Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market Size and Trends 2026 to 2035
The global subcutaneous drug delivery devices market size was estimated at USD 27.55 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach over USD 54.02 billion by 2035, poised to grow at a CAGR of 6.97% from 2026 to 2035.
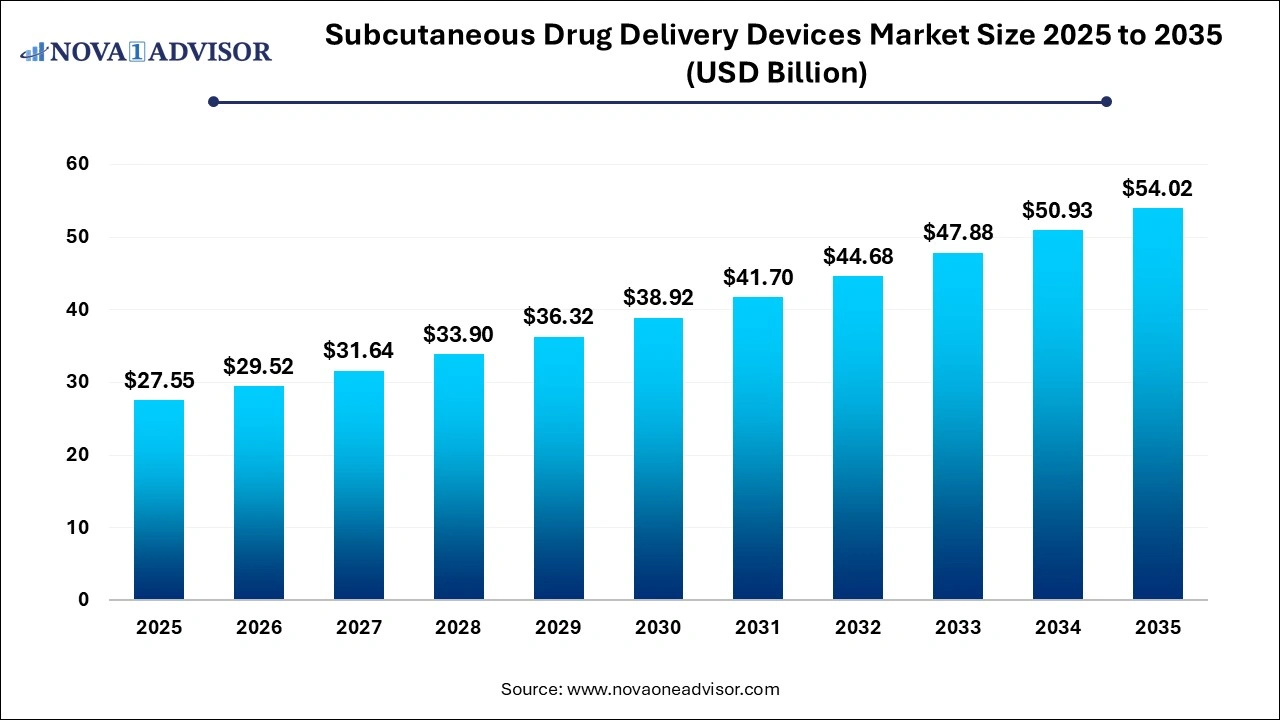
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the global subcutaneous drug delivery devices market, garnering a market share of over 38% in 2025.
- Based on the product type, the pen injectors segment dominated the market, accounting for over 37% of the subcutaneous drug delivery devices market share in 2025.
- Based on the distribution channel, the retail pharmacies segment accounted for around 49% of the market share and dominated the global subcutaneous drug delivery devices market in 2025.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market Overview
The Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market is undergoing transformative growth, driven by the increasing global burden of chronic diseases, the shift toward patient-centric healthcare, and a rising preference for minimally invasive drug administration methods. Subcutaneous drug delivery involves injecting medication into the tissue layer between the skin and the muscle, offering advantages such as ease of administration, reduced healthcare costs, and improved patient compliance.
Unlike intravenous methods that require clinical supervision, subcutaneous systems empower patients to self-administer drugs in home settings, reducing the need for hospital visits. This is especially valuable in managing long-term conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and various forms of cancer, where consistent dosing is critical.
The emergence of biologics and biosimilars has further catalyzed the adoption of these delivery platforms. Biologics, which often require chronic administration, benefit from the pharmacokinetics and patient-friendly nature of subcutaneous routes. Devices such as pen injectors, prefilled syringes, and wearable injectors are now being designed with ergonomic features, Bluetooth connectivity, and dose-tracking functions, revolutionizing patient engagement and adherence.
Additionally, the pandemic highlighted the need for decentralized healthcare solutions, where at-home drug delivery became a necessity. Subcutaneous devices played a vital role during this period and are expected to continue shaping future models of remote care and self-management.
Major Trends in the Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market
-
Rise of Smart Injectors with Connectivity Features: Devices now include sensors, reminders, and dose-tracking technologies that sync with mobile apps.
-
Increased Use of Wearable Injectors for Large-Volume Biologics: These devices offer slow, controlled drug delivery over extended periods, improving drug stability and patient comfort.
-
Shift Toward Needle-Free Injection Systems: Innovations in jet injectors and microneedles are improving user experience and reducing needle phobia.
-
Surge in Personalized Drug Delivery Systems: Devices are being tailored to individual dosing schedules, pharmacodynamics, and preferences.
-
Growing Adoption in Pediatric and Geriatric Care: Devices are being designed with adaptive features to cater to motor-challenged and sensitive patients.
-
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials in Injector Design: Manufacturers are investing in biodegradable components and reusable injector platforms.
-
Integration with Telehealth and Digital Therapeutics: Injectors are being paired with digital platforms for remote patient monitoring and compliance analytics.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 29.52 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 54.02 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 6.97% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
By Product, By Distribution Channel |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Insulet Corporation, Enable Injections, Amgen, BD, Consort Medical Plc, Ypsomed AG, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Merck, AstraZeneca |
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
One of the most critical drivers propelling the subcutaneous drug delivery devices market is the growing global burden of chronic illnesses, particularly diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. According to the WHO, non-communicable diseases account for over 70% of all deaths globally, with diabetes and arthritis witnessing alarming growth due to sedentary lifestyles, aging populations, and genetic predisposition.
Patients with these chronic conditions often require lifelong, routine treatment, making self-administered delivery solutions invaluable. Subcutaneous injectors especially pen injectors and prefilled syringes have emerged as the gold standard in diabetes care. For instance, insulin pens have become increasingly popular due to their portability, ease of use, and reduced dosing errors. Similarly, biologics used in conditions like Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis are commonly administered via subcutaneous auto-injectors, enhancing patient autonomy and reducing healthcare system burden.
Restraint: Device Malfunctions and User Errors
While subcutaneous devices offer numerous benefits, the potential for device malfunctions and patient-related administration errors remains a key market restraint. Despite advancements in safety engineering, auto-injectors and pen systems can sometimes fail due to mechanical issues, improper storage, or user mishandling.
In real-world scenarios, patients—especially the elderly or those with limited dexterity may face challenges in handling these devices properly. Inconsistent dosing, air bubble injections, and device misfiring can compromise drug efficacy or cause local tissue damage. These risks not only threaten patient health but can also erode confidence in self-managed care systems.
The complexity of biologic drug formulation also adds to the risk, requiring manufacturers to ensure precise compatibility between drug and device. Regulatory scrutiny around device reliability is intensifying, and companies need to invest significantly in usability studies, training programs, and post-market surveillance to overcome this challenge.
Opportunity: Expansion in Home-Based and Remote Healthcare Models
An emerging opportunity lies in the expansion of remote care and home-based healthcare systems, a trend accelerated by the pandemic and expected to define the future of chronic disease management. As healthcare shifts from hospital-centric models to patient-centric approaches, subcutaneous drug delivery systems are playing a pivotal role in enabling decentralized treatment.
This shift is especially beneficial in rural and underserved regions where access to specialty care is limited. Devices like wearable injectors allow controlled drug administration over time without professional supervision. For instance, Amgen’s Onpro wearable injector enables cancer patients to receive chemotherapy doses at home, freeing them from frequent hospital visits and exposure to infections.
Moreover, the growing integration of these devices with remote monitoring platforms and AI-driven compliance apps enhances patient adherence and enables physicians to adjust treatment regimens in real-time. As digital therapeutics and telemedicine services expand globally, the demand for smart subcutaneous delivery systems is poised to surge.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market Segments Insights
By Product Type Insights
Auto-injectors are the most dominant product type in the subcutaneous drug delivery devices market. Their success is attributed to their intuitive design, single-use format, and widespread application across emergency care (e.g., epinephrine for anaphylaxis) and chronic therapy (e.g., biologics for autoimmune diseases). They are especially prevalent in self-administration of medications like Humira and Enbrel, which treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Many of these devices include safety shields, auditory indicators, and ergonomic grips that cater to a wide range of users.
On the other hand, wearable injectors are the fastest-growing segment. These devices, also known as on-body delivery systems, allow the administration of large-volume biologics over extended durations—something not feasible with conventional pens or auto-injectors. For instance, insulin patch pumps and wearable oncology injectors deliver precise doses while minimizing discomfort. These devices are gaining acceptance in oncology, neurology, and metabolic disorders due to their convenience, integration with mobile apps, and improved adherence rates.
By Distribution Channel Insights
Retail pharmacies dominate the distribution landscape, given their accessibility and the availability of trained pharmacists who can guide patients on the usage of injectors. In many healthcare systems, retail pharmacies act as the first point of contact for injectable medications and chronic care supplies. Patients receiving injectable biologics or insulin typically rely on pharmacists for device training, refill scheduling, and support, especially in developing nations.
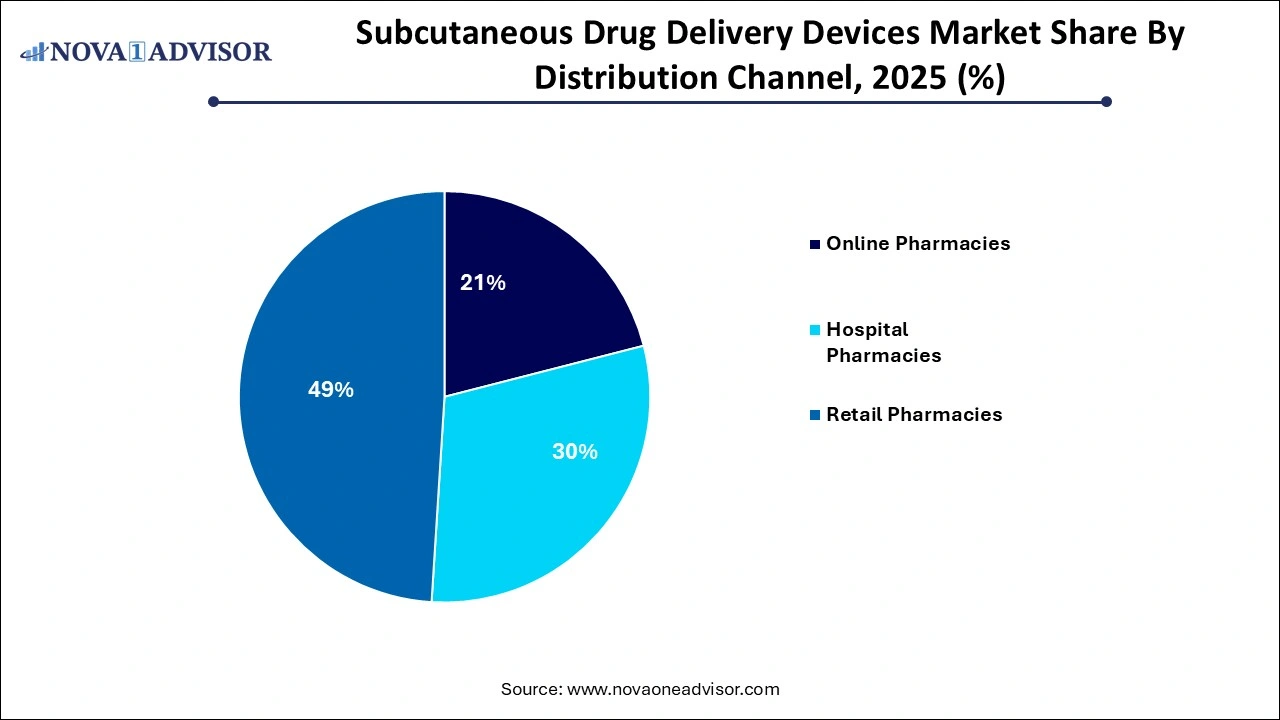 However, online pharmacies are emerging as the fastest-growing channel. As digital healthcare ecosystems mature, patients increasingly prefer ordering drug delivery devices online due to cost savings, home delivery convenience, and subscription-based refill models. E-commerce giants and specialized health-tech platforms are now offering auto-replenishment of injectors, remote consultations, and bundled patient education, fostering a robust D2C (direct-to-consumer) ecosystem. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated this transition, as consumers sought contactless options to manage their chronic conditions.
However, online pharmacies are emerging as the fastest-growing channel. As digital healthcare ecosystems mature, patients increasingly prefer ordering drug delivery devices online due to cost savings, home delivery convenience, and subscription-based refill models. E-commerce giants and specialized health-tech platforms are now offering auto-replenishment of injectors, remote consultations, and bundled patient education, fostering a robust D2C (direct-to-consumer) ecosystem. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated this transition, as consumers sought contactless options to manage their chronic conditions.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices Market Regional Analysis
North America, particularly the United States, leads the global subcutaneous drug delivery devices market. The region's dominance is supported by a confluence of factors: a high prevalence of chronic diseases, strong insurance coverage, favorable reimbursement policies, and the presence of major biopharmaceutical and medtech players. According to the CDC, over 37 million Americans have diabetes, and a significant portion rely on insulin administered via pen injectors and wearable devices.
Technological innovation is another cornerstone of North American market leadership. Companies like Becton Dickinson, Amgen, and Insulet Corporation are headquartered here and have pioneered next-generation injectors that enhance patient experience. Moreover, the regulatory landscape, while stringent, supports fast-track approvals for innovative drug-device combinations under the FDA's combination product framework.
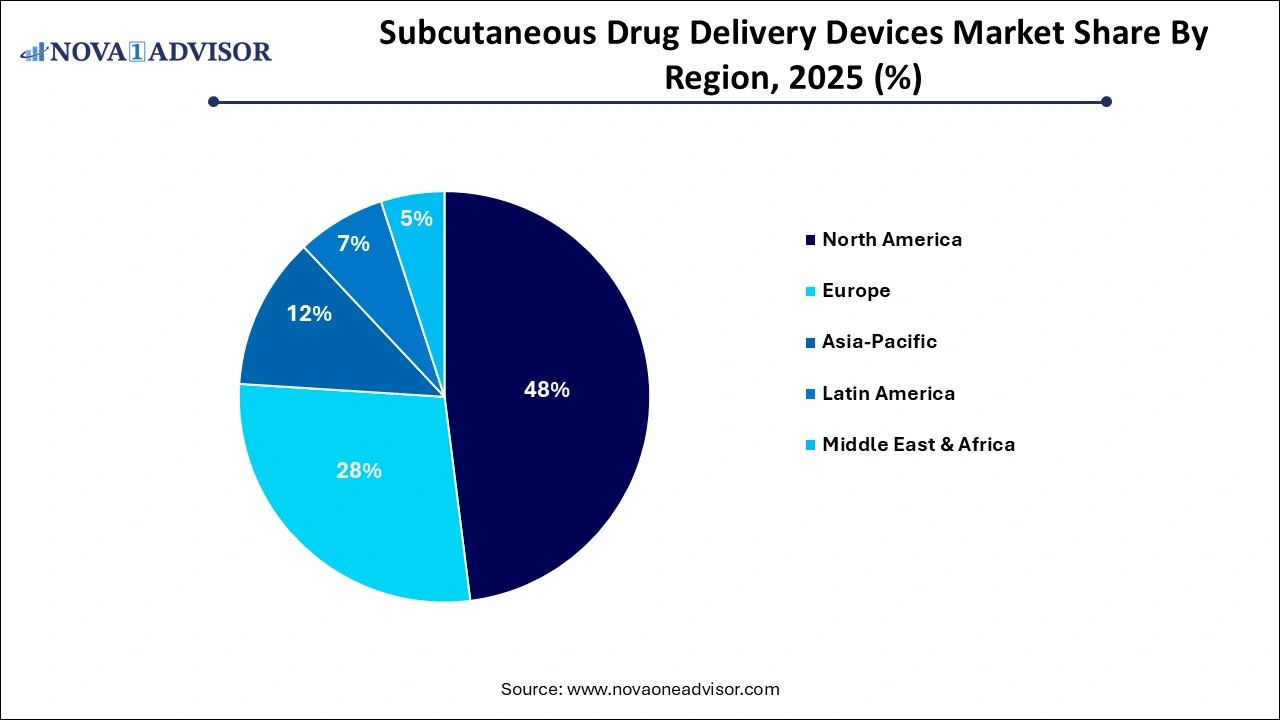
Asia-Pacific: Fastest Growing Region
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by expanding healthcare infrastructure, increasing diagnosis rates, and rising healthcare awareness. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing a surge in chronic diseases, coupled with improving patient access to biologics and delivery devices. Government initiatives such as India’s “Ayushman Bharat” and China’s “Healthy China 2030” are increasing the availability of life-saving treatments and devices to previously underserved populations.
Additionally, the region is becoming a hotbed for local manufacturing and innovation in drug delivery technologies. Startups and pharmaceutical firms in India and China are developing affordable injector systems tailored to domestic needs. Multinational companies are also expanding their footprints here through partnerships and local assembly units, making Asia-Pacific a critical engine for market expansion.
Key Market Developments
- In April 2021, Medtronic introduced a wearable injector that can be worn by the patients for 7 days for the treatment of diabetes.
- In April 2023, Sanofi acquired the US FDA approval for its new prefilled pen named Dupixent that serves the asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, and atopic dermatitis patients at homecare.
- In June 2019, Sanofi acquired the EMA approval for its ToujeoSoloStar Pens in Europe.
- In December 2019, LEO Pharma and Portal Instruments collaborated to develop a needle-free subcutaneous drug delivery solution
- In June 2018, Insulet Corporation acquired approval from US FDA for its insulin management system called Omnipod DASH.
The various developmental strategies like product launches, acquisitions, collaborations, and mergers fosters market growth and offers lucrative growth opportunities to the market players.
Some of the prominent players in the Subcutaneous drug delivery devices market include:
- Insulet Corporation
- Enable Injections
- Amgen
- BD
- Consort Medical Plc
- Ypsomed AG
- Eli Lilly
- Novo Nordisk
- Sanofi
- Merck
- AstraZeneca
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2026 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global subcutaneous drug delivery devices market.
By Product Type
- Auto-Injectors
- Pen Injectors
- Prefilled Syringes
- Wearable Injectors
- Needle-Free Injectors
By Distribution Channel
- Retail Pharmacies
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


 However, online pharmacies are emerging as the fastest-growing channel. As digital healthcare ecosystems mature, patients increasingly prefer ordering drug delivery devices online due to cost savings, home delivery convenience, and subscription-based refill models.
However, online pharmacies are emerging as the fastest-growing channel. As digital healthcare ecosystems mature, patients increasingly prefer ordering drug delivery devices online due to cost savings, home delivery convenience, and subscription-based refill models. 