Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market Size and Growth
The global Type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment market size was valued at USD 58.19 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 113.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% from 2024 to 2033.

Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment market with a share of 40.09% in 2023.
- In 2023, the insulin segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 32.18%
- The SGLT2 inhibitors segment is experiencing the fastest CAGR of 9.2%.
- The retail pharmacies segment held the largest revenue share of around 70.45% in 2023.
- Other distribution channels such as online pharmacies, long-term care pharmacies and specialty pharmacies is experiencing the fastest-CAGR of 8.9% over the forecast period.
- The oral segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 57.14% in 2023.
- The subcutaneous route of administration is anticipated to achieve the highest CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) treatment market is one of the most crucial sectors in global healthcare, addressing the needs of millions suffering from a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. Type 2 diabetes has reached epidemic proportions globally, driven by factors such as sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, obesity, and genetic predisposition.
Effective management of T2DM often requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, oral hypoglycemic agents, and injectable therapies such as insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs). Over the years, the treatment landscape has expanded significantly, with a surge in novel drug classes offering improved glycemic control, cardiovascular and renal benefits, and better patient adherence.
While traditional insulin therapy continues to dominate, newer classes like DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors are gaining rapid traction, owing to their favorable side effect profiles and additional health benefits beyond glucose lowering. Pharmaceutical innovation, rising patient awareness, government initiatives, and increased healthcare access in emerging economies are collectively propelling market growth.
However, disparities in drug accessibility, the high cost of newer therapies, and challenges related to long-term adherence continue to pose barriers. Nevertheless, the T2DM treatment market remains dynamic, competitive, and poised for further expansion, fueled by demographic shifts and ongoing therapeutic innovation.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Combination Therapies: Fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) combining multiple mechanisms of action are gaining popularity.
-
Focus on Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes: New therapies demonstrating cardioprotective and nephroprotective benefits are preferred.
-
Emergence of Once-weekly and Once-daily Injectables: Enhancing patient convenience and adherence.
-
Increased Adoption of Digital Health Solutions: Mobile apps, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, and telehealth integrations supporting treatment adherence.
-
Rising Popularity of Biosimilar Insulins: Cost-effective alternatives driving insulin market expansion in emerging economies.
-
Expansion of Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Revolutionizing treatment options beyond injections.
-
Growing Interest in Weight Management Solutions: Integrated therapies addressing diabetes and obesity ("diabesity").
-
Pharmacogenomics Advancing Personalized Medicine: Research targeting individualized therapeutic responses.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 USD |
62.21 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 USD |
113.40 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 6.9% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Drug class, route of administration, distribution channel, and region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
AstraZeneca PLC; Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH; Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd; Eli Lilly and Co.; Merck & Co. Inc; Novartis AG; Novo Nordisk AS; Sanofi SA; Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd |
Key Market Driver: Growing Global Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes
A powerful driver behind the T2DM treatment market is the escalating global prevalence of diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 537 million adults aged 20–79 years lived with diabetes in 2021, and this number is expected to rise to 643 million by 2030.
Rapid urbanization, lifestyle changes, increased consumption of processed foods, and rising obesity rates are major contributors to this surge. Aging populations also compound the issue, as the risk of Type 2 diabetes increases significantly with age.
This burgeoning patient population necessitates a wide spectrum of therapeutic options to manage blood sugar levels, prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and retinopathy, and ultimately reduce the global health burden. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in developing newer, more effective, and patient-friendly therapies to address this growing need, further boosting market momentum.
Key Market Restraint: High Costs and Limited Accessibility of Novel Therapies
Despite notable advancements, high treatment costs and limited accessibility to newer drugs remain significant restraints in the Type 2 diabetes treatment market.
Newly developed GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, despite their superior efficacy profiles and added benefits in heart and kidney health, come at premium prices compared to traditional therapies like metformin or sulfonylureas. In lower-income and even middle-income countries, these therapies are often financially inaccessible without insurance coverage or government subsidies.
Additionally, in resource-limited settings, healthcare infrastructure challenges further restrict widespread adoption. As a result, many patients continue to rely on older, less effective treatments, perpetuating disparities in diabetes management outcomes across different socioeconomic groups.
Key Market Opportunity: Innovation in Oral Delivery of Peptide-based Therapies
A remarkable opportunity is the innovation in oral delivery technologies for peptide-based therapies, particularly for GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Traditionally, peptide therapies require subcutaneous administration, which can deter patient compliance. However, breakthroughs like oral semaglutide (Rybelsus®) by Novo Nordisk have demonstrated that it is possible to deliver effective peptide-based therapies orally, using absorption enhancers and optimized formulation technologies.
Expanding oral options could significantly improve treatment adherence and patient satisfaction, opening vast new segments of the market, especially among populations hesitant to initiate injectable therapy. Companies investing in next-generation oral peptide delivery platforms are well-positioned to capture substantial market share in the coming years.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market By Drug Class Insights
Insulin dominates the drug class segment, especially for patients with advanced disease stages or significant pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Both basal (long-acting) and bolus (rapid-acting) insulins remain essential components of T2DM management. Major brands like Lantus (Sanofi) and Tresiba (Novo Nordisk) continue to lead the market. Biosimilar insulin products are expanding access in cost-sensitive markets, helping insulin maintain its central role despite competition from oral agents.
GLP-1 receptor agonists are the fastest-growing drug class, fueled by superior efficacy in glycemic control, weight reduction benefits, cardiovascular protection, and expanding approval for broader indications. Drugs like Ozempic (semaglutide) and Trulicity (dulaglutide) are setting new standards for T2DM management, often being initiated earlier in treatment algorithms, displacing older oral agents.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market By Distribution Channel Insights
Retail pharmacies dominate the distribution channel, owing to the chronic nature of diabetes requiring lifelong medication management and frequent prescription refills. Retail outlets provide convenient access and often serve as patient education hubs for diabetes management.
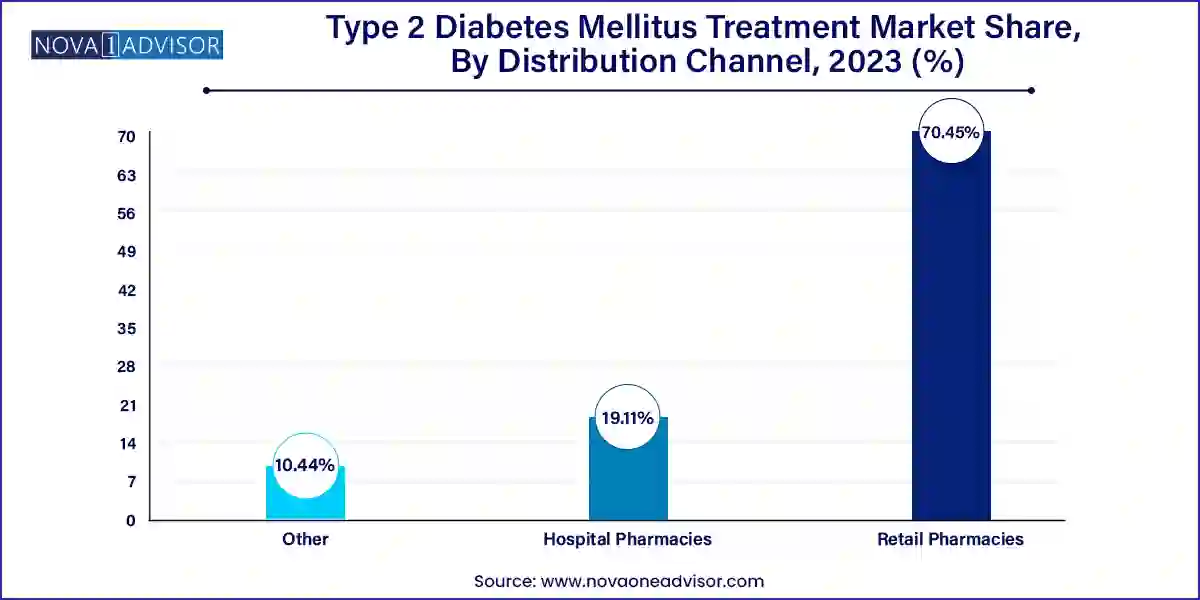
Hospital pharmacies are growing fastest, particularly for the administration of newer, high-cost injectable therapies requiring initial monitoring, as well as during acute admissions for diabetes complications. As T2DM patients increasingly experience comorbidities requiring integrated care, hospital-based diabetes management programs are gaining prominence.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market By Route of Administration Insights
Oral administration dominates, reflecting the initial standard treatment approach using metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Oral therapies offer simplicity, greater patient acceptance, and easier scalability for healthcare systems managing large diabetic populations.
Subcutaneous administration is expanding rapidly, driven by rising adoption of GLP-1 receptor agonists and insulin analogs. Innovations like once-weekly GLP-1 injections and ultra-long-acting insulins are mitigating the inconvenience associated with injectable therapies, enhancing their uptake among patients previously reluctant to move beyond oral medications.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market By Regional Insights
North America, particularly the United States, leads the global T2DM treatment market, due to its high diabetes prevalence, robust healthcare infrastructure, favorable insurance coverage for novel therapies, and strong presence of leading pharmaceutical companies like Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Merck.
The region benefits from early adoption of innovative treatments, extensive clinical trial activity, and aggressive marketing campaigns. Furthermore, proactive initiatives such as the American Diabetes Association's public awareness programs and CMS incentives for chronic disease management contribute to strong market fundamentals.
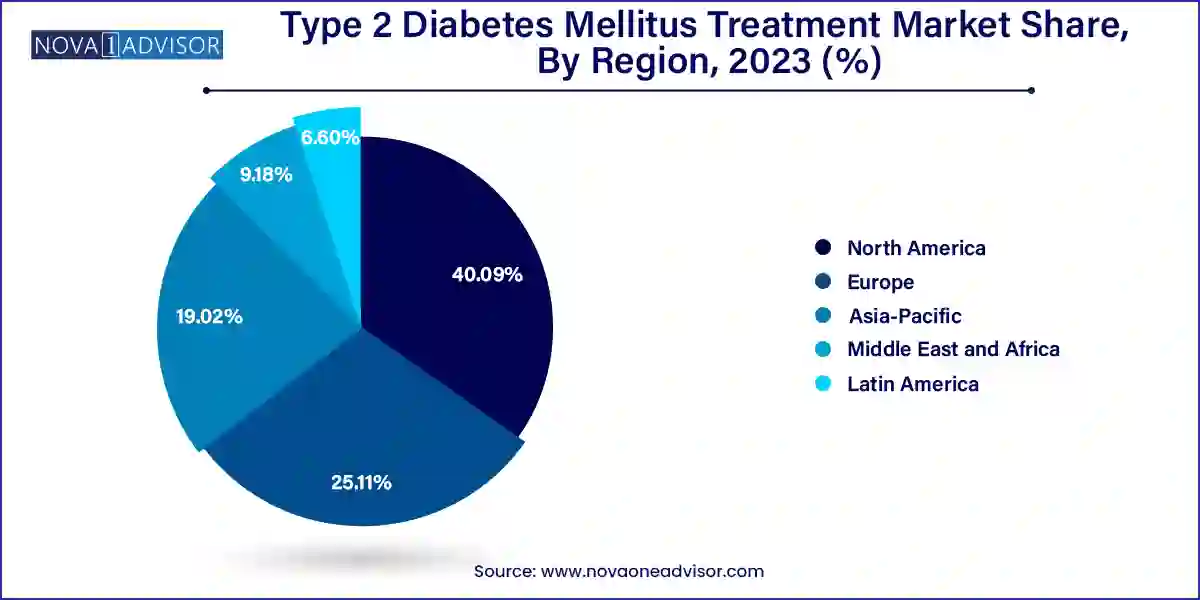
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by a diabetes epidemic in countries like China, India, and Indonesia. Rapid urbanization, lifestyle shifts, and genetic susceptibility are escalating diabetes incidence at unprecedented rates.
Governments across Asia are investing heavily in healthcare reforms, expanding insurance coverage, and implementing national diabetes prevention and control programs. Pharma companies are increasingly tailoring pricing strategies and product portfolios to serve these diverse, rapidly expanding patient populations, ensuring Asia-Pacific’s role as the next major growth engine for the T2DM treatment market.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market Top Key Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd
- Eli Lilly and Co.
- Merck & Co. Inc
- Novartis AG
- Novo Nordisk AS
- Sanofi SA
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Eli Lilly announced positive Phase III results for its dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide, showing superior A1C reduction and weight loss compared to existing treatments.
-
February 2025: Novo Nordisk launched its once-weekly insulin icodec in Europe after receiving EMA approval, offering a new paradigm for basal insulin therapy.
-
January 2025: Pfizer entered a strategic collaboration with a biotech firm to develop an oral SGLT2/GLP-1 co-formulation targeting improved glycemic and weight outcomes.
-
December 2024: Merck & Co. expanded the indications of its DPP-4 inhibitor Januvia to include patients with early-stage renal impairment based on new clinical data.
-
November 2024: Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly jointly announced expanded cardiovascular protection claims for their SGLT2 inhibitor Jardiance after favorable trial results.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment market.
By Drug Class
- Insulin
- DPP-4 Inhibitors
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
- SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Subcutaneous
- Intravenous
By Distribution Channel
- Retail Pharmacies
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Other
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



