Tissue Dissociation Market Size and Research
The Tissue Dissociation Market size was exhibited at USD 326.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 746.76 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.62% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
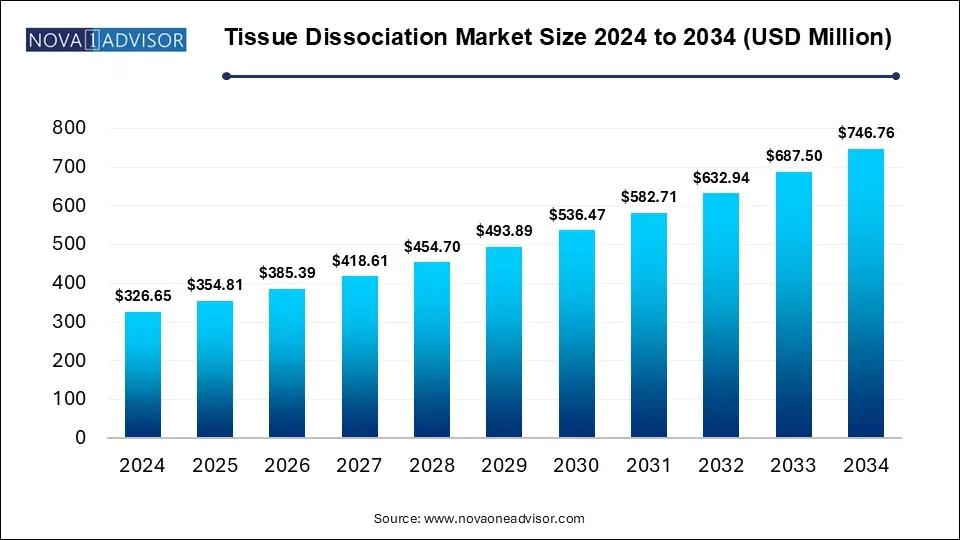
Key Takeaways:
- North America held the leading position in the tissue dissociation market in 2024, securing the highest revenue contribution.
- The Asia Pacific region is forecasted to exhibit the most robust CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- In 2024, human tissue accounted for the largest share of the market based on tissue type.
- Animal tissue is anticipated to register the highest growth rate throughout the forecast timeline.
- Enzymatic dissociation kits emerged as the dominant product category in 2024 in terms of market revenue.
- Mechanical dissociation kits are expected to see the fastest-paced growth in the upcoming years.
- Commercially sourced tissue dissociation materials made up the largest portion of market revenue in 2024.
- In-house sources are projected to grow at the highest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- Automated tissue dissociation systems took the lead in the market in 2024.
- Manual dissociation technologies are likely to experience the quickest growth during the forecast period.
- Cancer research was the top application segment in 2024, generating the greatest market share.
- Stem cell research applications are expected to expand rapidly in the years ahead.
- Pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms were the largest end users in 2024, contributing the majority of market revenue.
- Hospitals and diagnostic labs are poised to grow at the fastest rate in the forecast period.
Market Overview
The tissue dissociation market is a critical component of modern life sciences and biomedical research, providing the foundational step for downstream applications like single-cell analysis, stem cell research, and cancer biology. Tissue dissociation refers to the process of breaking down complex tissue samples into single-cell suspensions or smaller fragments for detailed study. This procedure is vital for obtaining viable and functionally intact cells from solid or liquid tissue sources.
As the demand for precision medicine, regenerative therapies, and advanced diagnostics surges, the role of tissue dissociation kits, instruments, and reagents has expanded significantly. Researchers rely on a blend of enzymatic and mechanical methods to ensure tissue integrity while maximizing cell yield. The increasing focus on cancer research, the booming stem cell therapy sector, and the surge in single-cell sequencing studies have propelled the global tissue dissociation market to the forefront of biomedical innovation.
Pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, diagnostic laboratories, and contract research organizations (CROs) are major stakeholders in this domain. With technological innovations such as automated dissociation systems, enzyme blends, and standardized protocols becoming mainstream, the market continues to grow at a steady pace across developed and developing economies.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Growing Adoption of Single-cell Omics: Rapid advancements in genomics and transcriptomics have increased the need for high-quality single-cell suspensions from tissues, driving demand for optimized dissociation protocols.
-
Rise of Automated Dissociation Technologies: Automated tissue dissociators are becoming popular due to their reproducibility, ease of use, and ability to handle large sample volumes with minimal manual input.
-
Shift Toward Enzyme Cocktail Formulations: Customized enzyme mixtures like collagenase-trypsin blends provide more efficient tissue breakdown for specific sample types.
-
Surge in Stem Cell and Regenerative Research: With stem cells playing a crucial role in therapies and organoids, tissue dissociation is essential for isolating stem cells from primary tissues.
-
Integration with High-throughput Workflows: Tissue dissociation platforms are increasingly designed to interface with microfluidics, flow cytometry, and other cell processing tools.
-
Increased Commercial Supply of Pre-formulated Kits: Ready-to-use dissociation kits from commercial vendors are replacing in-house preparations in labs due to their consistency and regulatory compliance.
Report Scope of Tissue Dissociation Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 354.81 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 746.76 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 8.62% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Tissue Type, Product Type, Source, Technology Type, Application, End User, and Regions |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Danaher Corp., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., HiMedia Laboratories,BD, Merck KGaA, Miltenyi Biotec, PAN-Biotech,S2 Genomics, Inc., STEMCELL Technologies, Sartorius AG, Thermo Fisher Scientific and Others. |
Market Driver: Growing Focus on Cancer Research
One of the primary drivers for the tissue dissociation market is the escalating investment in cancer research across the globe. Understanding the tumor microenvironment at the cellular level requires precise isolation of tumor cells, immune cells, and stromal components. Tissue dissociation enables researchers to extract viable cells from solid tumor biopsies, which are then analyzed using flow cytometry, immunophenotyping, or single-cell sequencing.
Institutes such as the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and pharma giants like Roche and Novartis are pouring billions into oncology research. Tissue dissociation tools serve as the starting point for analyzing heterogeneity in tumor samples, testing drug efficacy in patient-derived xenografts (PDX), and developing immunotherapies like CAR-T cells. As the oncology pipeline expands, so does the demand for efficient and standardized tissue processing methods.
Market Restraint: Enzyme Variability and Batch Inconsistency
Despite its advantages, tissue dissociation faces hurdles related to enzyme quality and reproducibility. Many enzymatic dissociation kits rely on biologically derived components such as collagenase or trypsin, which can vary from batch to batch. These inconsistencies may lead to poor cell viability, altered gene expression, or incomplete dissociation, ultimately compromising experimental outcomes.
Additionally, enzymatic digestion must be carefully optimized for each tissue type, as over-digestion can damage cell membranes, while under-digestion can result in clumped or heterogeneous cell populations. This variability not only affects data accuracy but also leads to repeat testing and increased operational costs, posing a challenge particularly for high-throughput or clinical-grade applications.
Market Opportunity: Rising Demand for Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine is a rapidly evolving field, offering potential cures for chronic and degenerative diseases using tissue-engineered products and stem cell-based therapies. One of the foundational steps in these procedures is isolating progenitor or stem cells from various tissue sources, a task reliant on high-quality tissue dissociation protocols.
Applications like 3D bioprinting, organ regeneration, and autologous cell therapies require precise and reproducible dissociation processes to ensure functional cell yield. Moreover, regulatory bodies are placing increased emphasis on standardized protocols for clinical-grade cell manufacturing, creating strong incentives for companies offering GMP-compliant dissociation kits and instruments. This rising need for scalable, clinical-ready tissue processing solutions represents a significant growth opportunity in the coming decade.
Segmental Analysis
By Tissue Type
Human Tissue Held the Dominant Share in 2024
Human tissue remains the most widely used sample type in dissociation applications due to its direct relevance in disease modeling, diagnostics, and personalized medicine. Biopsies from organs such as the liver, lungs, and tumors are routinely processed using both enzymatic and mechanical methods. Research institutions and pharma companies prioritize human tissues for translational research, and regulatory mandates for human-based testing have also boosted this segment.
Meanwhile, animal tissue is projected to exhibit the fastest growth. It is widely used in preclinical studies and basic research where human tissues are unavailable or ethically restricted. Rodent and porcine tissues are frequently employed for drug toxicity studies, developmental biology, and surgical training. The lower cost, ease of access, and compatibility with established lab models make animal tissue a preferred choice in early-stage biomedical research.
By Product Type
Enzymatic Dissociation Kits Led the Market in 2024
Enzymatic dissociation kits are the most widely adopted product category, owing to their specificity, efficiency, and ability to maintain cellular integrity. These kits include enzyme formulations like collagenase, trypsin, and dispase, each tailored for a specific tissue matrix. Enzymatic methods offer advantages over mechanical processes in terms of cell viability and yield, particularly when working with delicate or fibrous tissues.
Mechanical dissociation kits including tissue grinders and homogenizers—are projected to grow at the fastest CAGR. These tools are crucial in contexts where enzymatic treatment alone is insufficient or unsuitable, such as when preparing samples for proteomics. Their growing use in combination protocols and cost-effectiveness are contributing to the segment’s acceleration. The demand for durable, automated homogenizers that can handle high-throughput workflows is also increasing across research labs and CROs.
By Source
Commercial Sources Contributed the Largest Revenue Share in 2024
Commercial sources, including companies like Miltenyi Biotec, Worthington Biochemical, and Thermo Fisher Scientific, dominate the market by providing standardized, validated, and regulatory-compliant dissociation solutions. These products reduce variability, simplify workflows, and enhance reproducibility, making them attractive to academic and industrial users alike.
On the other hand, in-house sources are expected to grow at the fastest pace, particularly in academic settings. Custom protocols tailored to unique tissue types or experimental goals often necessitate in-house preparation. Additionally, budget-constrained labs prefer in-house solutions to minimize expenditure, contributing to the segment’s projected growth during the forecast period.
By Technology Type
Automated Tissue Dissociation Dominated in 2024
Automated tissue dissociation technologies are gaining prominence for their ability to standardize processing and reduce user dependency. Devices like the gentleMACS™ Dissociator enable reproducible dissociation with minimal manual handling, thereby reducing contamination risk and human error. These systems are widely used in clinical labs and high-throughput environments, contributing to their dominant market share.
Manual tissue dissociation systems are anticipated to expand swiftly, especially in emerging markets and low-resource settings where budget and infrastructure constraints limit automation. Manual tools offer flexibility and are indispensable in small-scale research or pilot experiments. Their ease of customization and lower capital investment continue to make them attractive to early-stage research teams.
By Application
Cancer Research Led the Market in 2024
Cancer research is the largest application segment for tissue dissociation, accounting for a significant share of revenue. Solid tumors and metastases require tissue processing to isolate cancer cells and analyze tumor heterogeneity, drug responses, and biomarker expression. Techniques like single-cell RNA sequencing and organoid generation rely heavily on high-quality cell suspensions obtained from dissociated tissues.
Stem cell research is projected to witness the highest growth. Stem cells must be precisely extracted from tissues like bone marrow, adipose, or umbilical cord blood, which necessitates effective dissociation techniques. As stem cell-based therapies advance into clinical trials and commercial therapies, the demand for standardized, GMP-grade dissociation tools for stem cell isolation and expansion will surge accordingly.
By End User
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies Dominated the Market in 2024
Pharmaceutical and biotech companies accounted for the largest end-user segment due to their extensive use of dissociation techniques in drug discovery, cell-based assays, and biologics development. These companies require scalable and validated solutions for processing both animal models and human tissues in compliance with regulatory guidelines.
Hospitals and diagnostic laboratories are expected to grow at the fastest CAGR, driven by the increasing use of personalized medicine and molecular diagnostics. As clinical labs expand their services to include tissue-based genomic profiling and immunophenotyping, they will rely more on dissociation technologies to generate viable cell suspensions from patient samples for downstream analysis.
Regional Analysis
North America Led the Market in 2024
North America, particularly the United States, was the dominant region in 2024 due to its advanced research infrastructure, significant funding for biomedical research, and concentration of top pharmaceutical firms and academic institutions. The presence of key players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Miltenyi Biotec, and BD Biosciences further strengthens the market in this region. Additionally, strong regulatory support for clinical research involving human tissues has enabled widespread adoption of tissue dissociation technologies.
Asia Pacific is Expected to Grow at the Fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034
Asia Pacific is poised to register the fastest growth, fueled by increasing government investments in biotechnology, rising awareness of regenerative therapies, and expanding clinical research activities. Countries such as China, India, and South Korea are rapidly modernizing their life sciences infrastructure, creating demand for high-quality cell and tissue processing solutions. The growth of contract research organizations (CROs) in the region is also accelerating adoption, especially for cost-effective manual and semi-automated systems.
Some of The Prominent Players in The Tissue Dissociation Market Include:
- Danaher Corp.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- HiMedia Laboratories
- BD
- Merck KGaA
- Miltenyi Biotec
- PAN-Biotech
- S2 Genomics, Inc.
- STEMCELL Technologies
- Sartorius AG
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
Recent Developments
-
April 2025 – Miltenyi Biotec introduced an upgraded version of its gentleMACS Octo Dissociator, featuring higher throughput and integrated data logging for GMP workflows.
-
March 2025 – Thermo Fisher Scientific expanded its product line with new enzyme kits optimized for neural and liver tissue dissociation, targeting the neuroscience research community.
-
January 2025 – Worthington Biochemical Corporation announced a partnership with a major U.S. stem cell research institute to supply custom enzyme blends for stem cell harvesting.
-
November 2024 – BD Biosciences launched a new mechanical tissue processing tool compatible with high-volume tissue samples for oncology trials.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Operating room equipment market
By Tissue Type
- Human Tissue
- Solid Tissue
- Liquid Tissue
- Animal Tissue
By Product Type
- Enzymatic Dissociation Kits
-
- Collagenase
- Trypsin
- Dispase
- Other Enzymes
- Mechanical Dissociation Kits
-
- Homogenizers
- Tissue Grinders
- Consumables
- Buffers
- Media
-
- Automated Tissue Dissociators
- Manual Tissue Dissociators
By Source
- Commercial Sources
- In-house Sources
By Technology Type
- Manual Tissue Dissociation
- Automated Tissue Dissociation
By Application
- Cancer Research
- Stem Cell Research
- Cell Therapy
- Regenerative Medicine
- Genomics & Proteomics
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals & Diagnostic Laboratories
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

