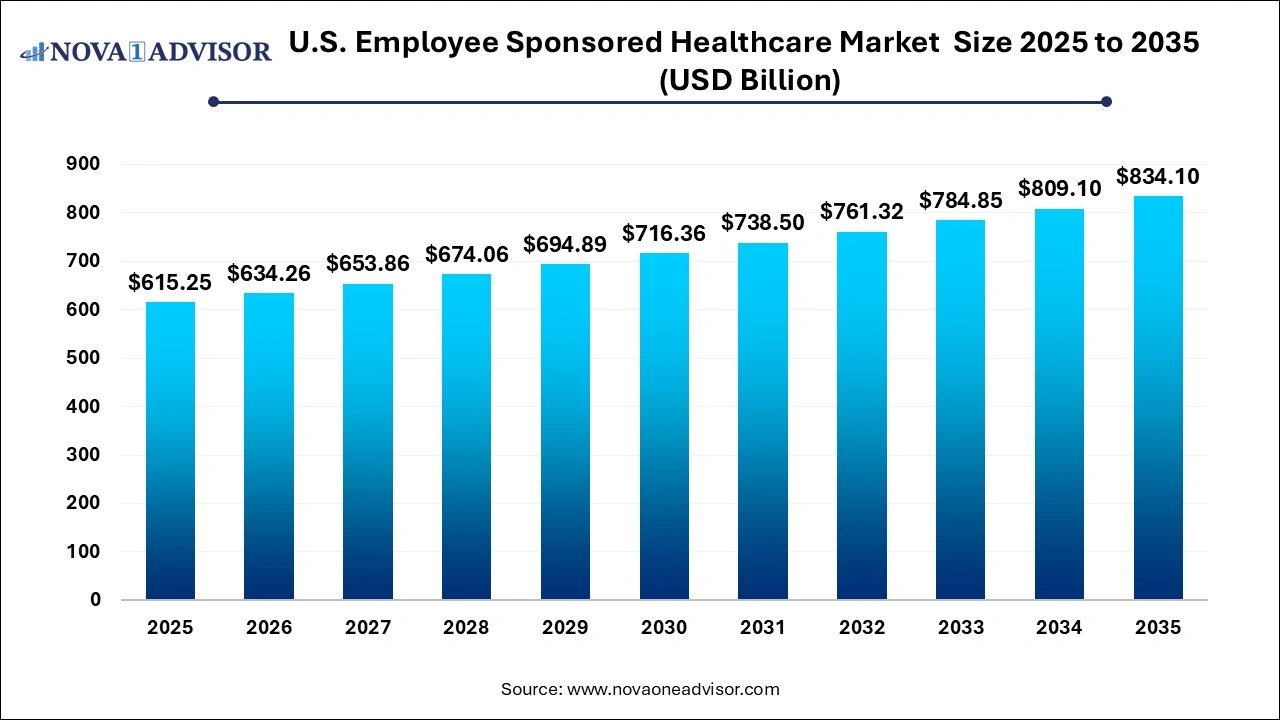
The U.S. employee-sponsored healthcare market size was exhibited at USD 615.25 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 834.10 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 3.09% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
 Key Takeaways:
Key Takeaways:
- The healthcare segment dominated the market in 2025 due to a large number of employees covered under healthcare insurance.
- The large-scale organization segment dominated the market with a share of 49.0% in 2025.
- The medium-scale organization segment is projected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years.
The U.S. Employer-Sponsored Healthcare Market continues to serve as the dominant source of health coverage for working-age Americans and their families. Employer-sponsored healthcare (also referred to as group health insurance) is a type of insurance coverage that businesses provide to their employees as part of their compensation package. This model dates back to World War II and has since evolved into a cornerstone of the U.S. healthcare financing system.
As of 2024, over 155 million Americans nearly half the U.S. population receive health insurance through their employers. The employer market comprises a diverse mix of coverage plans, including self-only and family plans, preventive wellness programs, mental health offerings, chronic disease management, and telehealth services. From small businesses with fully insured plans to Fortune 500 companies that self-fund healthcare benefits, employers are continuously adapting their offerings to attract and retain talent, reduce absenteeism, and comply with regulatory mandates.
The market operates within a dynamic framework shaped by healthcare inflation, policy reform, workforce changes, and increasing demand for personalized health experiences. Amid shifting work environments remote, hybrid, and on-site employers are reassessing benefit designs to match employee needs while keeping costs in check. The emergence of voluntary wellness programs, virtual care access, and bundled benefits are redefining the competitive landscape.
Major insurance providers such as UnitedHealthcare, Aetna, Cigna, Anthem (Elevance Health), and Blue Cross Blue Shield are key stakeholders, working alongside employers and brokers to offer customized plans. Simultaneously, new entrants like digital-first health platforms and third-party administrators (TPAs) are challenging the traditional models with more agile, tech-integrated solutions.
-
Personalization of Health Benefits: Employers are offering customizable plans based on employee demographics, health risks, and preferences.
-
Integration of Wellness and Preventive Services: Comprehensive benefits now include mental health support, gym memberships, nutrition coaching, and sleep tracking.
-
Increased Use of High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs): Employers are pairing HDHPs with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to manage premium costs and empower employees.
-
Growth of Telemedicine and Virtual Care: Virtual consultations and remote chronic care management are now core components of employee benefit packages.
-
Focus on Health Equity and Inclusive Coverage: Employers are extending benefits for LGBTQ+ families, fertility treatments, and gender-affirming care.
-
Value-Based Contracting with Providers: Employers are collaborating with insurers to adopt outcome-based reimbursement models.
-
Rise in Onsite/Shared Health Clinics: Large employers are investing in or partnering with primary care clinics near their workforce hubs.
-
Workforce Mental Health Prioritization: Digital behavioral health solutions are being bundled into core coverage to support employee resilience.
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 596.37 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 634.26 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 3.09% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Service, Organization Size |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
United HealthCare Services, Inc.; Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, Inc.; Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc.; Cigna; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association; Independence Blue Cross; Highmark Inc.; Health Net of California, Inc.; UPMC HEALTH PLAN, INC.; Nationwide Medical Insurance; ComPsych; Wellness Corporate Solutions; Virgin Pulse; EXOS; Marino Wellness; Privia Health; Vitality; Wellsource, Inc.; Central Corporate Wellness; Truworth Wellness; SOL Wellness |
Market Driver: Workforce Expectations and the Talent War
A major driver in the U.S. employer-sponsored healthcare market is the intensifying competition for talent across industries, which has pushed healthcare benefits to the forefront of workforce strategy. Employees increasingly view healthcare not as a perk, but as a core right ranking it among the top three considerations when choosing or remaining with an employer.
Especially in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, employees have grown more vocal about the need for comprehensive, flexible, and mental health-inclusive coverage. For example, a 2024 Mercer survey found that 73% of employees under age 35 would consider switching jobs for better health benefits. This pressure has led employers to enhance offerings beyond basic medical, adding mental health apps, fertility support, and caregiver assistance.
Moreover, employers are aligning healthcare benefits with their diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) strategies. Gender-affirming care, culturally competent mental health support, and chronic care plans tailored to diverse populations are becoming standard. Thus, benefits have become a strategic lever to both attract top talent and maintain workforce wellbeing solidifying demand in this market.
Market Restraint: Escalating Costs and Economic Uncertainty
One of the most significant restraints in the employer-sponsored healthcare market is the continuous rise in healthcare costs, which puts pressure on employer budgets and threatens long-term plan sustainability. According to a 2024 report by Modern Healthcare, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family coverage crossed $24,000 an increase of over 7% year-over-year. Employer contributions also rose, with small and mid-sized firms often absorbing disproportionate burdens.
The challenge is exacerbated by inflationary trends in drug prices, hospital services, and specialist care. Employers face a difficult balancing act: offering comprehensive benefits to retain talent while managing bottom-line expenses. Many respond by shifting costs to employees via higher deductibles, coinsurance, or narrower networks. This cost-sharing, however, risks reducing plan engagement and access to necessary care ultimately undermining the goal of better health outcomes.
Economic downturns or periods of market volatility further compound the issue, especially for smaller firms with tight cash flow. The inability to scale or hedge healthcare costs during lean years can cause benefit reductions, workforce dissatisfaction, and increased turnover.
Market Opportunity: Technology-Driven Wellness and Preventive Health Integration
An emerging opportunity in the market lies in leveraging technology to integrate wellness, prevention, and digital health engagement into core benefit designs. Employers are increasingly turning to data analytics, wearable integration, and mobile health tools to drive employee engagement and reduce claims costs.
For instance, some firms offer rewards for completing biometric screenings, logging physical activity through wearables, or engaging in stress management modules. Platforms such as Virgin Pulse, Omada Health, and Noom are being integrated into employer-sponsored plans, offering digital therapeutics for weight loss, diabetes prevention, or smoking cessation. Employers using data-driven insights can stratify risk and deploy targeted interventions improving employee health while reducing avoidable medical spend.
This opportunity is particularly potent among large-scale organizations and those operating under value-based care contracts. By integrating wellness with traditional coverage, employers can support population health strategies, reduce absenteeism, and demonstrate ROI from their health benefits investment.
Segmental Insights
By Service Insights
Healthcare coverage remains the dominant service in the employer-sponsored market, with employers legally obligated under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) to offer minimum essential coverage to full-time employees. Coverage typically includes hospital, surgical, preventive, and emergency care services. Within healthcare, family coverage plans form a substantial portion of the market due to rising dual-income households and dependent needs. Employers often subsidize up to 70-80% of premiums, especially in large firms, which helps keep participation high.
Wellness programs are the fastest growing service category, spurred by employer interest in preventive care and employee demand for holistic support. Programs now extend beyond traditional gym discounts and include mental health platforms, mindfulness tools, fertility support, musculoskeletal programs, and even financial wellness. In 2024, firms like Google, Salesforce, and Deloitte expanded employee wellness offerings to include burnout prevention, neurodiversity coaching, and digital health assessments. The increased integration of these services reflects a broader shift toward treating health as a spectrum prevention to recovery rather than episodic care.
By Organization Size Insights
Large-scale organizations dominate the employer-sponsored healthcare market, owing to their financial leverage, internal HR capacity, and ability to negotiate competitive rates with insurers. These firms often self-fund their health plans, allowing them to customize benefit structures, track utilization, and implement targeted wellness initiatives. Major companies like Amazon, Walmart, and JPMorgan Chase invest millions annually in internal health centers, employee navigation apps, and direct primary care partnerships.
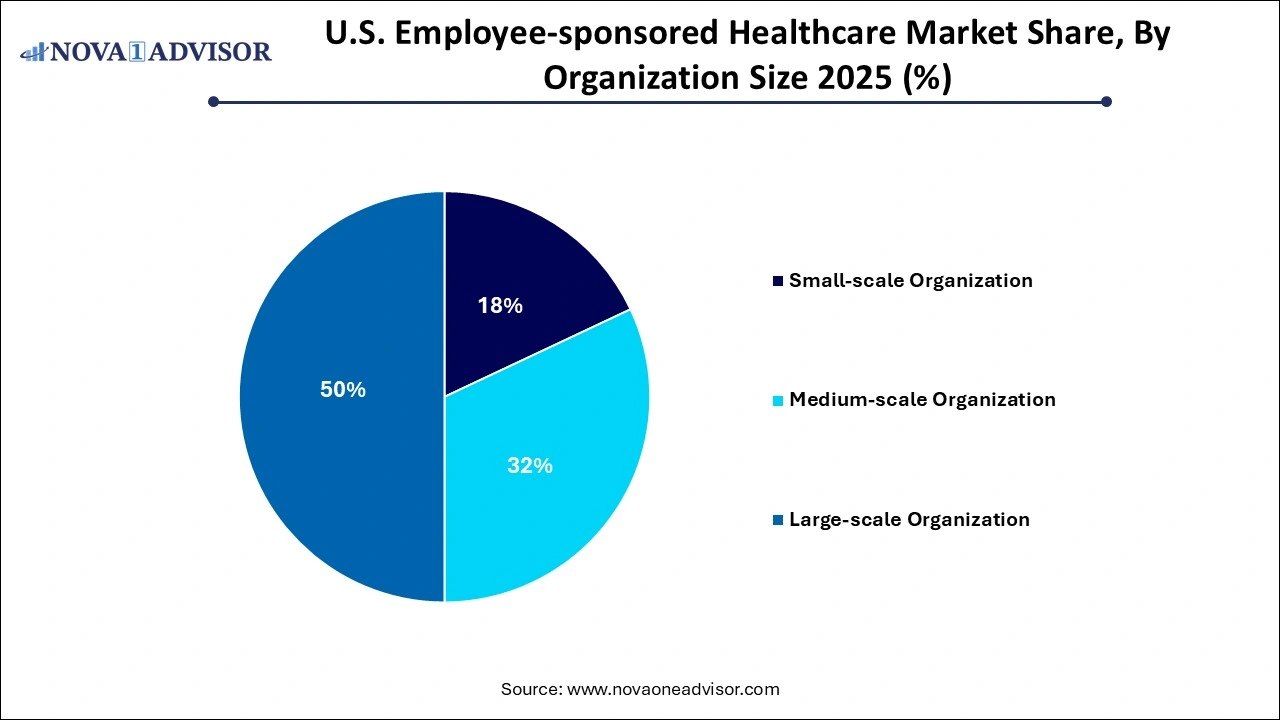
Medium-scale organizations are the fastest growing segment, driven by innovations in level-funded plans and digital-first insurance models. With between 100 and 999 employees, these firms are increasingly turning to third-party administrators (TPAs) and bundled service providers for cost control and scalability. Vendors now offer modular plans, digital enrollment, and performance-based incentives tailored for midsize employers. This has enabled these firms to offer robust benefits packages while avoiding the complexity of full self-insurance. As benefit expectations rise across the workforce, medium-scale firms are investing heavily in health programs to compete with larger peers for top talent.
Country-Level Insights – United States
In the United States, the employer-sponsored healthcare market remains the primary health insurance model for working adults and their families. The ACA continues to shape market dynamics through shared responsibility mandates, coverage benchmarks, and expanded reporting requirements. The tax-deductibility of employer-sponsored benefits also incentivizes continued participation from both employers and employees.
Geographically, adoption patterns differ based on workforce density, industry mix, and regulatory flexibility. For example, Silicon Valley firms tend to offer tech-integrated and mental health-forward plans, while manufacturing-heavy regions in the Midwest may prioritize musculoskeletal coverage and occupational health. National players adjust their benefit offerings based on federal and state compliance factors, telehealth parity laws, and consumer preferences.
The federal government also influences plan design via IRS HSA limits, CMS cost benchmarks, and pandemic-related emergency waivers. Looking ahead, shifts in policy such as proposals for public options or expanded Medicare eligibility could reshape the employer-sponsored model. However, in the near to mid-term, it remains the backbone of U.S. health insurance, especially among mid- and large-size employers.
- United HealthCare Services, Inc.
- Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, Inc.
- Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc.
- Cigna
- Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
- Independence Blue Cross
- Highmark Inc.
- Health Net of California, Inc.
- UPMC HEALTH PLAN, INC.
- Nationwide Medical Insurance
- ComPsych
- EXOS
- Wellness Corporate Solutions
- Marino Wellness
- Virgin Pulse
- Privia Health
- Wellsource, Inc.
- Vitality
- Central Corporate Wellness
- SOL Wellness
- Truworth Wellness
Recent Developments
-
March 2024 – UnitedHealthcare expanded its employer-sponsored plan portfolio with new virtual-first offerings for midsize employers, featuring embedded behavioral health and chronic care navigation.
-
February 2024 – Cigna announced an AI-powered platform for employers to track wellness engagement and forecast future claims risk based on biometric screening and wearable data.
-
January 2024 – Amazon launched a pilot health navigation service for warehouse employees, enabling personalized provider recommendations, benefit queries, and real-time claims support.
-
December 2023 – Blue Cross Blue Shield Association partnered with multiple Fortune 500 employers to test bundled maternity care packages with outcome-based provider reimbursement.
-
October 2023 – Aetna introduced an employer mental health toolkit for HR departments, featuring digital therapy partnerships, workplace peer support training, and stigma-reduction campaigns.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. employee-sponsored healthcare market
Service
-
- Self or Single Coverage
- Family Coverage
Organization Size
- Small-scale Organization
- Medium-scale Organization
- Large-scale Organization

 Key Takeaways:
Key Takeaways: