U.S. Hospice Market Size and Trends
The U.S. hospice market size was exhibited at USD 30.25 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 47.52 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.62% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
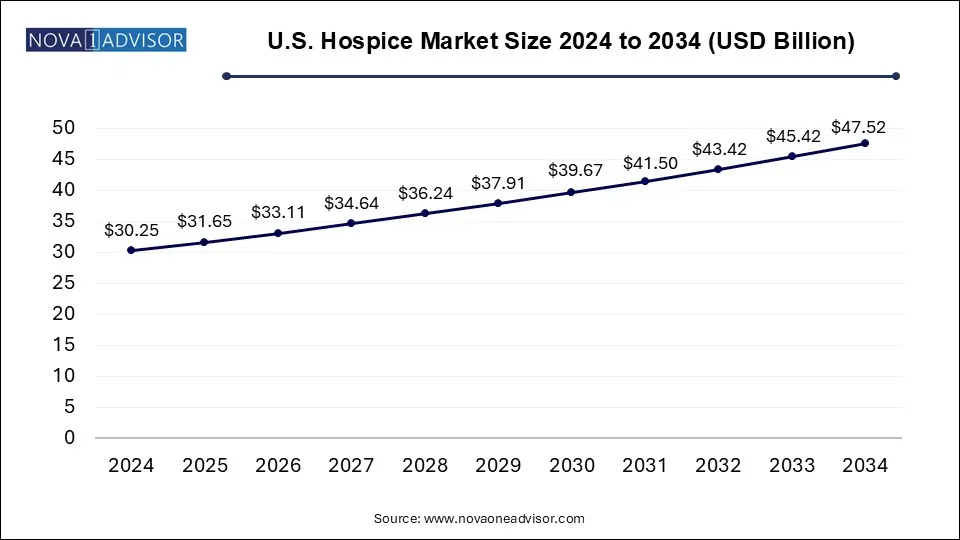
U.S. Hospice Market Key Takeaways:
- Based on type, Routine Homecare (RHC) segment dominated the market in 2024 and accounted for the largest revenue share of 92.98%.
- The inpatient respite care segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- The hospice center segment held the largest market share of 86.32% in 2024, owing to the various benefits offered by these facilities.
- The skilled nursing facility segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- The dementia segment held the largest market share of 26.0% in 2024
- The cancer segment is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. hospice market has emerged as a critical component of the nation’s healthcare system, offering comprehensive end-of-life care focused on palliative treatment and emotional support. With a demographic landscape marked by an aging population and rising prevalence of chronic and terminal illnesses, the hospice care model has increasingly been recognized for its role in enhancing patient quality of life while simultaneously optimizing healthcare costs. Hospice services are designed not to cure illness but to provide comfort, dignity, and quality of life to patients who are typically expected to live six months or less. These services are delivered by interdisciplinary teams, including physicians, nurses, social workers, spiritual counselors, and volunteers.
The growth of this market is further propelled by rising awareness about the benefits of hospice services, the expanding Medicare Hospice Benefit program, and policy support aimed at transforming the structure of care delivery. Over the past decade, hospice utilization has significantly increased among Medicare beneficiaries, and more providers—both for-profit and nonprofit—have entered the market, offering services in a range of settings including private homes, skilled nursing facilities, and dedicated hospice centers.
Healthcare reforms, reimbursement models, and the shift toward value-based care continue to influence how hospice services are delivered, measured, and reimbursed. Consequently, players in the hospice market are exploring ways to differentiate their offerings through service innovation, patient experience optimization, and expanded geographic reach.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration with Palliative Care: Many hospice providers are expanding their services to include upstream palliative care, helping to create a continuum of care before patients become eligible for hospice.
-
Technology Adoption: Use of telehealth, remote monitoring, and electronic health records (EHRs) has surged, enabling better patient tracking and reduced caregiver burden.
-
Workforce Shortages: A growing concern is the shortage of trained hospice professionals, especially nurses and home health aides, prompting investment in staff training and retention.
-
For-Profit Expansion: The rise in for-profit hospice organizations is reshaping the competitive landscape, especially in urban areas.
-
Home-Based Hospice Surge: Due to patient preference and cost-efficiency, home hospice care is becoming the most utilized setting.
-
Increased Focus on Quality Metrics: CMS and other regulators are emphasizing quality outcomes and patient satisfaction, leading to performance-based reimbursements.
-
Private Equity Investments: The hospice sector has become attractive for private equity firms, indicating high potential ROI and consolidation opportunities.
Report Scope of U.S. Hospice Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 31.65 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 47.52 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 4.62% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Location, Diagnosis |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Chemed Corporation (VITAS Healthcare); LHC Group, Inc. (UnitedHealth Group); Amedisys; Gentiva; Brookdale Senior Living, Inc; Crossroads Hospice (Agape Care Group); Seasons Hospice; Oklahoma Palliative & Hospice Care; Compassus; Chapters Health System |
Market Driver: Aging Population and Chronic Disease Burden
One of the most influential drivers of the U.S. hospice market is the aging population, particularly the surge in Baby Boomers entering retirement. As of 2024, over 77 million Americans are aged 65 and above, a figure projected to climb significantly in the coming decades. This demographic trend is closely tied to a higher prevalence of chronic diseases such as Alzheimer's, cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)—all common diagnoses for hospice admissions.
The intersection of longevity with increased comorbidity has created greater demand for specialized end-of-life care that addresses not only physical symptoms but also psychological, social, and spiritual needs. Hospice services reduce hospital readmissions, lessen intensive care utilization, and lower overall treatment costs for payers, making them a crucial pillar in the U.S. healthcare system. As awareness grows around these benefits, hospice is increasingly seen not just as a compassionate choice, but as a strategic healthcare model aligned with value-based outcomes.
Market Restraint: Regulatory Oversight and Fraud Concerns
Despite its rapid growth, the U.S. hospice market faces significant scrutiny from federal and state regulators due to increasing concerns about fraud, overutilization, and quality of care issues. Numerous reports from the U.S. Office of Inspector General (OIG) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have highlighted cases where hospice providers enrolled ineligible patients or failed to deliver adequate services, especially in the for-profit sector.
These issues have triggered tighter regulations and oversight mechanisms, including enhanced audits, stricter eligibility requirements, and the introduction of compliance programs. While these actions aim to protect patients and ensure appropriate use of Medicare funds, they also place operational and financial burdens on providers. Organizations must invest in compliance systems, training, and quality improvement programs to meet these regulatory demands, which can be particularly challenging for smaller or newly established hospice agencies.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Home-Based Hospice Services
One of the most promising opportunities lies in the continued expansion of home-based hospice care. Surveys consistently show that a majority of Americans prefer to receive end-of-life care in their own homes, surrounded by loved ones and familiar environments. This trend has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which heightened awareness of infection risks in institutional settings and led to a shift toward more personalized, in-home services.
This growing preference is supported by technological advancements, such as telehealth consultations, virtual bereavement counseling, and remote symptom monitoring. Moreover, home hospice care offers economic advantages by reducing hospital and emergency room visits, which is attractive to both payers and providers. Providers that can build robust home-based care models—bolstered by trained mobile teams and digital tools—stand to gain significant market share while enhancing patient satisfaction and outcomes.
U.S. Hospice Market By Type Insights
Routine home care remains the dominant segment in the U.S. hospice market, accounting for a substantial share of service utilization. This segment involves regularly scheduled visits by hospice professionals to a patient's residence and forms the backbone of hospice delivery in the country. The preference for routine home care stems from patient comfort, cost-efficiency, and the flexibility it offers in managing chronic symptoms without needing institutional admission. As healthcare reforms push for value-based care, payers and providers alike are endorsing routine home care as a preferred model. The integration of services like pain management, emotional support, and family education under this type further strengthens its position as the go-to hospice service.
In contrast, the continuous home care segment is growing rapidly, driven by the increasing complexity of patient conditions and the need for intensive symptom management at home. This segment provides round-the-clock nursing care during periods of acute medical crisis, helping prevent unnecessary hospitalizations. Advances in portable medical technologies and better-trained mobile hospice units have enabled this model to expand rapidly. As more families seek to manage terminal phases at home, continuous home care is likely to witness robust growth, particularly in urban areas with access to specialized care teams.
U.S. Hospice Market By Location Insights
Home hospice care leads the market in terms of location, largely due to the growing desire among patients to remain in familiar surroundings. Medicare and private insurance plans also tend to favor home-based care from a reimbursement perspective. The model has evolved significantly with the inclusion of interdisciplinary team visits, telehealth monitoring, and mobile medication administration. Additionally, families find this model emotionally and logistically preferable, as it offers flexibility, autonomy, and personalized attention. A large share of hospice enrollments under Medicare continue to be classified under home hospice care, reflecting its dominant position.
However, hospice centers have begun to grow faster in areas with dense populations or where home support systems are lacking. These dedicated facilities offer a structured environment for patients who may not have access to consistent in-home caregivers or require advanced medical interventions. Hospice centers also provide transitional care options for those shifting from hospital settings. Investments in standalone hospice centers, including those backed by healthcare systems and private equity, are expanding access and driving adoption in underserved areas.
U.S. Hospice Market By Diagnosis Insights
Cancer remains the leading diagnosis for hospice admissions in the U.S., particularly among Medicare beneficiaries. Oncology-related hospice services are well-established, with protocols that allow effective management of symptoms like pain, fatigue, and emotional distress. Hospice teams working with cancer patients often coordinate with oncologists and palliative care specialists to deliver a seamless care experience. The clear trajectory of terminal cancer stages and relatively predictable progression make patients with these diagnoses more likely to meet hospice eligibility requirements. Moreover, public awareness and support from cancer advocacy organizations have helped normalize hospice utilization among this population.
Meanwhile, dementia has become the fastest growing diagnosis category in hospice care, due to rising awareness and increasing prevalence. Alzheimer's disease and related dementias pose unique challenges due to their long and uncertain disease trajectory. Recent policy reforms and better diagnostic practices have allowed earlier identification and hospice enrollment of patients with cognitive decline. Moreover, families and caregivers are becoming more open to hospice support due to the behavioral and caregiving burdens associated with advanced dementia. As more hospice providers develop dementia-specific care programs and protocols, this segment is poised to grow significantly in the coming years.
Country-Level Analysis
In the U.S., hospice care utilization has grown steadily, with nearly 50% of Medicare decedents receiving hospice care in 2023. States such as Florida, Texas, and California lead in total hospice enrollments, reflecting both population size and a high share of aging residents. Notably, the regulatory landscape in the U.S. continues to evolve, with CMS introducing more stringent compliance requirements and quality metrics under programs such as the Hospice Quality Reporting Program (HQRP).
The U.S. market is characterized by a mix of for-profit and nonprofit providers, with large chains expanding through acquisitions and organic growth. Urban areas often see more provider competition, while rural regions face challenges related to access and staffing. The Medicare Advantage carve-in for hospice, part of the Value-Based Insurance Design (VBID) model, is also being tested in select markets, potentially reshaping how hospice services are delivered and reimbursed in the future.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. hospice market include:
- Chemed Corporation (VITAS Healthcare)
- LHC Group, Inc. (UnitedHealth Group)
- Amedisys
- Gentiva
- Brookdale Senior Living, Inc
- Crossroads Hospice (Agape Care Group)
- Seasons Hospice
- Oklahoma Palliative & Hospice Care
- Compassus
- Chapters Health System
U.S. Hospice Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Amedisys Inc. announced the opening of a new hospice care facility in Jacksonville, Florida, expanding its presence in the Southeastern U.S. This is part of its strategic initiative to enhance access to underserved markets.
-
February 2025: VITAS Healthcare launched a new telehospice platform aimed at supporting remote patient care and virtual family counseling. This marks the company’s digital transformation push amid increasing demand for home-based services.
-
January 2025: Gentiva Health Services, a new brand formed after the merger of Kindred at Home and Curo Health Services, announced its integration plans to standardize hospice care protocols across its network.
-
November 2024: Enhabit Inc. completed its acquisition of a regional hospice operator in the Midwest to strengthen its geographic footprint and clinical capabilities.
-
September 2024: The National Partnership for Healthcare and Hospice Innovation (NPHI) launched a national initiative to develop dementia-specific hospice protocols, targeting quality improvements across member organizations.
U.S. Hospice Market By Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. hospice market
By Type
- Routine Home Care
- Continuous Home Care
- Inpatient Respite Care
- General Inpatient Care
By Location
- Hospice Center
- Hospital
- Home Hospice Care
- Skilled Nursing Facility
By Diagnosis
- Dementia
- Circulatory/Heart
- Cancer
- Respiratory
- Stroke
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Others

