U.S. Capnography Devices Market Size and Growth
The U.S. capnography devices market size was exhibited at USD 415.35 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 844.97 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.36% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
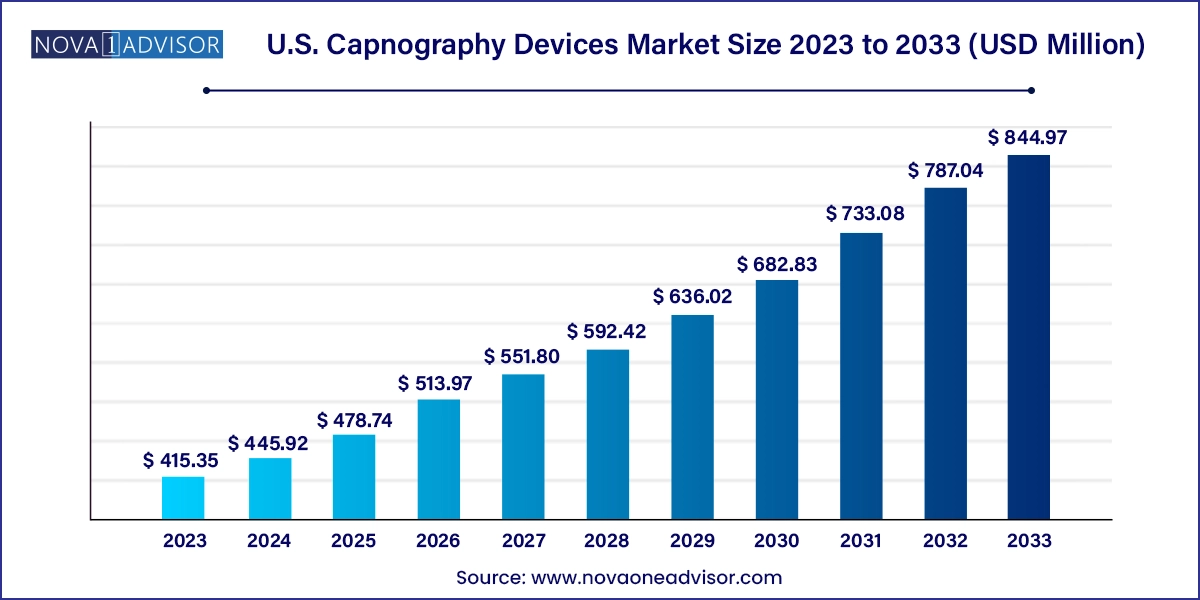
U.S. Capnography Devices Market Key Takeaways:
- The portable segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest share of more than 56% of the total revenue in 2023.
- The hospitals segment dominated the market, with the largest share of 46.0% in 2023.
- The others segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The integrated segment dominated the market, with the largest share of over 59% in 2023.
- The multiparameter capnography devices segment dominated the U.S. capnography devices market with the largest revenue share of 53.0% in 2023.
- The sidestream segment dominated the market, with the largest share of 38.0% in 2023.
- The microstream segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 9.6% during the forecast period.
- The sensors segment holds a substantial market share of approx. 31% in the U.S. capnography device market in 2023.
- The procedural sedation dominated the market with the largest share of over 25% in 2023.
Market Overview
The U.S. capnography devices market is witnessing substantial growth driven by increasing clinical emphasis on respiratory monitoring, the rise in procedural sedation, and an expanding elderly population prone to chronic respiratory conditions. Capnography, the monitoring of carbon dioxide (COâ‚‚) in respiratory gases, has become a critical tool in intensive care units, emergency departments, and operating rooms across the country. The ability of capnography to provide real-time, non-invasive insights into a patient’s ventilatory status has elevated its role from optional to standard in many clinical guidelines.
Historically, capnography was reserved for anesthetized surgical patients. However, it has rapidly expanded its utility to include emergency medicine, procedural sedation, pain management, and post-operative monitoring. In the U.S., capnography is increasingly mandated by clinical bodies like the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) and American Heart Association (AHA), further supporting its widespread adoption. The 2020 ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) guidelines, for example, reinforce the importance of waveform capnography in confirming endotracheal tube placement and monitoring CPR effectiveness.
Technological advancements have also contributed to market momentum. Compact, portable devices, multi-parameter monitors, and microstream technology have improved clinical accuracy and patient comfort. Capnography has also found its way into ambulatory care and home healthcare through portable units and wireless monitoring. As the U.S. healthcare system increasingly emphasizes outcomes, patient safety, and value-based care, capnography is becoming indispensable in respiratory care protocols, creating a strong and sustainable market opportunity.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Adoption in Non-Operating Room Settings: Capnography is increasingly used in ambulatory surgery centers, emergency rooms, and procedural sedation beyond the OR.
-
Integration with Multiparameter Monitors: Device manufacturers are offering capnography modules integrated into broader patient monitoring systems to enhance workflow efficiency.
-
Shift Toward Portable and Wireless Devices: Compact, lightweight, and Bluetooth-enabled capnographs are facilitating mobility in pre-hospital and home-care settings.
-
Standardization in EMS and Prehospital Care: Capnography is being included in standard protocols for paramedics and EMTs for use during resuscitation and airway management.
-
Microstream Technology Penetration: This technology is gaining ground for its accuracy in low tidal volumes and neonatal care.
-
OEM Module Demand from Device Integrators: Medical equipment manufacturers increasingly source capnography modules to add respiratory monitoring capabilities to their systems.
-
COVID-19 Reinforced Respiratory Monitoring Demand: The pandemic heightened awareness of respiratory monitoring, leading to increased procurement of capnography devices.
Report Scope of U.S. Capnography Devices Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 445.92 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 844.97 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 7.36% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Solution Offering, Parameter, Technology, Component, Application, End use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Infinium Medical, Inc.; Masimo; Medtronic; Nihon Kohden Corporation; ICU Medical Inc.; Nonin; BD; EdanUSA; Avante Health Solutions; Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA |
Key Market Driver
Surging Need for Respiratory Monitoring in Procedural Sedation and Critical Care
The primary driver of the U.S. capnography devices market is the growing demand for accurate and continuous respiratory monitoring, particularly in procedural sedation and critical care. With the rise of outpatient procedures involving conscious sedation such as gastrointestinal endoscopies, dental surgeries, and cosmetic procedures there is a clear clinical imperative to prevent adverse respiratory events. Studies indicate that hypoventilation and airway obstruction often precede oxygen desaturation, making COâ‚‚ monitoring a superior early indicator of patient deterioration compared to pulse oximetry alone.
In critical care units, capnography plays a central role in confirming endotracheal tube placement, managing mechanical ventilation, and assessing the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). The expanding elderly population and rising prevalence of COPD, sleep apnea, and post-operative respiratory depression further increase the need for effective ventilation monitoring. These factors collectively strengthen the demand for capnography as a standard of care, fueling the market's upward trajectory.
Key Market Restraint
High Device Cost and Limited Reimbursement for Outpatient Use
Despite its clinical value, one of the major restraints in the U.S. capnography devices market is the high initial cost of advanced systems and accessories, particularly for smaller outpatient settings. Hospitals and ambulatory surgery centers often face budgetary constraints and must prioritize equipment purchases based on reimbursement potential. While inpatient use is well-supported, reimbursement for capnography in outpatient sedation or transport settings is less standardized.
This cost barrier is compounded by the recurring expense of consumables such as sampling lines, filters, and sensors, especially for microstream and sidestream systems. Clinics and independent practitioners may hesitate to invest in capnography technology unless explicitly required by guidelines or mandates. Addressing these pricing and reimbursement concerns is critical to unlocking broader adoption across community-based healthcare settings.
Key Market Opportunity
Expansion into Ambulatory and Home Healthcare Monitoring
A promising opportunity lies in the increasing use of capnography in ambulatory and home care environments. The shift toward decentralized care, fueled by the COVID-19 pandemic and value-based care models, is creating demand for portable monitoring technologies. Patients discharged from hospitals, especially those with chronic respiratory conditions or post-surgical vulnerabilities, benefit from at-home COâ‚‚ monitoring to ensure safety and recovery.
Several manufacturers are responding by introducing compact, battery-operated capnographs with user-friendly interfaces, Bluetooth connectivity, and cloud integration for telemonitoring. The availability of cost-effective portable capnographs opens new frontiers in non-hospital care, especially for respiratory therapists, palliative care providers, and remote patient monitoring (RPM) services. This area is expected to gain momentum as digital health adoption accelerates nationwide.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By Product Insights
Portable capnography devices dominated the U.S. market due to their wide applicability in emergency medicine, ambulatory care, and transport settings. Their compact design, battery operation, and wireless capabilities make them ideal for EMS teams, ICU step-down units, and outpatient procedural suites. These devices enable continuous respiratory monitoring without restricting patient mobility, a critical factor in post-anesthesia care units (PACUs) and ERs. Their integration into wearable or handheld formats is also expanding their reach into home and rehabilitation settings.
Stationary capnography systems, while less flexible, continue to be essential in operating rooms and ICUs. They are often part of integrated anesthesia workstations or advanced patient monitors, offering continuous waveform analysis during critical procedures. However, as mobility and versatility become priority criteria in healthcare technology procurement, stationary units are witnessing slower growth compared to their portable counterparts.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By End Use Insights
Hospitals are the largest end users of capnography devices in the U.S., with ORs, ICUs, and ERs representing the highest utilization zones. Hospital systems procure both integrated and standalone capnography systems for use in anesthesiology, respiratory therapy, and cardiac life support. The need for 24/7 monitoring, regulatory compliance, and electronic health record (EHR) integration further drives hospital-based demand.
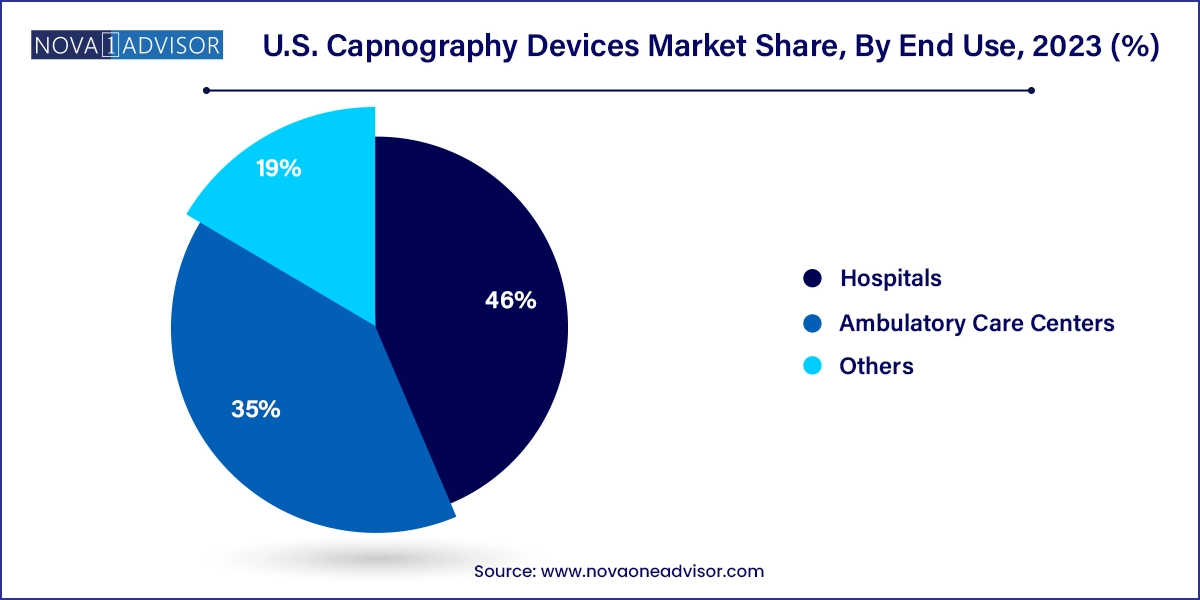
Ambulatory care centers are witnessing the fastest growth, particularly due to the rise of outpatient surgical procedures. These centers benefit from portable and standalone capnography systems that are easy to use and meet emerging accreditation standards. Additionally, dental and GI clinics performing sedation are investing in capnography to meet updated clinical safety protocols.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By Solution Offering Insights
Integrated capnography solutions led the market due to their seamless incorporation into multiparameter monitors used in critical care and operating rooms. Hospitals prefer integrated systems that combine ECG, SpOâ‚‚, blood pressure, and COâ‚‚ readings into a unified platform, enhancing workflow efficiency and reducing clutter. These systems provide comprehensive patient data in real time, facilitating better clinical decision-making and alarm management. Manufacturers like Philips, Medtronic, and GE Healthcare continue to invest in these all-in-one solutions for acute care environments.
On the other hand, standalone capnography units are growing steadily, particularly among EMS, dental, and outpatient procedural settings. Their affordability, portability, and easy deployment make them suitable for smaller practices or temporary monitoring needs. Moreover, advancements in microcontroller technology and touch-screen interfaces have made standalone units more capable than ever before.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By Parameter Insights
While single parameter devices (dedicated capnographs) are widely used in EMS and specialized applications, multiparameter capnography systems are the fastest-growing category. These systems integrate COâ‚‚ monitoring with other vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate, providing a holistic view of patient status. The convenience of a unified device reduces the need for multiple monitors and simplifies bedside operations.
Multiparameter systems are particularly valuable in high-acuity environments such as ICUs, cardiac care units, and procedural sedation settings. Their ability to deliver trend data and waveform analysis in conjunction with real-time physiological metrics supports proactive interventions and reduces risk.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By Technology Insights
Sidestream capnography remains the most widely used technology in the U.S., particularly in non-intubated and low-flow patients. Its flexibility in patient interface—allowing both intubated and non-intubated usage—makes it suitable for procedural sedation, emergency transport, and post-operative monitoring. Sidestream technology is relatively cost-effective and easy to deploy across various care settings, from ambulances to general wards.
Microstream technology, though currently smaller in market share, is the fastest-growing due to its precision and applicability in low tidal volume patients such as neonates and pediatric populations. It provides highly accurate waveform and ETCOâ‚‚ values even under challenging breathing conditions. Hospitals investing in neonatal intensive care and advanced respiratory therapy are increasingly adopting microstream systems.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By Component Insights
Among the components, sampling lines and filters dominate in terms of volume due to their consumable nature. Each patient interaction typically requires a new disposable sampling line to maintain hygiene and accuracy, leading to consistent demand. These components also account for a significant portion of recurring revenue for manufacturers.
OEM modules, sensors, and cuvettes are also critical, especially for system integrators and equipment manufacturers looking to add capnography functionality to broader devices. The demand for modularity and customization is growing, creating a robust OEM ecosystem within the capnography space.
U.S. Capnography Devices Market By Application Insights
Emergency medicine is the leading application area for capnography devices in the U.S., owing to their vital role in verifying airway placement, assessing ventilation during CPR, and monitoring sedation in trauma cases. Emergency departments, EMS providers, and critical care transport teams rely heavily on capnography for quick decision-making and patient stabilization.
Procedural sedation is the fastest-growing application segment. As sedation outside the OR becomes more common in dental clinics, GI suites, and radiology departments, capnography is increasingly used to prevent hypoventilation-related complications. Clinical societies now recommend or mandate COâ‚‚ monitoring during moderate to deep sedation, driving device adoption across outpatient and non-acute settings.
Country-Level Analysis
The United States is the largest and most mature market for capnography devices globally, supported by a robust regulatory framework, high clinical awareness, and ongoing technology adoption. Guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) and American Heart Association (AHA) emphasize the use of waveform capnography in multiple settings, effectively making it a clinical standard in many hospitals and prehospital care environments.
Hospital systems across states such as California, New York, and Texas are leading adopters of multiparameter monitors with integrated capnography. Meanwhile, emergency services in states like Massachusetts and Illinois have mandated the use of capnography in all advanced life support ambulances. The continued rise of outpatient surgical centers, driven by Medicare reforms and patient preferences, is expected to further fuel demand across the U.S.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. capnography devices market include:
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- Infinium Medical, Inc.
- Masimo
- Medtronic
- Nihon Kohden Corporation
- ICU Medical Inc.
- Nonin
- BD
- EdanUSA
- Avante Health Solutions
- Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. capnography devices market
Product
Solution Offering
Parameter
- Single Parameter
- Multiparameter
Technology
- Mainstream
- Sidestream
- Microstream
Component
- OEM Modules
- Filters
- Sensors
- Sampling Line
- Other Accessories (Cuvettes, Adaptors, etc.)
Application Area
- Emergency medicine
- Pain medicine
- Procedural sedation
- Critical care
- Others
End Use
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Care Centers
- Others


