Schizophrenia Drugs Market Size and Trends
The Schizophrenia drugs market size was exhibited at USD 8.75 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 15.38 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
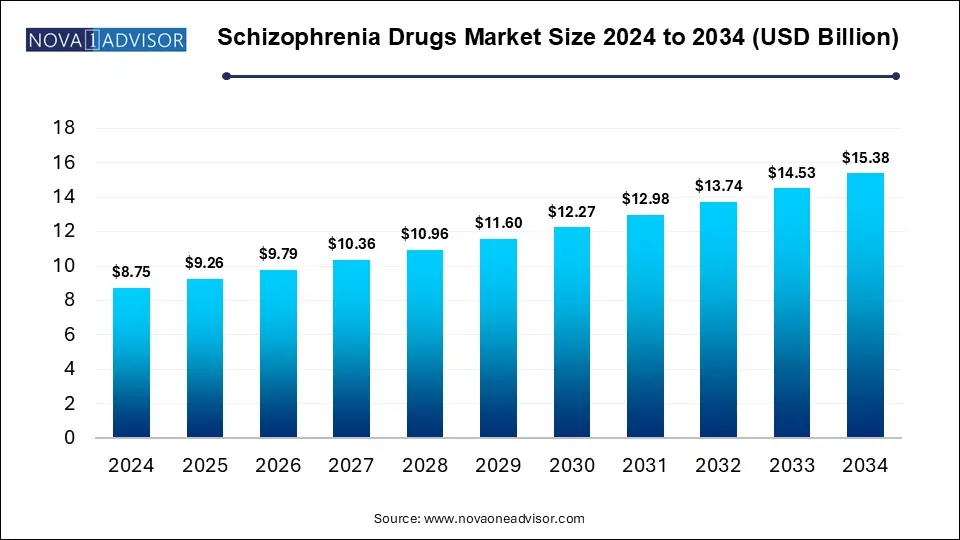
Key Takeaways:
The second-generation antipsychotics held the largest revenue share of 74% in the schizophrenia drugs industry in 2024.
The injectable antipsychotic segment held the largest revenue share of 68% in 2024.
The hospital pharmacies segment held the largest market revenue share of 42% in 2024.
North America schizophrenia drugs market held the largest revenue share of 39% in 2024.
Market Overview
Schizophrenia, a severe chronic mental disorder, affects how individuals think, feel, and behave, often detaching them from reality. It is characterized by hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, and cognitive impairments. Affecting approximately 20 million people globally according to WHO, schizophrenia remains one of the most complex and debilitating psychiatric conditions. Despite its relatively low prevalence, the disease imposes a significant economic and social burden due to its early onset, long-term nature, and high risk of comorbidity, hospitalization, and unemployment.
The global schizophrenia drugs market has grown consistently in response to the evolving pharmacological landscape and deeper understanding of the disorder's neurobiological underpinnings. Advances in antipsychotic drug development, coupled with greater awareness, improved diagnostic infrastructure, and broader health insurance coverage in many countries, have led to increased diagnosis and treatment rates. From first-generation antipsychotics to second- and third-generation options, the market has transitioned toward drugs that offer enhanced efficacy, fewer side effects, and more convenient delivery systems.
Moreover, the emergence of long-acting injectable antipsychotics and digital therapeutics to track adherence and symptom progression reflects the sector’s drive toward holistic care. The need to address treatment-resistant schizophrenia, reduce relapse, and enhance patient compliance is steering pharmaceutical companies to invest heavily in research and pipeline innovation. Despite existing challenges such as adverse effects, stigma, and treatment discontinuation, the schizophrenia drugs market continues to expand, propelled by unmet needs and increasing global mental health investments.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of Long-Acting Injectables (LAIs): LAI formulations like Aristada and Invega Sustenna are gaining popularity due to improved adherence and reduced hospitalization rates.
-
Transition to Atypical Antipsychotics: Second- and third-generation antipsychotics are replacing older, first-generation medications due to better side-effect profiles.
-
Digital Health Integration: Apps that support medication reminders and symptom tracking are being integrated with antipsychotic therapy for better compliance.
-
Increased R&D on Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Companies are focusing on addressing patients unresponsive to conventional drugs.
-
Growing Use of Polypharmacy: Some treatment protocols now include combining two antipsychotics or adding mood stabilizers, especially for treatment-resistant cases.
-
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Rising mental health awareness in countries like India, Brazil, and South Africa is boosting demand for antipsychotics.
-
Patent Expirations & Generics Launch: Patent cliffs for major drugs like Abilify have opened the door to cost-effective generics, reshaping market dynamics.
-
Focus on Personalized Psychiatry: Genetic testing and pharmacogenomics are increasingly being used to tailor treatment choices based on patient profiles.
Report Scope of Schizophrenia Drugs Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 9.26 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 15.38 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 5.8% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Drug Class, Route of Administration, Distribution Channel, and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company/ Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd.; Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd.; Eli Lilly and Company; Alkermes; VANDA PHARMACEUTICALS; AstraZeneca plc; AbbVie Inc.; Pfizer Inc.; H. Lundbeck A/S |
Market Driver: Advancements in Second- and Third-Generation Antipsychotics
One of the most potent drivers of the schizophrenia drugs market is the ongoing development and adoption of second- and third-generation antipsychotics. These drugs, including Risperdal, Invega, Latuda, and Abilify, offer greater efficacy with fewer extrapyramidal side effects than their first-generation predecessors. Their mechanism of action targets both dopamine and serotonin receptors, making them effective not only for psychotic symptoms but also for addressing negative symptoms such as emotional flatness, apathy, and social withdrawal areas where traditional antipsychotics often fall short.
Additionally, the availability of long-acting injectables like Aristada (aripiprazole lauroxil) helps ensure medication adherence, reducing relapse rates and improving patient outcomes. Third-generation drugs like Abilify (aripiprazole), a partial dopamine agonist, have introduced a more nuanced mechanism that stabilizes dopamine activity rather than simply blocking it, representing a paradigm shift in schizophrenia treatment. With several new pipeline candidates in phase II/III trials, continued innovation in this space is expected to expand treatment options and drive market growth.
Market Restraint: Side Effects and Poor Medication Adherence
Despite advancements, side effects and poor adherence remain major restraints in the schizophrenia drugs market. Many antipsychotics especially first-generation and some second-generation variants are associated with significant adverse effects such as weight gain, diabetes, sedation, sexual dysfunction, and extrapyramidal symptoms like tremors and rigidity. These side effects often lead patients to discontinue treatment or become non-compliant, raising the risk of relapse and hospitalization.
Moreover, schizophrenia itself often impairs insight, meaning patients do not believe they are ill or need medication. This lack of awareness further contributes to poor adherence. According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), about 50% of patients with schizophrenia do not adhere to prescribed treatment regimens, posing a significant challenge to long-term disease management. Addressing these issues requires not only better drug formulations but also psychosocial interventions, patient education, and technological aids all of which are still underutilized in many parts of the world.
Market Opportunity: Expansion in Digital Adherence Solutions
The schizophrenia drugs market stands to benefit significantly from integration with digital health technologies, particularly those focused on medication adherence. Adherence-tracking technologies such as smart pill bottles, ingestible sensors (like Abilify MyCite), and mobile apps that provide reminders and feedback can substantially improve compliance. These tools can also relay real-time data to caregivers and physicians, enabling proactive interventions before a full-blown relapse occurs.
As payers increasingly link reimbursement to health outcomes, digital adherence tools offer a way to ensure cost-effective, value-based care. The combination of digital and pharmacologic treatment represents a powerful approach, especially in outpatient and community care settings. With growing smartphone penetration and regulatory green lights for digital health tools, pharmaceutical firms that partner with tech companies will likely gain a competitive edge in this evolving ecosystem.
Segmental Analysis
Drug Class Outlook
Second-generation antipsychotics dominated the global schizophrenia drugs market, commanding a majority share in 2024. These medications, also known as atypical antipsychotics, include widely used agents such as Risperdal (risperidone), Invega (paliperidone), Latuda (lurasidone), and Seroquel (quetiapine). Their appeal lies in a dual mechanism of action affecting both dopamine and serotonin receptors, which translates to better control over positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms. Moreover, their reduced risk of movement disorders compared to first-generation agents ensures better tolerability and long-term adherence. Pharmaceutical players have also invested significantly in second-generation molecules with once-daily oral and monthly injectable options, expanding their reach across treatment settings.
Third-generation antipsychotics are the fastest-growing drug class segment, led by the success of Abilify (aripiprazole). These drugs work as dopamine partial agonists, which allows them to modulate neurotransmission more finely—enhancing deficient activity while suppressing excess stimulation. This pharmacological profile minimizes side effects such as sedation or metabolic disturbances. Abilify’s long-acting formulations and the novel Abilify MyCite—embedded with a sensor to monitor ingestion—underscore the innovation potential in this segment. As the industry shifts toward precision psychiatry, third-generation drugs are positioned to offer customized solutions for patients with unique symptom presentations or who are intolerant to conventional therapies.
Route of Administration Outlook
Oral antipsychotics accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024, owing to their widespread use, ease of administration, and availability in generic forms. Oral agents are preferred during early treatment and for patients who are capable of consistent self-management. Most second-generation drugs, such as olanzapine and quetiapine, are primarily available in oral formulations. Cost-effectiveness, convenience, and the flexibility to adjust doses quickly are among the key factors supporting the dominance of this segment. Moreover, fixed-dose combination pills and orally disintegrating tablets further enhance patient adherence.
Injectable antipsychotics are anticipated to grow at the fastest rate, driven by the increasing preference for long-acting injectables (LAIs). These formulations, administered biweekly or monthly, include options such as Invega Sustenna, Aristada, and Abilify Maintena. LAIs address non-adherence issues effectively and reduce the frequency of relapse and rehospitalization. Their utility in patients with poor insight or those with histories of frequent treatment discontinuation makes them valuable tools in outpatient psychiatric management. With increasing acceptance from caregivers and mental health practitioners, LAIs are expected to see continued adoption across both developed and developing markets.
Distribution Channel Outlook
Hospital pharmacies currently dominate the distribution channel landscape due to the acute nature of schizophrenia management and the need for initial stabilization of patients during psychotic episodes. Hospitals frequently administer injectable antipsychotics and also monitor for adverse reactions, necessitating well-equipped pharmacy support. In addition, the institutional settings are often where treatment-resistant cases or comorbid conditions are addressed, making hospital pharmacies critical points of care.
Online pharmacies are expected to be the fastest-growing channel, supported by the global shift toward digital healthcare. E-commerce platforms provide an efficient, discreet, and convenient way for patients and caregivers to access maintenance medications. They also offer automatic refills and home delivery, which are particularly useful in managing chronic psychiatric conditions like schizophrenia. With the increasing digitization of healthcare services and e-prescription adoption, online distribution will play a growing role in ensuring continuous drug supply, especially for oral antipsychotics.
Regional Analysis
North America led the global schizophrenia drugs market in 2024, with the United States being the largest contributor. The region's dominance is attributed to high awareness levels, strong healthcare infrastructure, and early access to newly approved therapies. A robust reimbursement framework and growing focus on mental health services have also propelled market growth. Companies such as AbbVie, Otsuka, and Teva have well-established distribution and R&D operations in the region, facilitating rapid adoption of innovative therapies. Moreover, North America is a pioneer in integrating digital adherence solutions with pharmacological therapy, further reinforcing its leadership.
Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region over the forecast period. Rising awareness about mental health, increasing healthcare access, and destigmatization of psychiatric disorders are fueling growth in countries such as India, China, and Japan. Government initiatives to bolster psychiatric care, combined with increasing investment from global pharmaceutical players, are unlocking new opportunities in this region. The large patient pool, particularly in underserved rural areas, presents a vast untapped market for both branded and generic antipsychotics. Additionally, regional players are investing in local manufacturing and affordable formulations to cater to diverse socioeconomic strata.
Some of The Prominent Players in The Schizophrenia drugs market Include:
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company/ Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Alkermes
- VANDA PHARMACEUTICALS
- AstraZeneca plc
- AbbVie Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- H. Lundbeck A/S
Recent Developments
-
April 2025: Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Lundbeck announced positive Phase III trial results for a new formulation of brexpiprazole targeting agitation in schizophrenia patients.
-
March 2025: Teva Pharmaceuticals launched a generic version of Latuda (lurasidone) in the U.S., increasing accessibility to second-generation antipsychotic therapy.
-
January 2025: Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen unit announced FDA approval for Invega Hafyera, a six-month injectable antipsychotic for maintenance treatment of schizophrenia.
-
November 2024: AbbVie expanded its neuroscience pipeline through the acquisition of Syndesi Therapeutics, targeting novel mechanisms for schizophrenia cognitive symptoms.
-
October 2024: Sunovion Pharmaceuticals launched a digital adherence platform paired with its long-acting agent Latuda in select clinical settings.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Schizophrenia drugs market
By Drug Class
- Second-Generation Antipsychotics
-
- Risperdal (Risperidone)
- Invega (Paliperidone)
- Zyprexa (Olanzapine)
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)
- Latuda (Lurasidone)
- Aristada (Aripiprazole Lauroxil)
- Fanapt (Iloperidone)
- Saphris (Asenapine)
- Vraylar (Cariprazine)
- Third-Generation Antipsychotics
-
- Abilify (Aripiprazole)
- Others
- First-Generation Antipsychotics
By Route of Administration
- Oral Antipsychotics
- Injectable Antipsychotics
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

