U.S. Advanced Wound Care Market Size and Trends
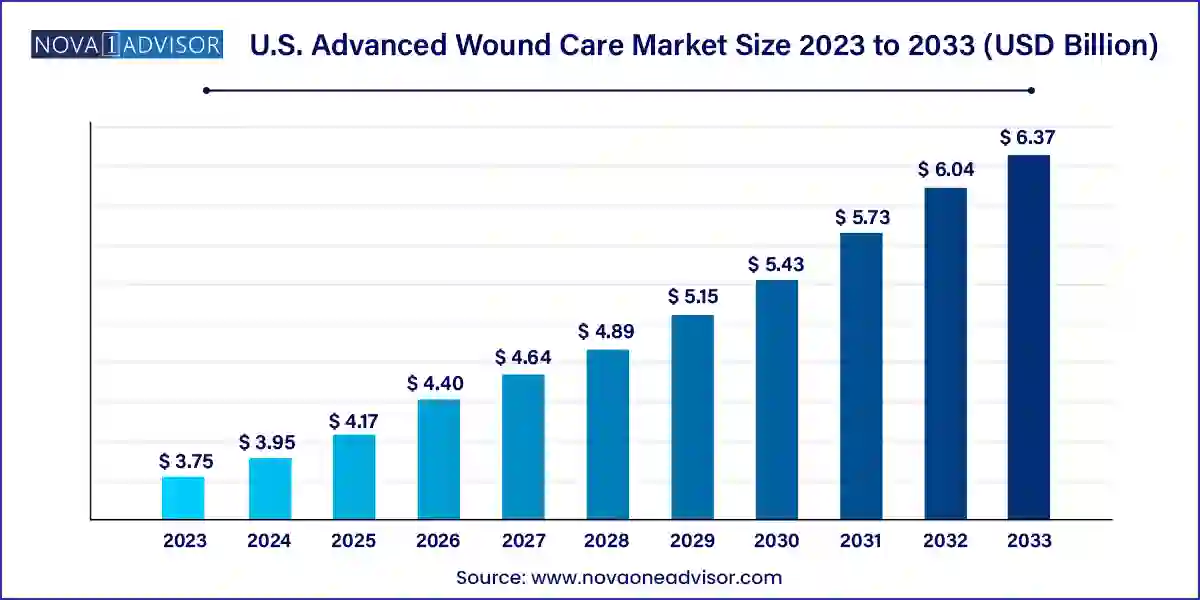
The U.S. advanced wound care market size was exhibited at USD 3.75 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 6.37 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.44% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- Moist dressings dominated the product segment in U.S. advanced wound care market by capturing a share of 59.83%.
- Hydrocolloid dressings is anticipated to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period.
- The chronic wounds segment held the largest market share of about 60% in 2023.
- The acute wounds segment is anticipated to witness fastest growth of 5.54% over the forecast period.
- The hospitals segment held the largest market share of around 45.0% in 2023.
Market Overview
The U.S. Advanced Wound Care Market is experiencing substantial evolution, driven by the rising prevalence of chronic wounds, advancements in biologically derived therapies, and increasing adoption of sophisticated wound healing technologies. Advanced wound care encompasses a broad range of treatments and devices designed to accelerate wound healing, reduce infection risk, and improve patient quality of life beyond what traditional gauze and basic dressings offer.
The United States, being home to one of the most developed healthcare infrastructures in the world, remains a global leader in the adoption of advanced wound care modalities. With chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers affecting millions annually, there is an urgent demand for more efficient and cost-effective wound management solutions. Additionally, aging demographics, rising obesity and diabetes rates, and increasing numbers of surgical procedures are creating a perfect storm for sustained growth in this sector.
Technological innovations from bioengineered skin substitutes to smart antimicrobial dressings are redefining treatment paradigms. These solutions not only target healing but also address underlying pathologies through moisture control, infection management, and tissue regeneration. Moreover, reimbursement reforms and the push for outpatient and home-based care are further shifting the dynamics, making advanced wound care more accessible and personalized than ever before.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise in Home-based Wound Care Solutions: With the increase in elderly and chronic patients, there is growing demand for wound care products suited for at-home treatment.
-
Biological and Cell-based Therapies Gaining Momentum: Active wound care using skin substitutes and bioengineered tissue is gaining approval and clinical acceptance.
-
Focus on Infection Control: Antimicrobial dressings, especially silver-based solutions, are increasingly favored for preventing and treating infected wounds.
-
Smart Wound Technologies and Sensors: Innovations like wound dressings with integrated biosensors that monitor pH, temperature, or bacterial load are emerging.
-
Shift to Value-based Healthcare: Payers and providers are increasingly focusing on outcome-driven care, prompting the use of products that ensure faster healing.
-
3D Printing in Skin Substitutes: Companies are exploring 3D bioprinting for customizable, patient-specific wound grafts and skin replacement therapies.
-
Increased Use of Collagen Dressings: Collagen-based solutions are being favored for their role in scaffolding and tissue regeneration.
-
Telehealth Integration in Wound Management: Remote monitoring of wound healing using digital imaging and AI platforms is on the rise.
Report Scope of The U.S. Advanced Wound Care Market
Market Driver – Growing Incidence of Chronic Wounds
A significant driver shaping the U.S. advanced wound care market is the growing burden of chronic wounds, especially among diabetic and elderly populations. It is estimated that over 6.5 million people in the U.S. suffer from chronic wounds, with diabetic foot ulcers alone accounting for a substantial portion. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) projects that diabetes prevalence could climb to over 14% by 2030, and with 15–25% of diabetics likely to develop foot ulcers during their lifetime, demand for specialized care is increasing.
Chronic wounds are not just a clinical issue they represent a massive financial burden. They lead to frequent hospitalizations, long healing times, and high morbidity rates. Advanced wound care products, such as bioactive dressings and engineered skin substitutes, offer accelerated healing and reduce hospital stays, making them indispensable for improving clinical outcomes and reducing overall healthcare costs. Hospitals and specialty clinics are thus investing more in advanced solutions that offer both clinical efficacy and economic advantage.
Market Restraint – High Cost of Products and Treatment
Despite the clinical benefits, the high cost of advanced wound care products acts as a major restraint, especially for uninsured or underinsured patients. Products like biologics, skin substitutes, and antimicrobial dressings often come at premium prices. For example, a single application of a skin substitute like Apligraf can cost upwards of $1000–$3000, making it inaccessible to many patients outside of hospital care or those lacking comprehensive insurance coverage.
Additionally, not all products are covered uniformly by Medicaid or private insurers. Limited reimbursement policies, especially for home healthcare settings, can delay or limit patient access. In some cases, physicians may opt for traditional methods simply because of financial constraints, even when advanced options are more clinically appropriate. This economic barrier is particularly visible in rural and under-resourced regions, further widening healthcare disparities in chronic wound treatment.
Market Opportunity – Advancements in Regenerative Wound Therapies
A major opportunity lies in the development and commercialization of regenerative wound care therapies, including bioengineered skin grafts, stem cell-infused scaffolds, and tissue-based solutions. These biologically active products not only cover the wound but actively participate in cellular regeneration, modulating inflammation, and promoting angiogenesis. Their growing success in clinical trials has brought them to the forefront of next-gen wound care.
For instance, products like Dermagraft and Epifix are seeing increased utilization in non-healing wounds and have demonstrated significant reductions in healing times. Startups and biotech firms are entering the market with novel collagen scaffolds, decellularized matrices, and even 3D printed grafts that are customized to patient wounds. With ongoing support from the U.S. FDA’s Breakthrough Devices Program and rising investment in biotech innovation, regenerative wound therapies are expected to redefine the standard of care in the coming decade.
U.S. Advanced Wound Care Market By Product Insights
Moist wound care products dominate the market, driven by their widespread use in hospitals, outpatient settings, and home care. Among moist dressings, foam dressings remain the most preferred due to their high absorbency and ability to maintain a moist healing environment. These products are especially effective for exuding wounds, making them a standard in pressure ulcer and diabetic wound management. Hydrocolloids and hydrogels also see substantial use, with clinicians favoring them for partial-thickness burns and surgical wounds due to their soothing, autolytic debridement capabilities.
However, active wound care products are the fastest-growing segment, fueled by innovations in bioengineered skin and extracellular matrix therapies. Skin substitutes like Integra and Epifix are being integrated into treatment pathways for complex, non-healing wounds, particularly in diabetic and surgical patients. Biomaterials derived from allogenic or xenogeneic sources are being increasingly utilized in surgical reconstruction and trauma-related wound care. As healthcare systems focus more on outcome-driven protocols, active therapies offering regenerative capabilities are rapidly gaining market share.
U.S. Advanced Wound Care Market By Application Insights
Chronic wounds continue to dominate the market, accounting for a majority of advanced wound care revenue. Diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure ulcers are particularly challenging due to their high recurrence rates and long healing timelines. These conditions often require comprehensive treatment strategies involving dressings, debridement, compression, and infection management. The rise of multidisciplinary wound care centers across the U.S. has further enhanced the uptake of advanced therapies in this category.
Meanwhile, acute wounds are the fastest-growing application, largely driven by the increase in surgical procedures, accidental trauma, and burn cases. With over 50 million surgeries performed annually in the U.S., postoperative wound care is a significant growth area. Surgeons are now incorporating advanced dressings like silver alginates and collagen matrices to reduce surgical site infections (SSIs) and improve healing outcomes. The expanding role of trauma care and emergency services is also contributing to the rising use of advanced solutions in acute wound scenarios.
U.S. Advanced Wound Care Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals are the dominant end-use segment, accounting for the bulk of advanced wound care consumption. These institutions handle complex wound cases that require continuous monitoring, surgical interventions, and use of expensive regenerative therapies. Hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) and surgical site infections have emerged as critical metrics under value-based care, prompting administrators to invest in advanced solutions to reduce complications and associated costs.
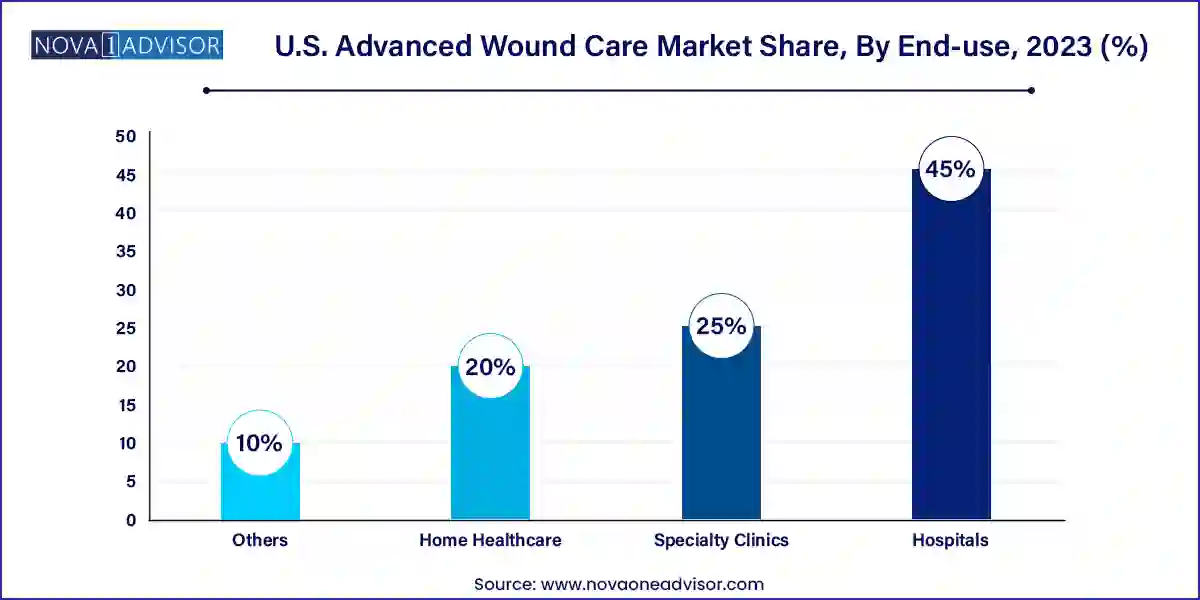
Conversely, home healthcare is the fastest-growing end-use segment, spurred by the shift toward outpatient care, aging populations, and the growing prevalence of chronic wounds managed at home. Reimbursement improvements, along with portable and self-applicable wound care solutions, are making it easier for patients and caregivers to administer treatment outside clinical settings. Companies are now designing dressings that require less frequent changes and offer extended wear time, catering to the growing demand in this segment.
Country-Level Analysis: United States
The United States represents the largest and most mature advanced wound care market globally, supported by a highly developed healthcare infrastructure, robust reimbursement mechanisms, and strong clinical adoption of next-generation products. The presence of top-tier healthcare institutions and a culture of innovation have created an environment where companies can rapidly pilot, test, and commercialize new wound care technologies.
From a policy perspective, the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has increasingly broadened coverage for advanced wound therapies, including skin substitutes and negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), enhancing access. The proliferation of outpatient wound care centers, especially affiliated with hospitals, has brought specialized treatment to more communities. Moreover, ongoing public health campaigns for diabetes prevention and pressure ulcer management are fueling awareness and early diagnosis, increasing demand for wound care products.
In 2024, the FDA granted breakthrough device designation to several bioengineered wound products, signaling the agency’s recognition of the critical role advanced therapies play in addressing unmet needs. The American Wound Healing Society, in collaboration with the Veterans Health Administration, has launched pilot programs for remote wound monitoring using digital wound imaging, highlighting the integration of telehealth in national care models. These trends collectively position the U.S. as both a pioneer and benchmark in global wound care practices.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. advanced wound care market include:
- Smith+Nephew
- Mölnlycke Health Care AB
- ConvaTec Group PLC
- Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson)
- URGO
- Coloplast Corp.
- 3M
- Integra LifeSciences
- PAUL HARTMANN AG
- McKesson
- Hydrofera
- Medline Industries, Inc.
- Organogenesis
- Kerecis
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – 3M Health Care launched a new line of Tegaderm antimicrobial dressings with extended wear time, optimized for diabetic ulcers and surgical wounds, expanding its presence in outpatient care.
-
January 2025 – Smith & Nephew announced a $250 million investment in its Fort Worth facility, aimed at scaling up production of collagen-based wound dressings and skin substitutes.
-
November 2024 – Organogenesis Inc. received expanded FDA clearance for PuraPly AM in treating acute traumatic wounds, increasing its market scope beyond chronic indications.
-
September 2024 – Convatec Group launched a pilot program with Mayo Clinic to evaluate AI-based wound assessment tools integrated into their Avelle NPWT system.
-
July 2024 – Mölnlycke Health Care acquired U.S.-based WoundTech Innovations, a startup focused on smart dressings and wearable wound sensors, signaling its entry into digital wound management.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. advanced wound care market
Product
-
- Foam
- Hydrocolloid
- Film
- Alginate
- Hydrogel
- Collagen
- Other Advanced Dressings
-
- Biomaterials
- Skin-substitute
Application
-
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Pressure Ulcers
- Venous Leg Ulcers
- Others
-
- Surgical & Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
End-use
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Home Healthcare
- Others


