U.S. Diabetic Retinopathy Market Size and Research
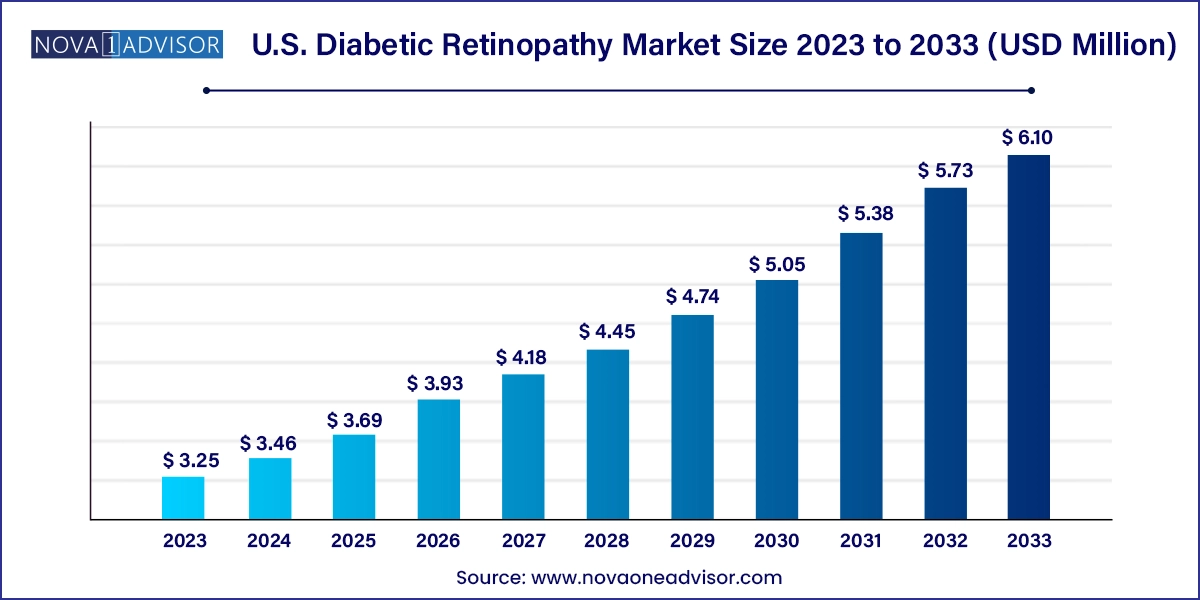
The U.S. diabetic retinopathy market size was exhibited at USD 3.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 6.10 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
U.S. Diabetic Retinopathy Market Key Takeaways:
- The Anti-VEGF segment dominated the market with a share of 91.84% in 2023.
- The non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy segment dominated the market with a share of 70.65% in 2023.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is expected to grow most over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. diabetic retinopathy market is poised for consistent expansion over the coming decade, driven by the country’s growing diabetic population, aging demographics, and increasing awareness about eye health. Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus and a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults in the United States. As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 37 million Americans have diabetes, and nearly one-third of them are expected to develop some form of retinopathy during their lifetime. This translates into a significant and continually expanding patient pool that requires long-term disease monitoring, timely intervention, and often, recurring treatments.
What differentiates the U.S. diabetic retinopathy market from others globally is its highly structured healthcare system, which encourages early screening and intervention. Advanced diagnostic modalities, robust reimbursement policies, and access to leading pharmaceutical therapies help maintain favorable conditions for market growth. Moreover, ongoing innovations in treatment—including long-acting anti-VEGF therapies, gene therapy trials, and non-invasive drug delivery systems—continue to reshape the clinical landscape of diabetic eye care.
This market is also benefiting from heightened efforts by federal and state governments to promote preventive ophthalmology. Initiatives such as annual diabetic eye exams under Medicare Part B, public health campaigns targeting underserved communities, and the integration of AI-enabled retinal screening in primary care have bolstered early detection rates. Collectively, these factors create a strong foundation for sustained growth and innovation in the U.S. diabetic retinopathy market.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rapid expansion of AI-powered retinal imaging tools in both ophthalmology and primary care clinics, enabling early detection and automated diagnosis.
-
Introduction of longer-acting anti-VEGF therapies, reducing treatment burden and improving patient compliance in chronic management.
-
Emergence of gene therapy and cell-based regenerative treatments for advanced-stage proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
-
Integration of tele-ophthalmology platforms to reach rural and underserved populations through remote retinal screenings.
-
Growing number of combination therapies (e.g., anti-VEGF + corticosteroids) for refractory cases of diabetic macular edema (DME).
-
Rising adoption of non-invasive delivery mechanisms, such as eye drops and sustained-release implants, in clinical trials.
-
Increased role of pharmacy chains and retail clinics in offering basic retinal imaging as part of chronic disease management.
-
Government and non-profit collaborations, promoting community-level diabetic retinopathy screening programs, especially for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries.
Report Scope of U.S. Diabetic Retinopathy Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 3.46 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 6.10 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 6.5% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Management |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Bayer AG; Abbvie Inc.; Novartis AG; Oxurion NV; Sirnaomics; Alimera Sciences; Ampio Pharmaceuticals Inc.; BCNPeptides; Kowa Company Ltd.; Genentech, Inc. |
U.S. Diabetic Retinopathy Market By Management Insights
Anti-VEGF therapy dominates the treatment landscape of the U.S. diabetic retinopathy market, accounting for the largest share in terms of both revenue and usage frequency. Drugs like ranibizumab (Lucentis), aflibercept (Eylea), and bevacizumab (Avastin) have set the standard for managing diabetic macular edema and preventing progression to PDR. These agents work by inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor, thereby reducing retinal swelling and halting abnormal vessel formation. The popularity of anti-VEGF therapy stems from its proven efficacy, relatively quick onset of action, and strong safety profile. With the recent introduction of longer-acting formulations, such as faricimab (Vabysmo), which also targets Ang-2 along with VEGF-A, treatment intervals are expanding—improving patient compliance and reducing clinic burden.
Intraocular Steroid Injections are emerging as the fastest-growing treatment segment, especially for patients unresponsive to anti-VEGF monotherapy or those who cannot tolerate frequent injections. Steroids like dexamethasone (Ozurdex implant) and fluocinolone acetonide (Iluvien implant) offer long-term intraocular drug release, ranging from three months to up to three years. These agents are particularly effective in reducing retinal inflammation and edema, making them suitable for chronic DME cases. The market trajectory for this segment is strengthened by ongoing clinical trials exploring new steroid molecules with fewer side effects, such as cataracts or elevated intraocular pressure. As combination therapy strategies become more prevalent, intraocular corticosteroids are poised to play a more prominent role in integrated DR management.
Laser Surgery and Vitrectomy also remain integral, especially for advanced DR cases. Laser photocoagulation continues to be used as adjunct therapy to prevent further neovascularization, while vitrectomy is a life-saving procedure for complications such as vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment. Though less frequently used than pharmacotherapy, these modalities remain essential in tertiary care settings.
U.S. Diabetic Retinopathy Market By Type Insights
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) dominated the U.S. diabetic retinopathy market by volume and value, as it represents the earliest and most common stage of the disease. In NPDR, patients may present with microaneurysms, intraretinal hemorrhages, or hard exudates, but typically without symptoms. As awareness about preventive care improves, more patients are being diagnosed with NPDR through routine retinal imaging during diabetes management. This early detection has led to a surge in demand for monitoring tools such as OCT (optical coherence tomography) and fluorescein angiography, creating a robust diagnostic ecosystem around NPDR care. Pharmaceutical strategies at this stage often focus on glycemic control and regular monitoring, though anti-VEGF therapy is increasingly being employed in moderate-to-severe cases of NPDR to prevent progression.
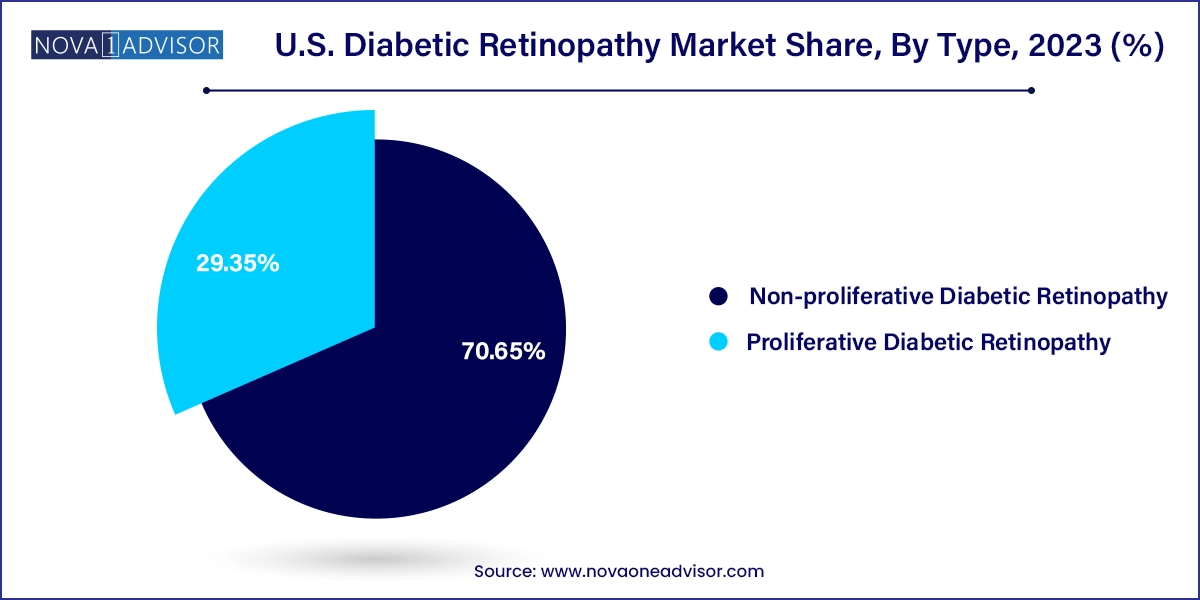
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) is the fastest-growing segment, primarily due to the rising number of long-term diabetic patients reaching advanced stages of retinal damage. PDR is characterized by neovascularization, retinal detachment, and vitreous hemorrhage, often leading to significant vision loss if not promptly treated. The growth of this segment is further driven by the increasing use of intravitreal anti-VEGF injections, surgical interventions like vitrectomy, and new therapies aimed at halting neovascular processes. As more therapies are being developed to reverse or stabilize PDR outcomes, especially in cases resistant to first-line treatments, this segment is projected to experience significant innovation and investment over the next decade.
Country-Level Analysis
The U.S. diabetic retinopathy market is uniquely positioned due to its high diabetes burden, advanced medical infrastructure, and well-established reimbursement models. States such as California, Texas, Florida, and New York report some of the highest diabetic populations, and consequently, a greater incidence of diabetic retinopathy. Urban centers are equipped with leading ophthalmology institutions and research hubs such as Bascom Palmer Eye Institute (Miami), Wilmer Eye Institute (Baltimore), and Wills Eye Hospital (Philadelphia) where innovative treatments and clinical trials are frequently initiated.
The federal government supports diabetic eye care through Medicare and Medicaid coverage, including annual dilated eye exams and many treatment procedures. Furthermore, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has advocated for routine DR screening, influencing clinical practice guidelines across the country. Private insurers have also started covering AI-based screening tools and newer intravitreal implants, expanding access beyond tertiary centers. Tele-retinal screening programs, often deployed in community health centers and Indian Health Services, are playing a pivotal role in reaching underserved populations. As digital health continues to be integrated across state-level programs, the U.S. stands at the forefront of diabetic retinopathy innovation and care delivery.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. diabetic retinopathy market include:
- Bayer AG
- ABBVIE INC.
- Novartis AG
- Oxurion NV
- Sirnaomics
- Alimera Sciences
- Ampio Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- BCNPeptides
- Kowa Company Ltd.
- Genentech, Inc.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. diabetic retinopathy market
Type
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Management
- Anti-VEGF
- Intraocular Steroid Injection
- Laser Surgery
- Vitrectomy


