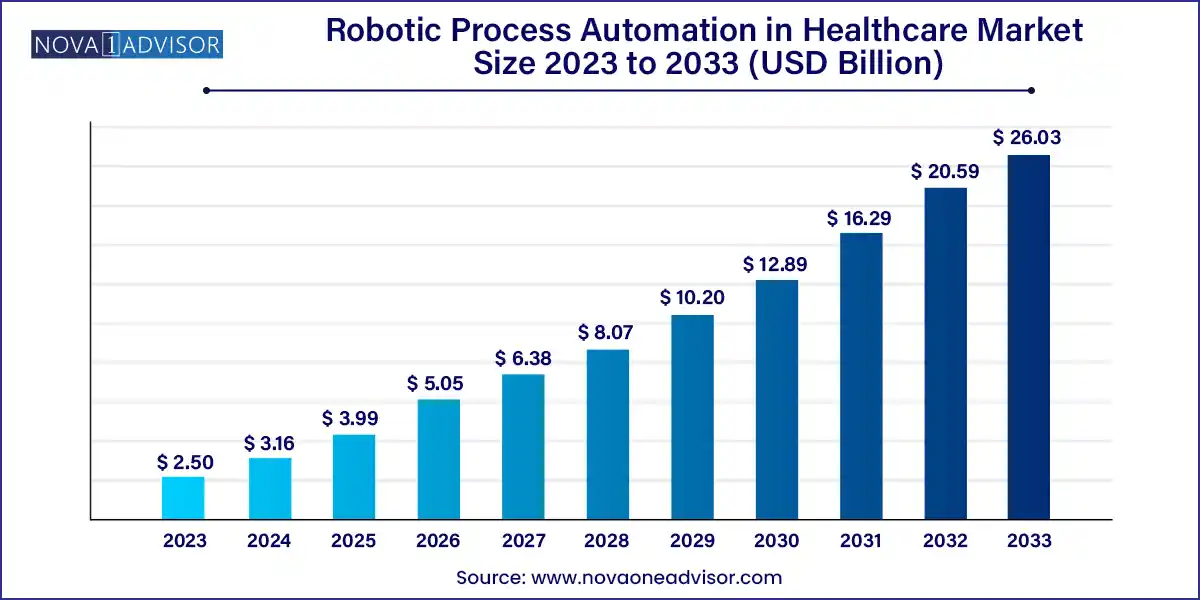
The global robotic process automation in healthcare market size was exhibited at USD 2.50 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 26.03 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 26.4% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- Due to its wide range of applications, the software sector led the worldwide market in 2023.
- The segment's greatest contribution to the worldwide market in 2023 was clinical documentation, billing, and workflow management, and it is very expected that this trend will persist over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare Market is at the cusp of a digital revolution, radically transforming how administrative and operational tasks are executed within healthcare systems. RPA, a technology that uses bots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, is being embraced by hospitals, insurance companies, diagnostics laboratories, and life sciences organizations to boost efficiency, accuracy, and patient satisfaction.
Healthcare institutions are under immense pressure to cut costs, improve operational outcomes, and enhance the patient experience all while complying with increasingly complex regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. RPA addresses these demands by streamlining high-volume workflows like claims processing, billing, data entry, and appointment scheduling. Unlike traditional software, RPA mimics human interactions with digital systems and can be deployed rapidly without disrupting existing IT infrastructures.
As healthcare shifts towards value-based care, the emphasis on automation has increased. RPA has emerged as a pivotal tool in this transformation by reducing administrative bottlenecks, minimizing human error, accelerating turnaround times, and freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed RPA adoption in hospitals and public health agencies by supporting contact tracing, case tracking, and vaccine scheduling.
Backed by technological advancements in AI and machine learning, modern RPA systems are evolving beyond simple rule-based bots to cognitive automation solutions that can analyze context, interpret unstructured data, and make recommendations further widening their scope of use in healthcare.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): RPA solutions are being combined with machine learning and natural language processing to handle unstructured data and make intelligent decisions.
-
Shift Toward Intelligent Automation: Organizations are evolving from task-level automation to end-to-end process orchestration using RPA combined with analytics and workflow engines.
-
Surge in Claims Automation: Payers are deploying RPA to fast-track claims processing, reduce rework, and ensure compliance, especially in the U.S. market.
-
Patient-Centric Automation Models: From appointment scheduling to post-discharge engagement, RPA bots are being deployed to improve patient interactions and reduce waiting times.
-
Cloud-Based RPA Solutions: Vendors are rolling out cloud-native RPA platforms to improve scalability, integration, and affordability, making automation accessible to smaller practices.
-
Focus on Security and Compliance: RPA providers are increasingly embedding audit trails, encryption, and access control features to meet healthcare's stringent data security regulations.
-
Growth in Consulting and Support Services: As adoption rises, the demand for RPA implementation, training, and support services is growing, especially among mid-sized healthcare providers.
Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare Market Report Scope
Market Driver: Need for Cost Optimization and Operational Efficiency
The primary catalyst behind the rapid growth of RPA in healthcare is the urgent need to optimize operational efficiency and reduce administrative costs. Healthcare systems are often burdened with redundant manual processes, from insurance verification to medical coding, that consume valuable time and resources. RPA allows these repetitive tasks to be completed quickly and accurately, thus significantly lowering operational overhead.
For instance, leading U.S.-based insurer Anthem Inc. implemented RPA to streamline claims adjudication, reducing processing time from several days to a few hours. Similarly, hospital systems in the UK’s NHS have deployed bots to automate patient data entry into Electronic Health Records (EHR), freeing up nurses and administrative staff for clinical tasks. These efficiency gains not only translate into cost savings but also enhance service delivery and staff morale.
Market Restraint: Resistance to Change and Legacy Infrastructure
Despite its promise, resistance to change and reliance on legacy systems pose significant hurdles to RPA adoption in healthcare. Many hospitals and healthcare providers still rely on outdated IT infrastructures, making it challenging to integrate modern RPA platforms without considerable customization.
Moreover, there is institutional hesitancy driven by fears of job displacement, cybersecurity risks, and compliance concerns. Healthcare leaders often face pushback from clinical and administrative staff who view automation as a threat to job security. Additionally, ensuring seamless interaction between RPA bots and legacy applications requires meticulous planning and testing, which can delay deployments and inflate costs.
Market Opportunity: RPA in Clinical and Administrative Convergence
An emerging opportunity lies in the convergence of clinical and administrative data automation, where RPA can act as a bridge between front-end patient care and back-end operations. Traditionally, these functions have been siloed, leading to data discrepancies, delays, and inefficiencies. RPA, integrated with AI and EHR platforms, can unify these processes.
For example, in clinical documentation, bots can assist physicians by extracting key information from voice transcripts, auto-filling patient charts, and coding diagnoses for billing dramatically reducing clerical workloads. This creates an opportunity for vendors to offer vertical RPA solutions tailored to specific hospital departments or specialties (e.g., radiology, oncology), enhancing both clinical accuracy and administrative throughput.
Segmental Analysis
By Solution
Software dominated the RPA solution segment, largely due to the rapid deployment and scalability of bot-based automation tools. RPA software is typically installed on-premises or hosted in the cloud, offering the ability to replicate human tasks with minimal intervention. Large hospital systems and insurance providers are investing heavily in software platforms to automate claims intake, billing, and interdepartmental workflows.
In contrast, the services segment is the fastest-growing, driven by growing demand for implementation support, customization, maintenance, and consulting. Mid-sized and smaller providers often lack the in-house expertise to deploy RPA and thus rely on third-party vendors. Services such as training, bot monitoring, bot lifecycle management, and post-deployment optimization are becoming essential, especially as RPA usage moves beyond pilot projects into enterprise-wide rollouts.
By Operations
Rule-based operations are the dominant mode, accounting for the majority of current deployments. These bots are ideal for handling structured, repetitive tasks like data migration, claims submission, appointment reminders, and inventory updates. Rule-based RPA has been widely adopted across healthcare administrative functions due to its simplicity, reliability, and quick ROI.
However, knowledge-based operations are rapidly gaining momentum, particularly with the integration of AI. These bots are capable of interpreting unstructured data, making conditional decisions, and learning from historical outcomes. For example, bots used in utilization management or revenue cycle optimization can now assess exceptions in claims and flag anomalies, a task previously dependent on human judgment. This evolution from robotic mimicry to cognitive assistance marks a significant leap in automation sophistication.
By Application
Claims management remains the dominant application of RPA in healthcare. Health insurers and hospital billing departments process thousands of claims daily a labor-intensive process prone to human error. RPA automates tasks such as eligibility verification, policy checks, claim filing, and rejection management. Companies like UnitedHealth Group and Cigna have reported significant reductions in processing times and increased first-pass claim resolution rates by deploying RPA bots.
Meanwhile, clinical documentation is the fastest-growing application, fueled by physician burnout and the push for digitization. Bots assist in scribing, populating EHRs, and transcribing consultations, enabling clinicians to spend more time with patients. Startups such as Suki.ai and Nuance (acquired by Microsoft) have pioneered AI-integrated RPA solutions that reduce charting time by 70%, significantly improving clinical productivity and documentation accuracy.
By Region
North America dominates the RPA in healthcare market, with the U.S. leading in adoption due to its advanced healthcare IT ecosystem, regulatory mandates, and high healthcare spending. U.S. health systems like Kaiser Permanente, Mayo Clinic, and Cleveland Clinic are early adopters of automation in back-office operations. In addition, the presence of major RPA vendors such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism ensures robust implementation support and platform evolution.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by countries like India, China, Japan, and Australia. This growth is attributed to expanding healthcare infrastructure, a tech-savvy workforce, and government digitization initiatives. For example, India’s National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) is encouraging hospitals and insurance providers to digitize and automate workflows. Furthermore, outsourcing hubs in the region are integrating RPA into healthcare BPO services, making Asia-Pacific a critical player in the global automation landscape.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – UiPath launched a specialized healthcare RPA module in collaboration with Cerner to automate patient scheduling and claims data exchange within electronic health records systems.
-
January 2025 – Blue Prism (SS&C Technologies) announced a partnership with Mayo Clinic to deploy AI-enabled RPA bots across revenue cycle and patient management workflows.
-
November 2024 – Automation Anywhere unveiled a cloud-based “Healthcare Bot Store” offering pre-built RPA bots for claims processing, prior authorizations, and discharge planning.
-
August 2024 – Cognizant expanded its healthcare automation division by acquiring a boutique RPA implementation firm specializing in payers and providers, enhancing its consulting capabilities.
-
June 2024 – NHS Digital (UK) launched a national RPA framework agreement to allow regional trusts easier access to approved RPA solutions and services, improving procurement and standardization.
Some of the prominent players in the Robotic process automation in healthcare market include:
- UiPath
- Blue Prism
- Automation Anywhere
- Kofax
- WorkFusion
- Jidoka
- Kryon Systems
- EdgeVerve Systems
- PegaSystems
- Another Monday
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global robotic process automation in healthcare market.
By Solution
- Software
- Services
- Implementation
- Support and Maintenance
- Training and Consulting
By Operations
- Rule-based Operation
- Knowledge-based Operation
By Application
- Claims Management
- Clinical Documentation
- Billing and Compliance Management
- Appointment Scheduling
- Workflow Management
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

