Robotic Process Automation Market Size and Growth
The robotic process automation market size was exhibited at USD 6.25 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 225.52 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 43.13% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
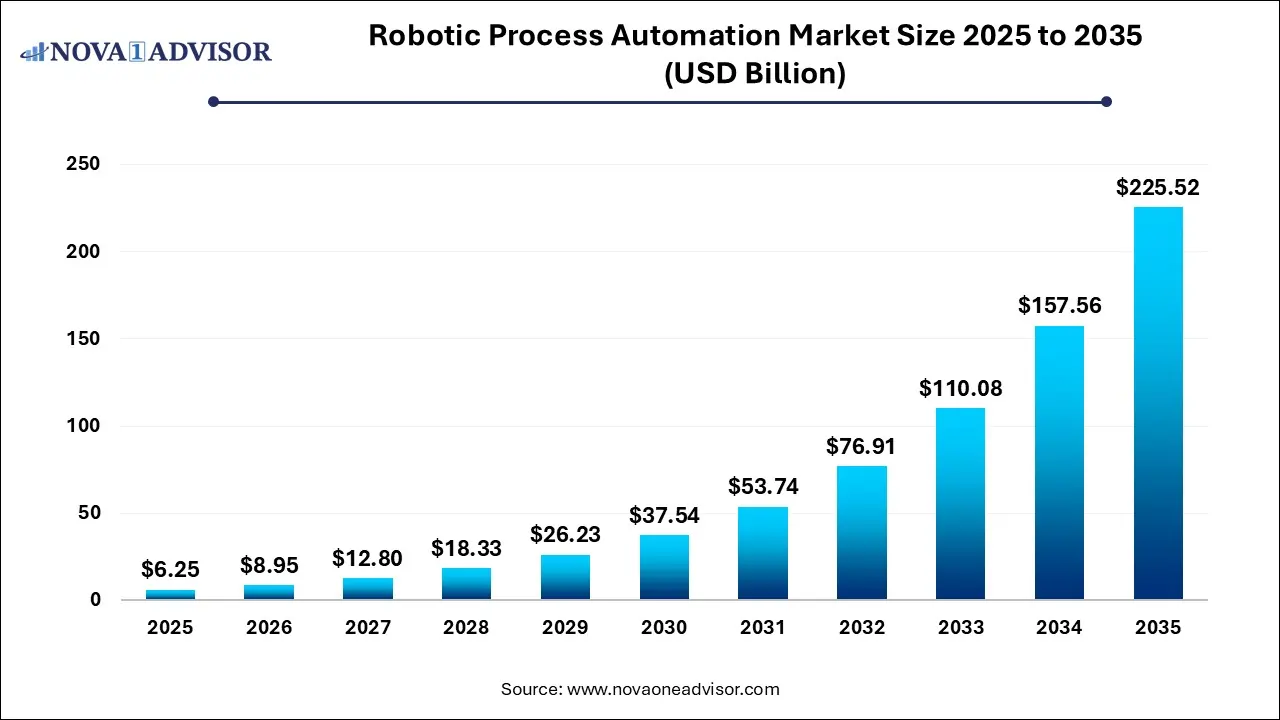
Robotic Process Automation Market Key Takeaways:
- The services segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 64.0% in 2025.
- The software segment is expected to grow at a significant rate from 2026 to 2035.
- The cloud segment accounted for the largest revenue share of over 55.0% in 2025.
- The on-premise segment is expected to grow at a significant rate from 2026 to 2035.
- The large enterprise segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2025.
- The small & medium enterprise (SME) segment is expected to grow at the 46.0% during the forecast period.
- The BFSI end use segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2025.
- The pharma & healthcare segment is expected to grow at a 48.2% during the forecast period.
- The rule based segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2025.
- The knowledge based segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate from 2026 to 2035.
- North America robotic process automation market held the major share of over 40.0% of the robotic process automation industry in 2025.
Market Overview
The Robotic Process Automation (RPA) market is experiencing exponential growth, transforming how businesses operate by automating routine and repetitive tasks using software bots. RPA emulates human interactions with digital systems and software, enabling enterprises to increase efficiency, accuracy, and scalability while reducing operational costs. From data entry to transaction processing, RPA streamlines workflows without modifying existing infrastructure, making it a highly accessible form of digital transformation.
Over the past decade, RPA has evolved from simple task automation to intelligent automation by integrating with technologies like AI, machine learning, and natural language processing. This evolution enables bots not just to execute rules-based activities but also to learn from patterns and make decisions. Organizations across industries—such as banking, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail—are adopting RPA to enhance productivity, compliance, and customer experience.
As digital initiatives accelerate globally, the demand for RPA is rising not only in large enterprises but also among small and medium businesses that aim to scale with lean resources. The global RPA market is poised to continue its upward trajectory as companies seek operational agility, cost optimization, and enhanced service delivery.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Hyperautomation Adoption: Businesses are moving toward hyperautomation, combining RPA with AI, analytics, and process mining for end-to-end workflow automation.
-
Cloud-based RPA Solutions: The shift toward cloud deployment for scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency is gaining momentum, especially among SMEs.
-
Rise of Citizen Developers: Low-code/no-code platforms are enabling non-technical users to create automation workflows, democratizing RPA deployment.
-
AI-enhanced Bots: Integration with AI and ML is enabling bots to handle unstructured data, language processing, and decision-making tasks.
-
RPA in Cybersecurity: Bots are increasingly used to monitor systems, flag anomalies, and automate responses in cybersecurity operations.
-
Demand for Scalable Governance Models: Enterprises are seeking RPA Centers of Excellence (CoE) to ensure scalable, secure, and compliant bot deployment.
-
Vertical-Specific Automation: RPA is being tailored to specific industries, such as healthcare claims processing, retail inventory tracking, and telecom service provisioning.
Report Scope of Robotic Process Automation Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 8.95 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 225.52 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 43.13% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Deployment, Enterprise Size, Operations, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Automation Anywhere Inc.; BlackLine Inc.; Blue Prism Limited; EdgeVerve Systems Limited; FPT Software; Microsoft; NICE; NTT Advanced Technology Corporation; OnviSource, Inc.; Pegasystems Inc.; SAP SE; Tungsten Automation Corporation; UiPath, Uniphore, WorkFusion, Inc. |
Key Market Driver: Growing Demand for Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
The primary driver of the RPA market is the increasing demand for operational efficiency and cost optimization. Organizations are constantly pressured to deliver faster services while maintaining profitability. RPA offers a compelling solution by automating high-volume, rule-based processes that are typically time-consuming and error-prone when performed manually.
For example, in the banking sector, RPA bots can automate credit card application processing, KYC verification, and compliance reporting, cutting down processing times from days to hours. Similarly, in insurance, bots manage claims administration, policy renewals, and regulatory submissions. By reducing manual intervention, businesses not only cut costs but also improve accuracy, scalability, and customer satisfaction.
Key Market Restraint: Process Complexity and Change Management
A major restraint to RPA adoption is the complexity of processes and resistance to organizational change. While RPA thrives in structured, rules-driven environments, many enterprise workflows are semi-structured or dependent on decision-making, making automation more difficult without extensive redesign or AI integration.
Additionally, change management is a hurdle. Employees may fear job displacement, leading to internal resistance. Without clear governance, training, and stakeholder alignment, RPA initiatives may stall. Organizations must therefore invest in culture change, process standardization, and stakeholder education to maximize ROI from automation.
Key Market Opportunity: RPA Integration in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
The expanding availability of cloud-based, low-code RPA solutions presents a significant opportunity in the SME segment. Traditionally, automation technologies were considered out of reach for small businesses due to high costs and IT requirements. However, with SaaS models and simplified RPA platforms, even small firms can automate tasks like invoice processing, employee onboarding, customer support, and lead management.
For instance, an SME in the retail sector could deploy RPA to reconcile inventory, update pricing databases, and process online orders without needing a large IT team. These solutions often come with built-in templates, drag-and-drop features, and scalability, allowing SMEs to adopt automation at their own pace and budget.
Robotic Process Automation Market By Type Insights
Software solutions dominate the RPA market, as the core of automation lies in robust and scalable software platforms that enable bots to interact with enterprise applications. These platforms offer orchestration, monitoring, scheduling, and analytics capabilities, allowing organizations to deploy and manage thousands of bots simultaneously. Vendors like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism are leading in innovation, offering AI-infused platforms with pre-built connectors and cross-functional capabilities.
Services are the fastest-growing segment, particularly implementation and consulting. Many organizations lack in-house RPA expertise and turn to service providers for process assessment, deployment strategy, and training. As RPA adoption grows across sectors, demand for post-deployment support, bot monitoring, and performance tuning is also rising, fueling the services segment.
Robotic Process Automation Market By Deployment Insights
On-premise deployment has been dominant, especially among large enterprises with data-sensitive processes or compliance mandates. Industries such as BFSI and healthcare prefer on-premise RPA for greater control, customization, and security. These deployments integrate closely with internal systems and are ideal for high-throughput, mission-critical operations.
Cloud deployment is the fastest-growing, driven by the scalability and low cost of SaaS-based RPA tools. Cloud-native bots can be accessed from anywhere, updated in real time, and scaled as business needs grow. Startups and SMEs, in particular, are embracing cloud RPA to reduce infrastructure burdens and enable remote process management.
Robotic Process Automation Market By Enterprise Size Insights
Large enterprises lead in RPA adoption, owing to their complex processes, high volumes of transactions, and capacity to invest in digital transformation. These organizations use RPA to streamline functions across finance, HR, procurement, and customer service. They are also more likely to build RPA Centers of Excellence and scale automation enterprise-wide.
SMEs represent the fastest-growing customer base, thanks to the emergence of affordable, user-friendly RPA platforms. Tools tailored for SMEs offer intuitive interfaces, pre-built workflows, and limited infrastructure dependency. This democratization of automation is enabling smaller firms to improve productivity, reduce costs, and remain competitive.
Robotic Process Automation Market By End-use Insights
BFSI is the largest end-use segment, with banks and insurers leveraging RPA for compliance, onboarding, transaction processing, and reporting. Automation helps reduce errors, meet regulatory deadlines, and enhance client interactions through faster response times.
Healthcare is among the fastest-growing, utilizing RPA for appointment scheduling, patient data management, billing, and claims processing. With rising demand for digital health services, RPA offers a non-invasive solution to automate workflows without disrupting clinical systems.
Other high-growth sectors include:
-
Retail & Consumer Goods: Automating inventory updates, order processing, and loyalty programs.
-
IT & Telecom: Managing service provisioning, ticketing, and configuration.
-
Manufacturing: Automating procurement, supply chain operations, and regulatory documentation.
Robotic Process Automation Market By Operations Insights
Rule-based automation remains dominant, as most early-stage RPA implementations focus on structured, repetitive tasks such as data entry, reconciliation, and report generation. These tasks are easier to automate and deliver quick ROI with minimal configuration.
Knowledge-based RPA is rapidly growing, driven by the integration of cognitive capabilities like natural language understanding and predictive analytics. These bots can handle more nuanced processes such as sentiment analysis, fraud detection, and intelligent document processing, making them suitable for customer service and compliance.
Robotic Process Automation Market By Regional Insights
North America dominates the global RPA market, owing to its mature IT ecosystem, high RPA adoption across industries, and strong presence of leading vendors. Enterprises in the U.S. and Canada have rapidly adopted RPA to streamline operations, manage labor costs, and gain competitive advantage. Regulatory pressures in banking and healthcare have also spurred automation for compliance.
Major companies like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and IBM operate out of North America, fostering innovation and partnerships. The region is also witnessing robust startup activity and academic collaboration in automation research.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing RPA market, fueled by digital transformation in emerging economies, labor-intensive industries, and supportive government policies. Countries like India, China, Japan, and Australia are leading in RPA adoption across BFSI, telecom, and manufacturing.
In India, the IT services industry has integrated RPA into client delivery, while banks and insurance firms automate back-office functions. In China, RPA is used in logistics, public services, and eCommerce. The region’s cost sensitivity, digital readiness, and expanding SME base make it a fertile ground for RPA expansion.
Some of the prominent players in the robotic process automation market include:
Recent Developments
-
April 2025: UiPath launched an AI-powered "Autopilot" assistant to generate automation workflows from natural language inputs, enhancing citizen developer capabilities.
-
March 2025: Automation Anywhere announced a partnership with AWS to integrate its RPA platform with Amazon Bedrock for generative AI-based automation.
-
February 2025: Microsoft expanded Power Automate with GPT-4-based intelligent automation, allowing dynamic response handling in customer support scenarios.
-
January 2025: Blue Prism (now part of SS&C) released new analytics tools to monitor bot ROI, helping enterprises track performance metrics in real time.
-
December 2024: NICE Ltd. introduced AI-enhanced attended automation bots aimed at frontline workers in retail and telecom industries.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the robotic process automation market
By Type
-
- Consulting
- Implementing
- Training
By Deployment
By Enterprise Size
- Large Enterprises
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
By Operations
- Rule Based
- Knowledge Based
By End Use
- BFSI
- Pharma & Healthcare
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Information Technology (IT) & Telecom
- Communication and Media & Education
- Manufacturing
- Logistics, and Energy & Utilities
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

