U.S. E-bike Market Size and Growth
The U.S. e-bike market size was exhibited at USD 2.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 11.39 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15.7% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
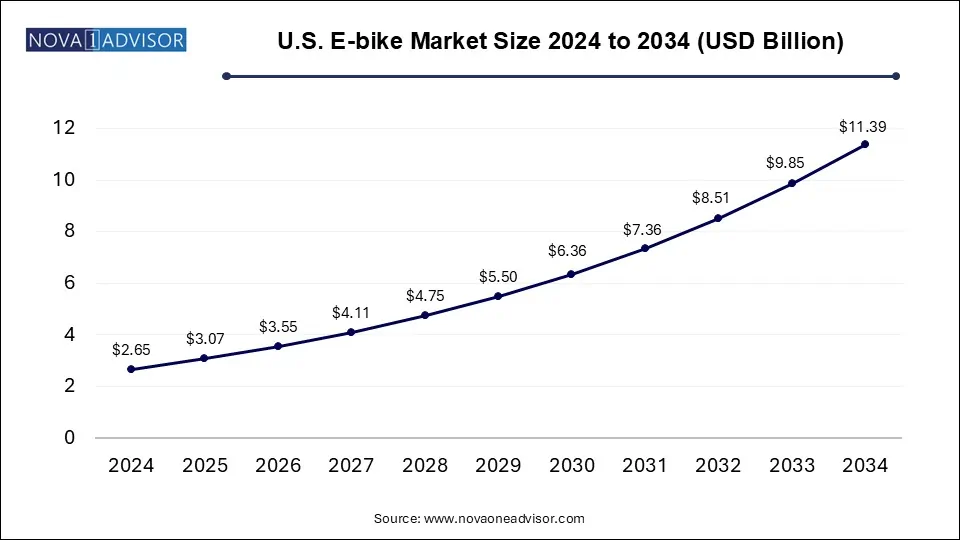
U.S. E-bike Market Key Takeaways:
- The pedal-assisted segment accounted for the largest share of over 85% of the market in 2024.
- The throttle-assisted segment is projected to grow with the fastest CAGR of over the forecast period.
- The chain drive segment accounted for the largest market share of over 91% in 2024.
- The belt drives segment is projected to grow at the highest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The trekking segment accounted for over 49% share of the market in 2024.
- The cargo segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The lithium-ion segment dominated with over 54% market share in 2024.
- The personal segment accounted for the largest share of around 92.0% of the U.S. e-bikes market in 2024.
- The commercial segment is expected to witness the highest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. electric bicycle (e-bike) market has entered a new phase of growth, evolving from a niche urban transportation option into a mainstream mobility solution. E-bikes, which integrate an electric motor to assist pedaling or provide full throttle-driven propulsion, have surged in popularity as consumers seek environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and health-conscious transportation alternatives. Whether for commuting, leisure, or delivery purposes, e-bikes offer a flexible and convenient mode of travel in increasingly congested cities.
What was once a technology embraced primarily by early adopters and fitness enthusiasts has now captured the attention of city planners, logistics companies, and average commuters. U.S. cities like New York, San Francisco, and Portland are seeing a rapid expansion in e-bike usage, with infrastructure such as bike lanes and e-bike-friendly policies reinforcing adoption. The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed a significant uptick in personal mobility solutions, leading to record sales across the bicycle industry, with e-bikes emerging as the most resilient and fastest-growing segment.
Moreover, the market is supported by government initiatives encouraging clean mobility, incentives for electric vehicle purchases, and urban sustainability goals. Several states, including California and Colorado, have launched rebate programs specifically for e-bikes, making them more accessible to low- and middle-income residents. Manufacturers are responding with improved battery life, better performance, and more specialized offerings tailored to commuting, trekking, cargo, and commercial logistics applications.
From pedal-assist to throttle-powered models, and from personal use to fleet-based operations, the U.S. e-bike market is riding a wave of growth shaped by innovation, demand diversification, and sustainability imperatives.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Popularity of Cargo E-bikes: Businesses are increasingly adopting cargo e-bikes for last-mile delivery in congested urban areas.
-
Government Subsidies and Tax Incentives: State-level rebate programs and tax credits are making e-bikes more affordable for broader demographics.
-
Integration of Smart Technologies: Features such as GPS tracking, theft prevention, connected mobile apps, and smart diagnostics are becoming common.
-
Growing Demand for Subscription and Rental Models: Companies like Lime and Revel are expanding e-bike sharing platforms in major U.S. cities.
-
Expansion of E-bike Infrastructure: Cities are investing in e-bike-friendly lanes, parking, and integration with public transit systems.
-
Surge in Lithium-ion Battery Adoption: Lightweight, long-lasting batteries are becoming standard, replacing lead-acid alternatives across most models.
-
Customization and Specialization: Brands are developing models specifically for women, seniors, and delivery personnel, expanding the user base.
Report Scope of U.S. E-bike Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.07 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 11.39 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 15.7% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Propulsion Type, Drive Type, Application, Battery, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Trek Bicycle Corporation; Aventon Bikes; Rad Power Bikes, Inc.; Lectric eBikes; Blix Electric Bikes; KHS Bicycles; Rambo Bikes; Juiced Bikes; Ride1UP; Cannondale |
Market Driver: Demand for Sustainable and Efficient Urban Mobility
One of the most powerful forces driving the U.S. e-bike market is the growing demand for sustainable, efficient, and accessible urban transportation solutions. As metropolitan areas grapple with increasing traffic congestion, air pollution, and the limitations of existing public transit infrastructure, e-bikes have emerged as an ideal solution for short-to-medium-distance travel.
E-bikes not only help reduce vehicle emissions but also offer a more practical and cost-effective alternative to cars, especially for city residents. According to the U.S. Department of Transportation, nearly 60% of all car trips are under six miles—a distance ideally suited for e-bikes. The growing awareness of climate change and the push for decarbonization at state and federal levels are reinforcing this transition. Cities are actively encouraging e-bike use through bike-sharing systems, parking incentives, and integration with multimodal transit hubs.
Further, the low cost of ownership, combined with the health benefits of pedal-assist riding, makes e-bikes an attractive proposition for environmentally conscious and cost-sensitive consumers alike. This driver is further supported by new federal proposals for an e-bike tax credit, signaling continued policy alignment with the market’s sustainable mobility goals.
Market Restraint: Regulatory Ambiguity and Safety Concerns
Despite its rapid growth, the U.S. e-bike market is constrained by inconsistencies in regulation and lingering concerns about safety. While the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has outlined basic classifications for e-bikes (Classes 1, 2, and 3), state and municipal laws vary widely, creating confusion for both consumers and manufacturers.
In some cities, Class 3 e-bikes (which can reach speeds up to 28 mph) are banned from bike paths. In others, throttle-assist e-bikes are treated like mopeds and require licensing. This regulatory patchwork complicates nationwide product rollouts and limits the scope of mass adoption, particularly in regions lacking clear e-bike guidelines.
Safety concerns are another issue. As e-bike usage rises, so have reports of crashes and battery-related fire incidents. Many riders are first-time users who may lack the training to operate at higher speeds. Additionally, inexpensive or imported e-bikes with uncertified batteries have posed fire hazards, prompting cities like New York to impose new safety standards. These factors, while addressable, continue to hinder broader market penetration.
Market Opportunity: Commercial and Delivery E-bike Applications
A major opportunity in the U.S. e-bike market lies in the commercial and delivery sector. With the explosive growth of e-commerce and food delivery services, there is an increasing need for agile, low-cost, and sustainable last-mile transportation solutions. E-bikes, especially cargo models, are perfectly suited for this role.
Companies like FedEx, Domino’s, and Uber Eats have begun piloting or expanding e-bike delivery fleets in urban areas. E-bikes offer cost savings in fuel and maintenance, faster delivery in congested zones, and a reduced carbon footprint—all of which align with ESG and cost-efficiency goals. Moreover, delivery riders benefit from easier navigation, parking flexibility, and reduced physical strain due to pedal assist.
As cities enact low-emission zones and stricter traffic regulations, traditional delivery vans are becoming less viable in dense urban areas. This opens a path for purpose-built commercial e-bikes with specialized cargo modules and smart logistics integrations. For manufacturers, this presents a high-growth B2B sales channel with recurring fleet upgrade and maintenance revenue streams.
U.S. E-bike Market By Propulsion Type Insights
Pedal-assisted e-bikes dominate the U.S. market due to their fitness appeal, intuitive design, and legal flexibility across most jurisdictions. These bikes require the rider to pedal in order to activate motor assistance, offering a natural riding experience that appeals to health-conscious consumers. They are especially popular among commuters, seniors, and recreational riders seeking extended range without the physical strain of a traditional bicycle. Additionally, pedal-assisted models are more widely accepted under state and local e-bike regulations, allowing them to be used on multi-use trails, bike lanes, and pedestrian paths.
On the other hand, throttle-assisted e-bikes are growing at a rapid pace, particularly among urban riders and delivery workers who prioritize convenience and speed over exercise. These models can be operated without pedaling, making them attractive for users who need to travel quickly, often in stop-and-go traffic. Throttle bikes are especially common in Class 2 and Class 3 categories and are finding favor in short-distance logistics and commercial applications. Despite facing some legal restrictions in specific jurisdictions, their user-friendly appeal and accessibility are fueling strong growth.
U.S. E-bike Market By Drive Type Insights
Chain drive systems are the leading drive type in the U.S. e-bike market, primarily due to their familiarity, mechanical efficiency, and ease of repair. Most mid-range and high-performance e-bikes still use chain drives, as they provide reliable torque transfer and compatibility with existing drivetrain components. Chain drive systems also support a wide range of gear options, which is important for riders in hilly areas or those using bikes for trekking and long-distance travel.
Belt drive systems, while currently representing a smaller market share, are gaining traction due to their low maintenance needs and quiet operation. Belt drives are increasingly being adopted in premium e-bike models and urban commuter designs, where cleanliness, durability, and simplicity are key selling points. Unlike chains, belts do not require lubrication and are less prone to rust or stretching. As more consumers prioritize convenience and as commercial fleets demand minimal maintenance downtime, belt drives are expected to gain a significant foothold in the market.
U.S. E-bike Market By Application Insights
City and urban e-bikes dominate the U.S. market, driven by increasing urbanization, traffic congestion, and the push for clean city transportation. Commuters are adopting e-bikes to avoid high fuel costs, eliminate parking hassles, and reduce their environmental impact. Urban e-bikes often feature sleek designs, lightweight frames, and smart connectivity—attributes that resonate with tech-savvy and environmentally conscious city dwellers. Municipal investments in cycling infrastructure are further enhancing the viability of e-bikes as a primary urban transport mode.
Cargo e-bikes, meanwhile, are the fastest growing application segment. Their utility in transporting goods, groceries, and even children makes them attractive to both commercial operators and families. With the ability to carry over 300 lbs and navigate narrow city streets, cargo e-bikes offer a compelling alternative to vans and scooters. In cities with delivery restrictions or emissions caps, cargo e-bikes offer unmatched flexibility. Manufacturers are responding with innovative modular designs, integrated GPS routing, and extended battery life tailored to logistics use cases.
U.S. E-bike Market By Battery Insights
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the U.S. e-bike market due to their superior energy density, longer lifecycle, and faster charging capabilities. These batteries power nearly all premium and mid-range models, enabling ranges of up to 75 miles on a single charge. They are lightweight, compact, and compatible with fast-charging technologies, making them ideal for urban commuting and commercial delivery use. Advances in lithium-ion chemistry, including solid-state and silicon-anode variations, are pushing the performance envelope even further.
Lead-acid batteries, once common in early e-bike models, are rapidly becoming obsolete. Their heavy weight, short lifespan, and poor cold-weather performance make them less attractive for modern riders. While they still appear in low-cost imports and entry-level models, rising safety concerns and recycling limitations are reducing their presence. U.S. consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for the performance and reliability of lithium-ion systems, effectively phasing out lead-acid from mainstream offerings.
U.S. E-bike Market By End-use Insights
Personal use is the dominant segment in the U.S. e-bike market, with consumers turning to e-bikes for commuting, leisure, and fitness. The accessibility of e-bikes across various age groups and fitness levels has expanded their appeal beyond the cycling enthusiast crowd. Whether it's young professionals replacing car commutes or retirees exploring longer trails, e-bikes are reshaping how Americans perceive urban mobility and recreation.
Commercial use is the fastest growing segment, fueled by demand from delivery services, hospitality, tourism, and corporate mobility programs. Food delivery and courier businesses are deploying e-bikes to reduce delivery times and emissions. Hotels and resorts are offering e-bike rentals as a sustainable amenity. Tech campuses and industrial parks are investing in e-bike fleets for internal mobility. These trends are opening a high-volume, high-visibility market that is redefining the role of e-bikes in commercial transportation.
Country-Level Analysis
As the sole country analyzed in this market, the United States presents a diverse and evolving e-bike landscape. Urban centers like New York, Portland, and San Francisco are at the forefront of adoption, supported by extensive bike infrastructure and e-bike sharing programs. Suburban and rural areas are also seeing growth, especially among older populations seeking mobility alternatives.
Federal efforts, such as the proposed Electric Bicycle Incentive Kickstart for the Environment (E-BIKE) Act, signal a shift toward national-level support. Meanwhile, states like California, Vermont, and Colorado are leading with robust incentive programs and educational initiatives. The U.S. consumer base is increasingly valuing performance, convenience, and sustainability—making it one of the most promising markets globally for e-bike proliferation.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. e-bike market include:
Recent Developments
-
April 2025: Rad Power Bikes announced a partnership with Uber Eats to launch commercial-grade cargo e-bikes for delivery riders in major U.S. cities.
-
March 2025: Trek Bikes unveiled a new lineup of belt-drive commuter e-bikes featuring onboard diagnostics and mobile app connectivity.
-
February 2025: California expanded its e-bike rebate program with an additional $30 million to support low-income households in switching to electric bicycles.
-
January 2025: Bosch eBike Systems launched its Smart System in the U.S., integrating real-time tracking, anti-theft technology, and performance tuning via smartphone app.
-
December 2024: Lectric eBikes opened a new manufacturing and assembly plant in Phoenix, Arizona, to meet surging domestic demand and reduce import dependency.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. e-bike market
By Propulsion Type
- Pedal-assisted
- Throttle-assisted
By Drive Type
By Application
- City/Urban
- Trekking
- Cargo
- Others
By Battery
- Lead-acid Battery
- Lithium-ion Battery
By End-use

