Teleradiology Software Market Size and Research
The teleradiology software market size was exhibited at USD 2.36 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 6.12 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The expansion of the teleradiology software market is driven by the surging demand for imaging services, advancements in remote diagnostics solutions, and rising prevalence of chronic disorders, especially in the geriatric population. Increased investments for advancing healthcare infrastructure is driving the adoption of teleradiology software across various healthcare settings.
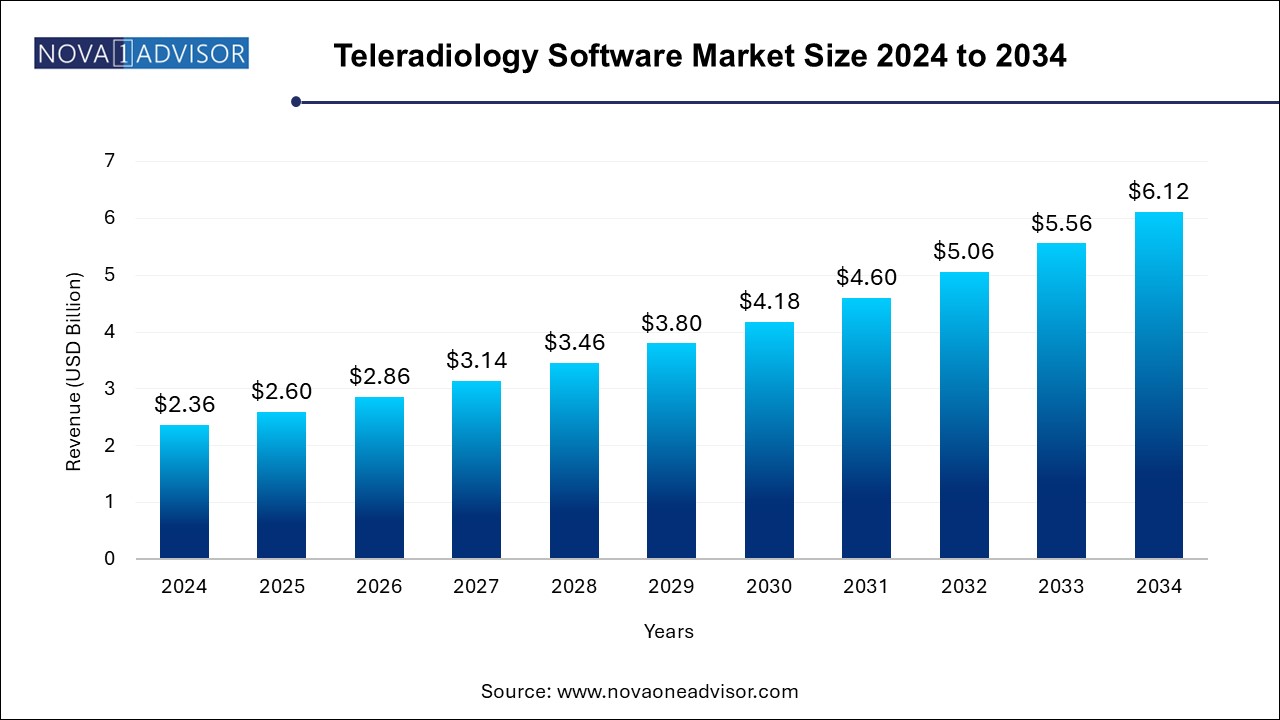
Teleradiology Software Market Key Takeaways:
- Picture Archive and Communication System (PACS) accounted for the largest market revenue share of approximately 48.0% in 2024.
- Vendor Neutral Archive is expected to register the fastest CAGR of 11.9% during the forecast period.
- Web-based held the largest revenue share of 40.0% in 2024.
- Cloud-based is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 9.7% over the forecast period.
- North America teleradiology software market led the global teleradiology software market with a revenue share of 40.4% in 2024.
Market Overview
The Teleradiology Software Market has experienced a paradigm shift in recent years, driven by the growing need for accessible, efficient, and expert diagnostic imaging services across geographies. Teleradiology refers to the electronic transmission of radiographic images from one location to another for the purposes of sharing studies with other radiologists and physicians. At the heart of this technological advancement is teleradiology software, which powers the acquisition, transmission, storage, and interpretation of medical images through sophisticated platforms.
The demand for teleradiology software has surged significantly due to critical challenges faced by the global healthcare system—most notably, the shortage of skilled radiologists, especially in rural or underserved regions. Teleradiology offers a scalable solution by enabling qualified radiologists to deliver real-time consultations and interpretations from remote locations. This technology has proved particularly invaluable during emergencies, after-hours reporting, and in providing specialist expertise where local availability is limited.
Furthermore, with the digitization of healthcare and the increased reliance on radiographic imaging for diagnosis and treatment planning, teleradiology has become a central pillar of modern diagnostic services. From CT and MRI to PET and ultrasound, these software platforms are capable of handling a diverse range of imaging modalities, delivering high-speed image transfers, secure archiving, and seamless integration with hospital systems.
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst for the teleradiology software market. Hospitals and imaging centers worldwide turned to remote solutions to mitigate the risk of in-person consultations, ensuring continuity of care while adhering to safety protocols. As a result, teleradiology moved from being a supplementary service to a strategic healthcare necessity. Even in the post-pandemic era, the momentum for remote diagnostics continues, reinforcing the role of teleradiology software in future-ready healthcare infrastructure.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): Teleradiology software is increasingly being embedded with AI algorithms to assist in image analysis, automate workflow prioritization, and improve diagnostic accuracy.
-
Cloud-first Deployments: The transition from traditional on-premise to cloud-based platforms is accelerating, offering flexibility, scalability, and reduced IT overhead.
-
Increased Adoption of Mobile Access: Teleradiologists are leveraging mobile platforms to review and interpret images on tablets and smartphones, enhancing convenience and responsiveness.
-
Blockchain for Data Security: Blockchain-based solutions are being explored to enhance data security and ensure compliance with stringent healthcare data protection regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
-
Growing Role in Emergency and Nighttime Radiology: Teleradiology is becoming essential for 24/7 emergency reporting, especially in trauma centers and rural hospitals.
-
Expanding Global Outsourcing: Countries in Asia Pacific and Latin America are becoming global teleradiology hubs, offering outsourced services to the U.S. and Europe due to cost advantages.
-
Vendor Neutral Archives (VNA): Hospitals and diagnostic centers are moving towards VNA-based teleradiology systems for better interoperability and centralized image storage.
How Are Industrial Shifts Reshaping the Teleradiology Software Market?
Rising shift towards cloud-native solutions and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models enhancing scalability and reducing costs of IT infrastructure for healthcare providers are improving accessibility for remotely working radiologists. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine algorithms is enhancing image analysis, automated reporting and workflow prioritization processes leading to quick turnaround times and reduced radiologist burnout.
Deployment of robust cybersecurity measures such as advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, frequent scrutiny audits and reliable data transmission protocols are enabling protection of sensitive patient information and enhancing regulatory compliance. Continuous improvements in user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) by software vendors offering user-friendly interfaces, adaptive dashboards, efficient navigation and tools minimizing mental workload for radiologists is accelerating processes.
Report Scope of Teleradiology Software Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 2.60 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 6.12 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 |
CAGR of 10.0% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Software Type, Mode of Delivery, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Carestream Health; Telerad Tech; GE Healthcare; Comarch SA; Perfect Imaging Solution's, LLC; Radical Imaging LLC; OpenRad; RamSoft, Inc.; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Pediatrix Medical Group |
Market Driver: Rising Demand for Radiology Services Amid Radiologist Shortage
A key driver of the teleradiology software market is the increasing demand for radiology services in the face of a persistent shortage of radiologists worldwide. The demand for diagnostic imaging, including CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays, has escalated due to an aging global population, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and expanded health screening programs. However, the number of trained radiologists has not kept pace, particularly in rural and semi-urban healthcare settings.
Teleradiology software bridges this gap by enabling remote image interpretation from centralized hubs. For example, a hospital in Nebraska can outsource its nighttime CT interpretations to a radiologist based in India, ensuring 24-hour service availability without compromising quality. By facilitating efficient image transmission and diagnosis across borders, the software reduces delays in treatment and optimizes radiologist workload, thereby addressing a critical healthcare bottleneck.
Market Restraint: Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Risks
Despite the immense benefits, the concern over data security and patient privacy remains a significant restraint for the teleradiology software market. The transmission of sensitive patient data and high-resolution medical images across networks creates vulnerabilities to cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States, GDPR in Europe, and similar standards globally requires robust encryption, audit trails, and secure authentication mechanisms. Implementing these security layers can be both costly and technically complex, especially for small or mid-sized imaging centers. A single data breach could result not only in regulatory penalties but also in the loss of trust from patients and healthcare partners—making data security a critical concern for market players.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Telehealth Ecosystems and Remote Care Models
The widespread adoption of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has laid a strong foundation for integrated remote diagnostic ecosystems, creating a major opportunity for teleradiology software vendors. As healthcare providers continue to scale their telemedicine services, teleradiology is emerging as a core component for virtual care delivery, particularly in specialties like neurology, oncology, and orthopedics, which rely heavily on imaging.
Software platforms that integrate seamlessly with telehealth portals, patient data repositories, and EHRs (Electronic Health Records) are gaining traction. For instance, a patient undergoing a teleconsultation for stroke symptoms can have their CT scan instantly shared with a remote neurologist, who can interpret it in real time and initiate treatment. The expansion of this real-time diagnostic ecosystem presents a tremendous opportunity for teleradiology vendors to align with hospitals, insurers, and telehealth providers to deliver holistic and time-sensitive patient care.
Teleradiology Software Market By Software Type Insights
Picture Archive and Communication System (PACS) accounted for the largest market revenue share of approximately 48.0% in 2024. PACS serves as the digital backbone of imaging departments and is a vital component of teleradiology workflows. It facilitates secure transmission and remote viewing of images like CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays, making it an indispensable tool for both on-site and remote radiologists.
The adoption of PACS in hospitals and imaging centers has been accelerated by its ability to improve workflow efficiency, eliminate physical film handling, and reduce diagnostic turnaround time. Moreover, modern PACS systems offer AI-powered functionalities and mobile access, enhancing their appeal across healthcare settings. Integration with other hospital systems like Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and VNA platforms further strengthens their utility and market dominance.
Vendor Neutral Archive is expected to register the fastest CAGR of 11.9% during the forecast period. Driven by the increasing need for interoperability and long-term data storage. VNAs enable centralized access to imaging data across multiple PACS and hospital systems, eliminating vendor lock-in and streamlining enterprise-wide data management.
With the rising number of healthcare mergers, partnerships, and remote facilities, VNAs are becoming crucial in consolidating patient imaging records into a unified archive. For example, a healthcare network operating across five cities can use a VNA to ensure that a radiologist in one location can instantly access a scan performed at another site. This flexibility and scalability are driving their rapid adoption, particularly in larger healthcare organizations looking to future-proof their imaging infrastructure.
Teleradiology Software Market By Mode of Delivery Insights
Web-based deployment dominated the teleradiology software market, especially among small and medium healthcare providers. These solutions offer a practical middle ground between legacy on-premise systems and cloud-native platforms, delivering remote accessibility without requiring significant IT investment. Web-based software allows radiologists to log into secure portals and access images from any location with internet connectivity, thus enhancing flexibility and coverage.
Their ease of use, relatively lower implementation cost, and compatibility with existing hospital IT systems have made web-based teleradiology platforms especially popular in outpatient imaging centers and diagnostic labs. In regions where healthcare digitization is still evolving, web-based systems provide a stepping stone towards full cloud migration.
Cloud-based solutions are growing at the fastest pace, propelled by the global digital transformation of healthcare and the demand for scalable, cost-effective, and secure image management systems. Cloud teleradiology software eliminates the need for extensive onsite hardware, offers seamless multi-site integration, and ensures data backup and disaster recovery capabilities.
For example, multinational teleradiology service providers prefer cloud-native solutions to serve clients across different time zones and jurisdictions. These systems allow images to be uploaded from one country and interpreted by radiologists located halfway around the globe within minutes. As healthcare providers embrace hybrid and remote care models, cloud-based software is poised to become the new standard in teleradiology delivery.
Teleradiology Software Market By Regional Insights
North America teleradiology software market led the global teleradiology software market with a revenue share of 40.4% in 2024. owing to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, early adoption of digital health technologies, and a significant radiologist workforce shortage in rural areas. The U.S. alone accounts for a major share, with high investment in telemedicine and government support for healthcare IT expansion through programs like the HITECH Act.
Major U.S. hospitals and imaging networks have established extensive teleradiology operations, often relying on outsourcing to international radiologists during nighttime hours. The region is also home to leading software vendors and innovation hubs that continuously develop AI-enhanced and secure teleradiology solutions. Regulatory compliance with HIPAA, combined with robust reimbursement frameworks, further cements North America's leadership in the market.
Asia Pacific is the fastest growing region, driven by the rapid digitization of healthcare, rising patient volumes, and increasing penetration of teleradiology services. Countries such as India, China, and Singapore are investing in healthcare infrastructure and embracing cloud-based solutions to expand diagnostic services into underserved areas.
India, in particular, has emerged as a global teleradiology hub, offering outsourced services to hospitals in the U.S. and Europe. Additionally, growing awareness about early disease diagnosis and government initiatives to digitize healthcare records are boosting local demand. As public and private healthcare providers aim to scale their diagnostic capacity without proportional increases in staff or capital expenditure, teleradiology software offers a powerful solution for addressing these challenges.
What Factors Drive the Expansion of Teleradiology Software Market in China?
China is expected to show significant growth in the teleradiology software market in Asia Pacific. Lack of medical imaging expertise in rural and remote areas due to shortage of radiologists as well as huge population with rising chronic disease burden is driving the need for efficient teleradiology software solutions to reduce the workload on radiologists. Increased penetration of digital technologies in healthcare, emergence of telemedicine platforms and growing demand for medical imaging services are the factors driving the adoption of teleradiology software in China.
Some of the prominent players in the teleradiology software market include:
Teleradiology Software Market Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc., in collaboration with NewVue launched Exa Teleradiology, a cloud-native solution developed for enhancing experience of a radiologist in a teleradiology setting. The solution powered by NewVue features a Radiologist Cockpit, zero-footprint viewer, an AI-curated intelligent worklist and a full suite of quality workflows which includes peer review, critical results, discrepancy management and technologist quality improvement (Tech QI).
- In August 2024, Hexarad, a teleradiology platform founded by a physician, secured about $14 million in a funding round led by MTIP, a Switzerland-based private equity organization.
- In June 2024, Radical Imaging, a pioneering medical imaging viewer solutions provider, received the U.S. FDA approval for its FlexView Diagnotic, a SaaS web DICOM viewer product for diagnostic use.
- In June 2024, Carestream introduced Image Suite MR 10 Software which offers a user-friendly interface designed for optimizing imaging performance in both Digital Radiography (DR) and Computed Radiography (CR) imaging systems with its specialized measurement tools and also features an optional Mini-PACS module.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the teleradiology software market
Software Type
- Radiology Information System
- Picture Archive and Communication System
- Vendor Neutral Archive
Mode Of Delivery
- Web-based
- Cloud-based
- On-premise
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

