U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The U.S. cell and gene therapy market was valued at USD 6.35 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 51.15 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 23.2% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The growth of the market is attributed to the rising demand for personalized therapies and increasing investments in cell and gene therapy R&D.
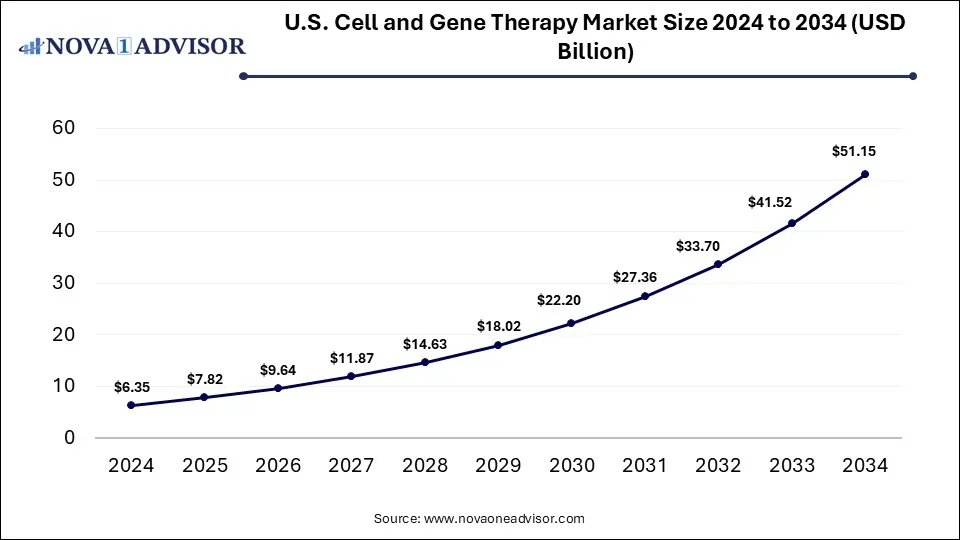
U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Key Takeaways
- By therapy type, the cell therapy segment held the largest market share of 86.2% in 2024.
- By therapy type, the gene therapy segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate over the forecast period.
- By therapeutic class, the infectious disease segment dominated the market with around 29.3% share in 2024.
- By therapeutic class, the oncology segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By delivery method, the In vivo segment captured the largest share of 79.37% in the market in 2024.
- By delivery method, the EX vivo segment is likely to grow at the highest CAGR in the upcoming period.
- By end-user, the cancer centers segment led the market with a 40.18% share in 2024.
- By end-user, the hospitals segment is expected to grow at the fastest pace during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. cell and gene therapy market is a rapidly expanding segment of the biopharmaceutical industry focused on treating, preventing, and potentially curing diseases by modifying or replacing genes and using cellular treatments. These therapies target a wide range of conditions, including genetic disorders, cancers, and rare diseases, offering personalized and often one-time treatment options. The market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing approvals from the FDA, significant R&D investments, and a rising number of clinical trials.
Artificial Intelligence: A Catalyst for Growth in Cell and Gene Therapy
AI has the ability to significantly revolutionize the U.S. cell and gene therapy market. AI algorithms accelerate drug discovery by analyzing vast datasets to identify potential drug targets and predict treatment outcomes. AI-driven platforms are also enhancing the design and optimization of clinical trials, improving efficiency and reducing costs. In manufacturing, AI can optimize cell culture processes and ensure product quality control. Moreover, AI enables the development of personalized medicine, tailoring therapies to individual patients based on their genetic profiles. This integration of AI is expected to lead to faster development cycles, improved success rates, and more effective therapies, ultimately transforming the cell and gene therapy landscape.
Major Trends in the U.S.
- Expanding Therapeutic Areas: The market is broadening beyond oncology to include treatments for genetic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological conditions. This expansion reflects the versatility of cell and gene therapies and their potential to address a wide range of diseases with unmet medical needs.
- Advancements in Manufacturing: There is a strong focus on improving manufacturing processes to increase scalability and reduce costs. This includes developing more efficient methods for cell culture, gene delivery, and product purification to meet growing demand.
- Personalized Medicine: The trend toward personalized medicine is growing, with therapies tailored to individual patients based on their genetic makeup. This approach aims to improve treatment efficacy and minimize side effects by targeting specific patient profiles.
- Strategic Partnerships and Investments: Companies are increasingly forming partnerships and attracting significant investments. This trend is driven by the high costs of development and the need for expertise, leading to collaborative efforts to advance research and commercialization.
Report Scope of U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 7.82 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 51.15 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 23.2% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
By Therapy Type, By Therapeutic class, By Delivery Method, By End-User |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
STEMCELL Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Miltenyi Biotec, Charles River Laboratories, Bio-Techne, Editas Medicine, CRISPR Therapeutics, Sangamo Therapeutics, Intellia Therapeutics, Poseida Therapeutics, BioLife Solutions , Cryoport, Inc. , VWR International, QuickSTAT (a subsidiary of Kuehne + Nagel), Charles River Laboratories , Parexel , Pall Corporation , Sartorius , Novartis, Bluebird Bio, Vericel Corporation, Sana Biotechnology, Beam Therapeutics, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Gilead Sciences (Kite Pharma), Pfizer |
Market Dynamics
Driver
High Unmet Medical Needs
The high unmet medical needs significantly drive the growth of the U.S. cell and gene therapy market. Diseases like cancer, genetic disorders, and rare diseases often lack effective treatments or cures, which creates a strong demand for innovative therapies. Cell and gene therapies have the potential to address these unmet needs, offering long-lasting or curative outcomes by targeting underlaying causes of diseases. This potential fuels investment and research, as companies and researchers strive to develop treatments that can transform patient outcomes. The promise of these therapies to provide long-term solutions for previously untreatable conditions is a major factor driving market growth. Consequently, the focus on addressing these needs accelerates the development and adoption of cell and gene therapies.
Restraint
High Cost and Complex Manufacturing
High costs and complex manufacturing processes of cell and gene therapies restrain the growth of the market. The development and production of these therapies are expensive, involving sophisticated technologies and specialized facilities. The high cost of treatments can limit patient access. Manufacturing these therapies is complex, requiring the need for highly skilled personnel and stringent quality control. This significantly leads to high costs. Additionally, these complex manufacturing processes can lead to production bottlenecks and supply chain challenges, hindering the widespread availability of these therapies.
Opportunity
Development of Allogenic Therapies and Improvements in Reimbursement
The development of allogeneic therapies and improvements in reimbursement create significant opportunities in the U.S. cell and gene therapy market. Allogeneic therapies, derived from healthy donors, offer the advantage of being "off-the-shelf," which can reduce manufacturing complexities and costs compared to autologous therapies. This shift could increase patient access and accelerate market growth by streamlining the treatment process. Moreover, advancements in reimbursement models, such as value-based pricing and payment plans, are helping to make these expensive therapies more affordable. As payers and manufacturers collaborate on innovative reimbursement strategies, it improves patient access and incentivizes the adoption of these potentially curative treatments.
Segment Outlook
By Therapy
Why Did the Cell Therapy Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The cell therapy segment dominated the U.S. cell and gene therapy market by holding the biggest share in 2024. This is mainly due to the high success and adoption rate of CAR-T cell therapies. Cell therapies have been in development and clinical use for a longer period than gene therapies, leading to a more established market presence. This longer history has resulted in more approved products and a greater understanding of their efficacy and safety profiles. Furthermore, cell therapies often address a broader range of diseases, including various cancers and autoimmune disorders, expanding their potential patient populations. The manufacturing processes for cell therapies are also more established, allowing for greater scalability and commercial viability.
The gene therapy segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period due to the growing pipeline of gene therapy candidates. Technological breakthroughs have improved the efficiency and safety of gene delivery methods, making treatments more effective and reducing risks. Gene therapies offer the potential for one-time cures for genetic diseases, which is a highly attractive proposition for both patients and the healthcare system. Furthermore, the increasing number of successful clinical trials and regulatory approvals for gene therapies has built confidence among investors and healthcare providers.
- In November 2024, PTC Therapeutics, Inc. announced that the U.S. FDA accelerated approval of its gene therapy for the treatment of AADC deficiency. This is the first-ever gene therapy approved in the U.S. that is directly administered to the brain.
By Therapeutic Class
What Made Infectious Disease the Dominant Segment in the Market?
The infectious disease segment dominated the U.S. cell and gene therapy market with a major share in 2024. This is mainly due to the increased focus on pandemic preparedness, driven by heightened awareness of infectious disease threats. Advances in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, have improved the ability to target and modify viral genomes, opening new therapeutic possibilities. There is an increasing recognition of the potential for cell and gene therapies to offer durable and potentially curative treatments for infections, especially those caused by drug-resistant pathogens. Growing investment and research efforts are focused on developing therapies for diseases like HIV, hepatitis, and influenza. Furthermore, the prove effectiveness of gene-based vaccine in infectious disease management bolstered the segmental growth.
- In May 2025, Moderna, Inc. announced positive interim data from a Phase 1/2 clinical study (NCT05972174) evaluating the safety and immunogenicity of its investigational pandemic influenza vaccine, mRNA-1018, in approximately 300 healthy adults aged 18 years and older. The interim results focus on a vaccine candidate targeting the H5 avian influenza virus subtype.
The oncology segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR in the upcoming period due to the high unmet need in cancer treatment. Cancer is a leading cause of death, and there is a high unmet medical need for more effective treatments. Advances in immunotherapy, particularly CAR-T cell therapy, have shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer, driving both clinical and commercial interest. Increased investment in research and development has led to a surge in clinical trials and the approval of new therapies.
- In August 2024, The U.S. FDA approved a gene therapy named Tecelra (afamitresgene autoleucel). This novel gene therapy is indicated for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy and whose tumor expresses the MAGE-A4 antigen as determined by FDA authorized companion diagnostic devices.
By Delivery Method
How Does the In Vivo Segment Dominate the U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market in 2024?
The in vivo segment dominated the U.S. cell and gene therapy market while holding the largest share in 2024. This is mainly due to its growing clinical success, scalability, and broad therapeutic potential. This approach, where genetic material is delivered directly into a patient’s body, has several advantages that contributed to its leading position. In vivo therapies eliminate the need to extract, modify, and reinfuse cells outside the body (as in ex vivo methods). This streamlines the treatment process, making it faster, less resource-intensive, and easier to scale, particularly for conditions like genetic disorders or infectious diseases. Several in vivo therapies received FDA approval or fast-track status in 2024, reinforcing confidence in this segment. These approvals also paved the way for commercial scaling, helping in vivo therapies gain a larger market share compared to more complex ex vivo approaches.
The ex vivo segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR in the upcoming period due to its precision, customization, and demonstrated clinical success, particularly in treating complex diseases like cancer and genetic disorders. Ex vivo methods are central to CAR-T cell therapies, where a patient’s T cells are extracted, genetically modified outside the body, and reinfused to target cancer cells. The success of FDA-approved therapies like Yescarta, Kymriah, and Abecma has validated the effectiveness of this approach, especially in hematologic cancers. Ex vivo therapy allows scientists to precisely edit, expand, and quality-check cells before returning them to the patient. This high degree of control improves treatment safety and efficacy, making it particularly valuable in developing personalized therapies.
By End-User
Why Did the Cancer Care Centers Contribute the Most Revenue Share in 2024?
The cancer care centers segment led the U.S. cell and gene therapy market, holding the largest share in 2024. This is mainly due to their specialized infrastructure, clinical expertise, and focus on oncology, which aligns closely with where most cell and gene therapies are currently applied. These centers are typically equipped with the advanced lab capabilities and infusion infrastructure required for handling cell-based therapies, cryopreservation, and patient monitoring. This infrastructure gives them a logistical and operational advantage over general hospitals. As awareness of cell and gene therapy has grown, more patients and providers refer to cancer centers for treatment due to their proven track record and expertise in handling high-risk therapies, further increasing patient volumes.
The hospitals segment is likely to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years, as they provide more accessible treatment locations for patients, especially those in areas without specialized cancer care centers, improving overall patient reach and therapy uptake. Many hospitals are investing in advanced facilities and training healthcare professionals to administer complex therapies, enabling them to offer cell and gene treatments that were traditionally limited to specialized centers. Moreover, growing insurance coverage and government initiatives to support advanced therapies have encouraged hospitals to expand their cell and gene therapy services, making treatments more financially viable.
Country Level Analysis: Why the U.S. is a Global Leader in the Cell and Gene Therapy Race?
- Early Scientific Breakthroughs: Many foundational discoveries in gene editing, stem cell research, and viral vector development originated in U.S. academic institutions and research centers (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9 development at UC Berkeley and MIT).
- Robust Funding Ecosystem: The U.S. attracts the highest levels of public and private investment in biotechnology, including significant NIH funding and venture capital backing for startups in the cell and gene therapy space.
- High Volume of Clinical Trials: The U.S. consistently leads in the number of cell and gene therapy clinical trials, with major hospitals and research institutions at the forefront.
- Strong Industry Presence: U.S.-based companies like Kite Pharma, Bluebird Bio, CRISPR Therapeutics (with U.S. ties), and Vertex Pharmaceuticals are among the leaders in developing and commercializing cell and gene therapies.
- Regulatory Support and Infrastructure: The FDA has created expedited approval pathways (e.g., RMAT designation), supporting faster development and access to these advanced therapies.
U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Value Chain Analysis
1. Raw Material Sourcing
This is the starting point for any CGT product. The type and quality of source materials (stem cells, viral vectors, plasmids, reagents) directly impact product safety, efficacy, and scalability.
Key Players:
- STEMCELL Technologies
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Miltenyi Biotec
- Charles River Laboratories
- Bio-Techne
2. Process Development & Cell Engineering
In CGT, modifying or engineering the cells (e.g., CAR-T cells, gene-edited iPSCs) is core to the therapy. This stage is essential for defining the therapeutic mechanism.
Key Players:
- Editas Medicine
- CRISPR Therapeutics
- Sangamo Therapeutics
- Intellia Therapeutics
- Poseida Therapeutics
3. Cryopreservation, Storage & Logistics
Many cell and gene therapies are temperature-sensitive. Maintaining product stability and viability during storage and transportation is essential, particularly for autologous treatments.
Key Players:
- BioLife Solutions
- Cryoport, Inc.
- VWR International
- QuickSTAT (a subsidiary of Kuehne + Nagel)
4. Quality Control & Regulatory Affairs
Regulatory compliance (FDA in the U.S.) ensures that therapies meet rigorous safety and efficacy standards. This step is also necessary for successful BLA (Biologics License Application) submissions. This process includes identity, potency, sterility, and genetic stability testing and preparing regulatory filings (IND, BLA).
Key Players:
- Charles River Laboratories
- Parexel
- Pall Corporation
- Sartorius
5. Clinical Trials & Therapeutic Validation
Clinical development proves the therapy’s effectiveness and safety in human populations. This is a crucial determinant of product success and future market entry.
Key Players:
- Novartis
- Bluebird Bio
- Vericel Corporation
- Sana Biotechnology
- Beam Therapeutics
6. Commercialization & End-User Delivery
After FDA approval, cell and gene therapies must be delivered to clinical settings. Success here depends on physician training, reimbursement access, and supply chain coordination.
Key Players:
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Novartis
- Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS)
- Gilead Sciences (Kite Pharma)
- Pfizer
Competitive Landscape
1. Novartis AG
Novartis is a leader in the gene therapy space, especially through its FDA-approved treatment Zolgensma for spinal muscular atrophy, showcasing its innovation in one-time, curative therapies.
2. Gilead Sciences (Kite Pharma)
Gilead, through its Kite Pharma subsidiary, has pioneered CAR-T cell therapies like Yescarta, playing a crucial role in advancing personalized cancer treatment in the U.S.
3. Bristol Myers Squibb
BMS offers Breyanzi and Abecma, two leading CAR-T therapies, and significantly contributes to expanding access to cell therapy for hematologic cancers.
4. Pfizer Inc.
Pfizer is actively developing gene therapies for rare diseases like hemophilia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, leveraging its R&D and manufacturing scale to accelerate commercialization.
5. bluebird bio, Inc.
bluebird bio focuses on genetic treatments for severe genetic disorders, including Zynteglo for beta-thalassemia and Skysona for cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy, contributing to the rare disease segment.
6. CRISPR Therapeutics
In partnership with Vertex, CRISPR Therapeutics is advancing gene-edited therapies using CRISPR-Cas9, especially for sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia, setting a foundation for gene editing in clinical practice.
7. Vertex Pharmaceuticals
Vertex co-developed Casgevy, a gene-editing therapy for sickle cell disease, marking a significant milestone in the commercialization of CRISPR-based treatments in the U.S.
8. Sarepta Therapeutics
Sarepta is a leader in gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), with multiple FDA interactions and partnerships to deliver targeted therapies to pediatric patients.
9. Legend Biotech
Legend co-developed Carvykti, a BCMA-targeted CAR-T therapy for multiple myeloma, contributing to the diversification of cell therapies in oncology.
10. Precision BioSciences
This company is developing off-the-shelf gene-edited cell therapies using its ARCUS genome editing platform, aiming to improve scalability and reduce treatment costs.
Some of these players like Novartis, Gilead, and Pfizer are expanding their businesses through acquisitions and focusing on CAR-T and gene therapies. Emerging biotech firms such as CRISPR Therapeutics and bluebird bio are advancing novel gene editing solutions. To stay ahead, these companies are leveraging partnerships, scaling manufacturing capabilities, and vertically integrating to streamline development and commercialization.
For instance, in April 2025, Novartis announced USD 23 billion investment over 5 years in U.S.-based infrastructure, ensuring all key Novartis medicines for U.S. patients will be made in the U.S. This commitment enables Novartis to expand on its current manufacturing, research and technology presence across the country with 10 facilities, including 7 brand new facilities. The production capacity will cover both active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and biologics drug substances.
U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Recent Developments
- In April 2025, Cencora has been selected by Neurotech Pharmaceuticals, Inc. to provide integrated distribution and commercialization services to support the launch of Neurotech’s cell therapy in the U.S. The U.S. FDA recently approved the therapy for the treatment of adults with idiopathic Macular Telangiectasia type 2 (MacTel).
- In April 2025, Abeona Therapeutics Inc. announced that the U.S. FDA approved its ZEVASKYN™ (prademagene zamikeracel) gene-modified cellular sheets, also known as pz-cel, as the first and only autologous cell-based gene therapy for the treatment of wounds in adult and pediatric patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), a serious and debilitating genetic skin disease. The ZEVASKYN is the only FDA-approved product to treat RDEB wounds with a single application.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. cell and gene therapy market.
By Therapy Type
-
- Stem Cells
- T Cells
- Dendritic Cells
- NK Cells
- Tumor Cells
By Therapeutic class
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Cancer
- Genetic Disorder
- Rare Diseases
- Oncology
- Hematology
- Ophthalmology
- Infectious Disease
- Neurological Disorders
- Others
By Delivery Method
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Cancer Care Centers
- Others

