U.S. Biosensors Market Size and Research
The U.S. biosensors market size was exhibited at USD 11.62 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 23.20 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 7.16% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
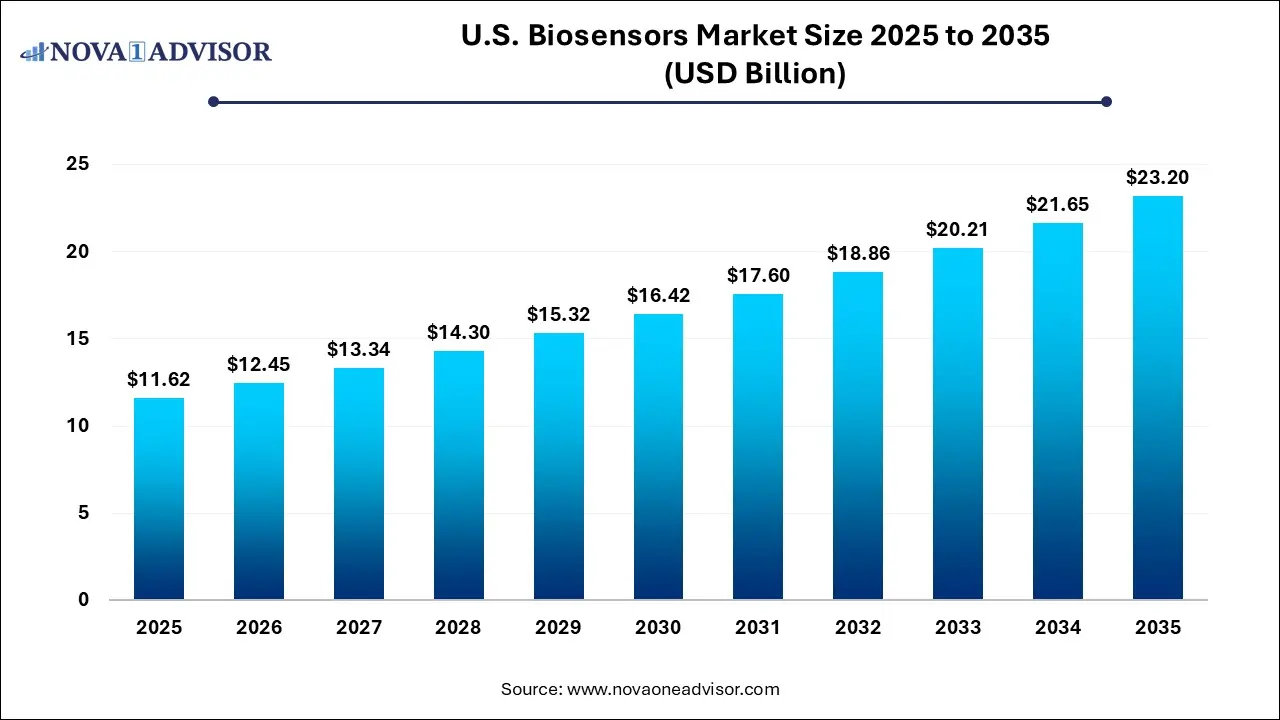
Key Takeaways:
- Based on technology, the electrochemical segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 73.0% in 2025.
- The optical segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Based on application, the medical segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 67.57% in 2025.
- The agriculture segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Based on end-use, the PoC testing segment held the market with the largest revenue share of 47.67% in 2025.
- The home healthcare diagnostics segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. biosensors market stands as a pivotal segment in the country’s broader healthcare and biotechnology ecosystem, underpinned by advances in digital health, personalized medicine, diagnostics, and smart monitoring systems. A biosensor is an analytical device that converts a biological response into an electrical, optical, or thermal signal. Its application spans across several domains including medical diagnostics, food safety, environmental monitoring, biodefense, and industrial biotechnology.
Over the past decade, the biosensors market in the U.S. has witnessed a transformative evolution—from being dominantly used in glucose monitoring devices to becoming indispensable tools in early disease detection, drug discovery, point-of-care (PoC) testing, and even homeland security. The healthcare sector remains the largest end-use domain, accounting for a considerable share of revenue, with biosensors embedded in wearables, implantables, and non-invasive diagnostic devices. However, applications in agriculture, environmental safety, and food quality testing are gaining rapid momentum, reflecting the interdisciplinary utility of biosensor technologies.
The U.S., with its strong base of biomedical research institutions, high healthcare expenditure, proactive patient adoption of innovative diagnostics, and government support for public health surveillance, is uniquely positioned as a global leader in biosensor adoption. The increased prevalence of chronic diseases, pandemic preparedness efforts, and technological convergence (such as biosensors with IoT or AI) further contribute to the market's dynamic expansion.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration of biosensors with wearable and mobile health platforms for continuous, real-time monitoring of vitals like glucose, cardiac biomarkers, and hydration levels.
-
Rising demand for point-of-care biosensors to deliver immediate results in remote and ambulatory settings.
-
Miniaturization and nanotechnology-driven innovation, enabling implantable and lab-on-chip biosensor devices.
-
Expansion of biosensors beyond healthcare, especially into food industry, environmental monitoring, and biodefense applications.
-
Increasing deployment of electrochemical biosensors due to their cost-effectiveness and sensitivity.
-
Development of AI-powered biosensors capable of predictive analytics and self-diagnosis, enhancing early detection.
-
Proliferation of non-invasive and wearable biosensors tailored for chronic disease management, particularly diabetes and cardiovascular conditions.
-
Surging R&D investments by federal bodies and private institutions to develop next-gen biosensing platforms, especially for infectious disease outbreaks.
Report Scope of U.S. Biosensors Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 12.45 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 23.20 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 7.16% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Technology, Application, End-use, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott; Medtronic; Roche Diagnostics; Dexcom; SENTINEL; Intricon Corporation; Quanterix; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Masimo; Siemens Healthcare Private Limited; Molecular Devices, LLC.; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; PerkinElmer Inc.; Covaris, LLC. |
One of the most significant drivers propelling the U.S. biosensors market is the surge in chronic and lifestyle-related diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and obesity. According to the CDC, nearly 37 million Americans have diabetes, and about one in three adults has prediabetes. This alarming statistic has led to widespread adoption of biosensors especially glucose biosensors for continuous monitoring, early detection, and personalized intervention.
Wearable biosensors, embedded in smartwatches and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), allow real-time data collection and alert systems for patients and physicians alike. These tools reduce hospital admissions by detecting anomalies before they escalate into critical situations. Additionally, biosensors are now evolving to track multi-analyte parameters such as glucose, ketones, and lactate providing a comprehensive metabolic profile. The ability of biosensors to support at-home, non-invasive disease monitoring empowers patients to self-manage their conditions effectively, ultimately reducing healthcare costs and improving patient outcomes.
Market Restraint: Regulatory Challenges and Standardization Issues
Despite their revolutionary potential, regulatory hurdles and lack of standardization remain critical barriers for the U.S. biosensors market. Because biosensors operate at the intersection of biology and electronics, their validation and approval process must meet both medical device standards and clinical diagnostic benchmarks. This dual-layer complexity increases the time to market for novel products.
Moreover, the FDA has stringent guidelines around biosensor calibration, biocompatibility, signal fidelity, and clinical accuracy, especially for medical applications. The challenges multiply when biosensors are designed for use in unconventional domains like environmental or food monitoring, where there’s a lack of harmonized regulatory frameworks. As a result, several promising biosensor startups often face delayed commercialization or limited scalability. Addressing these regulatory roadblocks through collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies is imperative for sustained growth.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Biosensors into Food Safety and Environmental Monitoring
An emerging opportunity lies in broadening the biosensor application landscape into food safety and environmental surveillance. Foodborne illnesses affect nearly 48 million people in the U.S. annually, as per the FDA. This has accelerated the demand for biosensors capable of real-time detection of contaminants like E. coli, Salmonella, or pesticide residues in food processing lines.
Simultaneously, concerns over air and water pollution—amplified by climate change and urbanization—have fueled demand for environmental biosensors that can detect toxins, pathogens, heavy metals, and hormonal disruptors in real time. These biosensors can be deployed in water treatment plants, agriculture, industrial sites, and disaster zones. The cost-efficiency, portability, and rapid responsiveness of biosensors make them ideal tools for decentralized, continuous environmental monitoring—presenting significant untapped market potential outside traditional clinical settings.
U.S. Biosensors Market By Technology Insights
Electrochemical biosensors dominated the U.S. biosensors market in 2025 and are expected to retain their lead. Electrochemical biosensors, known for their affordability, portability, and fast response time, are widely used in glucose monitors and cholesterol tests. Their versatility across medical diagnostics, food toxicity detection, and environmental surveillance contributes to their dominant market share. With the growth in wearable health tech, electrochemical biosensors embedded in fitness bands and CGMs have seen surging demand. For instance, Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre and Dexcom’s G6 are key examples of successful electrochemical sensor-based devices.
Meanwhile, optical biosensors are witnessing the fastest growth due to their high specificity and potential for multiplexed detection. Optical biosensors use mechanisms like fluorescence and surface plasmon resonance to detect biomolecules, enabling highly sensitive assays. These are particularly valuable in drug discovery and oncology diagnostics. Companies like Genalyte have developed multiplexed optical biosensors for fast serological testing, while research institutions are investing in wearable optical platforms that detect cortisol and dehydration levels. Their high analytical performance and capability to handle complex analyte mixtures are driving adoption across R&D labs and specialized healthcare settings.
U.S. Biosensors Market By Application Insights
The medical application segment dominated the market, accounting for the largest share owing to the widespread use of biosensors in chronic disease management, diagnostics, and personalized care. Within this segment, blood glucose monitoring remains the cornerstone application. Devices such as CGMs have seen exponential adoption due to the diabetes epidemic in the U.S. Furthermore, biosensors for drug discovery have also gained momentum, facilitating rapid compound screening and toxicity profiling in pharmaceutical R&D. Infectious disease biosensors, particularly for COVID-19, saw an unprecedented demand surge during the pandemic, reinforcing their clinical value.
Conversely, the food toxicity segment is the fastest-growing application area, driven by rising food safety concerns and regulatory enforcement. Biosensors capable of detecting mycotoxins, pathogens, or spoilage indicators are being adopted by food manufacturers and quality control agencies. Portable devices using aptamer-based or electrochemical detection mechanisms are helping companies comply with FDA food safety modernization mandates. Startups such as SafeTraces and SnapDNA are actively commercializing food biosensor platforms to enable traceability and contamination alerts in real time.
U.S. Biosensors Market By End-use Insights
Home healthcare diagnostics emerged as the dominating end-use segment, powered by consumer preference for personalized, at-home health tracking tools. The adoption of biosensors embedded in wearables, mobile diagnostics, and self-testing kits has accelerated in tandem with trends in telehealth and decentralized care. Particularly for elderly populations and chronic disease patients, devices like heart-rate monitors, CGMs, and oximeters offer freedom from hospital dependency. Companies like Fitbit, Apple, and BioIntelliSense are reshaping the health monitoring paradigm through consumer-friendly biosensor integration.
On the other hand, PoC testing is the fastest-growing segment due to its relevance in emergency care, rural healthcare delivery, and outpatient settings. Biosensors used in PoC platforms offer rapid turnaround times, facilitating immediate treatment decisions. During the COVID-19 pandemic, PoC biosensor-based antigen tests proved vital for mass testing. Looking ahead, the demand for PoC biosensors for cardiac markers, STDs, and drug abuse detection is expected to surge, especially with government focus on rural healthcare equity and pandemic preparedness.
Country-Level Analysis
The U.S. biosensors market is deeply intertwined with the country’s technological infrastructure, healthcare reform, and innovation pipeline. States like California, Massachusetts, and Texas lead the biosensor R&D and commercialization efforts, hosting top-tier universities, research hubs, and medtech startups. The FDA’s proactive stance on digital diagnostics, combined with reimbursement expansions for remote patient monitoring, has catalyzed biosensor adoption.
Furthermore, military and homeland security agencies have shown growing interest in deploying biosensors for biodefense—such as early detection of biowarfare agents or chemical threats. In agriculture, biosensor-equipped drones and soil sensors are being tested in midwestern states to improve yield and crop health monitoring. The American Rescue Plan and NIH funding initiatives are also channeling investments into biosensor-centric healthcare innovations, especially for underserved communities.
Recent Developments
-
February 2025 – Abbott Laboratories received expanded FDA clearance for its FreeStyle Libre 3 biosensor to be used in pediatric patients aged 2 and up, marking a major development in pediatric diabetes care.
-
January 2025 – Siemens Healthineers launched a new biosensor-integrated PoC analyzer for cardiac biomarker testing in emergency settings, significantly reducing turnaround time.
-
December 2024 – BioIntelliSense entered a strategic partnership with the Department of Veterans Affairs to deploy wearable biosensors for remote monitoring of veterans with chronic diseases.
-
November 2024 – Dexcom announced clinical trials for a multi-analyte biosensor capable of measuring glucose, lactate, and hydration levels, designed for athletes and high-risk cardiovascular patients.
-
October 2024 – Sensonor Technologies introduced an optical biosensor platform for food pathogen detection, aimed at U.S.-based meat processing plants.
-
September 2024 – Apple Inc. filed a patent for sweat-analyzing biosensors to be embedded in the next generation of Apple Watch, enabling real-time electrolyte balance tracking.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. biosensors market include:
- Abbott
- Medtronic
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Dexcom, Inc.
- SENTINEL
- Intricon Corporation
- Quanterix
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- Masimo
- Siemens Healthcare Private Limited
- Molecular Devices, LLC.
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- Covaris, LLC
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. biosensors market
Technology
- Thermal
- Electrochemical
- Piezoelectric
- Optical
Application
-
- Cholesterol
- Blood Glucose
- Pregnancy Test
- Drug Discovery
- Infectious Disease
- Food Toxicity
- Bioreactor
- Agriculture
- Environment
- Others
End-use
- Home Healthcare Diagnostics
- PoC Testing
- Food Industry
- Research Laboratories
- Security and Bio-defence
Regional
- West
- Midwest
- Northeast
- Southwest
- Southeast

