U.S. mHealth Apps Market Size Trends Analysis and Forecast till 2034
The U.S. mHealth apps market size was estimated at USD 12.75 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 37.53 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 11.4% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2034. The growth of the market is driven by rising smartphone penetration, increasing chronic disease prevalence, and a strong focus on digital health and remote patient monitoring.
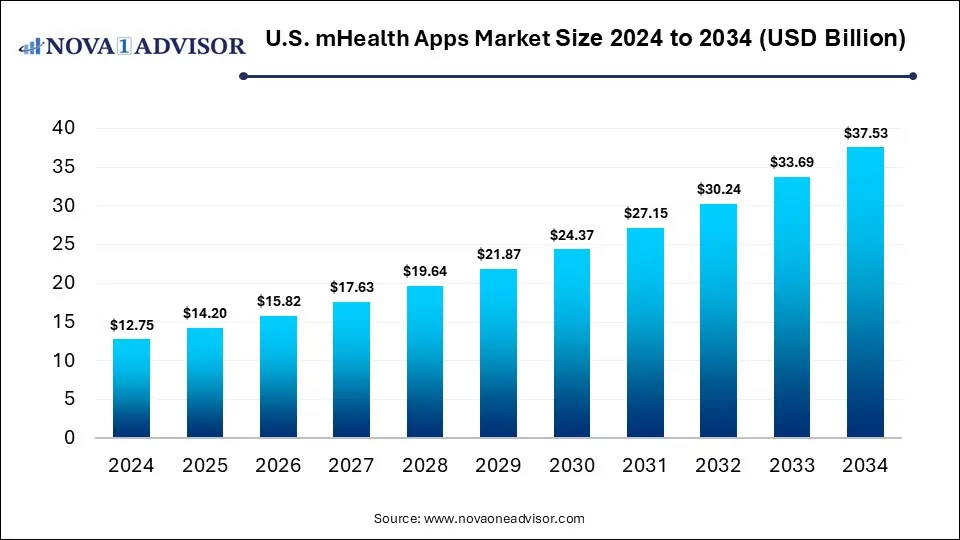
Key Takeaways
- By type, the medical apps segment held the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By type, the fitness apps segment is expected to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period.
- By platform, the iOS segment led the market in 2024.
- By platform, the android segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR over the projection period.
How is AI Impacting the U.S. mHealth Apps Market?
AI is profoundly impacting the U.S. mHealth apps market by enabling more personalized, accurate, and efficient healthcare solutions. Through machine learning algorithms and data analytics, AI-powered apps can offer tailored health recommendations, predictive diagnostics, and early detection of medical conditions. This enhances patient engagement and supports proactive disease management, improving overall health outcomes. Additionally, AI automates routine tasks like symptom checking and medication reminders, reducing the burden on healthcare providers. As AI technology continues to evolve, it is driving innovation and expanding the capabilities of mHealth apps, making them more valuable and widely adopted.
- In July 2025, Samsung Electronics announced that it will roll out a beta version of its AI-powered health coach within the Samsung Health app in the U.S. by the end of this year. The chatbot analyzes users' health data to help incorporate doctors' prescriptions and medical advice into daily routines. The feature allowed users to access health records from wearables, manage medications, and track food intake.
Market Overview
The U.S. mHealth apps market encompasses mobile applications designed to support health and wellness through remote monitoring, disease management, fitness tracking, and telemedicine services. These apps offer numerous benefits, including improved patient engagement, enhanced access to healthcare services, real-time health data tracking, and better chronic disease management. They enable users to manage their health conveniently, reduce hospital visits, and promote preventive care. The market is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing smartphone penetration, supportive government policies, advancements in technology such as AI and wearable integrations, and rising chronic disease prevalence.
- According to a report published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in February 2024, an estimated 129 million people in the U.S. have at least one major chronic disease, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, obesity, or hypertension. Five of the top 10 leading causes of death are linked to preventable and treatable chronic conditions. The prevalence of these diseases has steadily increased over the past two decades and is expected to continue rising.
Major Market Trends
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI-powered mHealth apps are increasingly offering personalized health insights, predictive analytics, and smarter disease management, enhancing both user experience and clinical outcomes.
- Need for Remote Monitoring: mHealth apps enable patients to track vital signs, medication adherence, and symptoms in real time from the comfort of their homes. This capability enhances preventive care, reduces the burden on healthcare facilities, and promotes continuous engagement between patients and providers.
- Increased Demand for Mental Health Apps: There is a growing demand for apps addressing mental health, providing tools for stress management, therapy, meditation, and mood tracking, reflecting rising awareness and acceptance.
- Wearable Device Compatibility: mHealth apps are increasingly designed to sync with wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers, allowing real-time health data collection and more accurate monitoring.
Report Scope of U.S. mHealth Apps Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 14.20 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 37.53 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 11.4% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
By Type, By Platform |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Apple Inc., Google LLC, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Fitbit, Inc. MyFitnessPal, Inc., Teladoc Health, Inc., Medisafe Limited, Johnson & Johnson, Ada Health GmbH, Noom, Inc., AliveCor, Inc., WellDoc, Inc., HealthTap, Inc. |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Increasing Smartphone & Internet Penetration
Increasing smartphone and internet penetration is a major factor driving the growth of the U.S. mHealth apps market, as it provides a scalable and accessible platform for delivering healthcare services digitally. With over 90% of U.S. adults owning a smartphone and widespread availability of high-speed internet, users can easily download and use apps for fitness tracking, chronic disease management, and teleconsultations. This high level of connectivity enables real-time health monitoring, remote patient engagement, and personalized health interventions without the need for in-person visits. Furthermore, mobile access empowers users across demographics, including rural and underserved populations, to participate in their healthcare more actively. As digital health becomes a core part of the healthcare ecosystem, smartphone and internet adoption continues to expand the reach and impact of mHealth applications.
Supportive Government Policies
Supportive government policies are significantly driving the growth of the market by creating a favorable regulatory and financial environment for digital health adoption. Initiatives such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reimbursement for remote patient monitoring and telehealth services have encouraged healthcare providers to integrate mHealth solutions into their practice. Additionally, legislation like the 21st Century Cures Act promotes interoperability and patient access to electronic health records, enabling smoother integration of mHealth apps with clinical systems. Government-backed funding and innovation programs further stimulate research and development in mobile health technologies. Together, these policies lower adoption barriers, enhance app credibility, and accelerate widespread use among both providers and patients.
- In July 2025, President Donald Trump announced a major initiative to digitize America’s healthcare by enabling personal health data sharing across systems and apps run by private tech companies. Joined by leaders from Google, Amazon, Apple, CVS Health, and UnitedHealth Group, he called it a vital step to modernize medical networks. Over 60 companies have joined the effort, focusing initially on chronic conditions like diabetes and obesity, using digital tools such as QR codes, mobile apps, and conversational AI to improve access and wellness tracking.
Rising Healthcare Costs
Rising healthcare costs are driving the growth of the U.S. mHealth apps market as both providers and patients seek more cost-effective ways to manage health and deliver care. mHealth apps offer affordable alternatives to traditional in-person visits by enabling remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and early disease detection, which help reduce hospital readmissions and emergency room visits. By improving medication adherence and promoting preventive care, these apps can lower long-term treatment expenses for chronic conditions. Additionally, payers and healthcare systems are increasingly adopting digital health tools to optimize resource utilization and control rising expenditures. This cost-conscious environment is fueling demand for scalable, technology-driven solutions like mHealth apps.
Restraints
Data Security & Privacy Concerns
Data security and privacy concerns significantly restrain the growth of the market because users and healthcare providers are often wary of how sensitive health information is collected, stored, and shared. High-profile data breaches and the risk of unauthorized access to personal health data undermine trust in these digital platforms. Compliance with strict regulations like HIPAA adds complexity and cost to app development, deterring some developers and limiting innovation. Additionally, many users hesitate to fully engage with mHealth apps due to fears over data misuse or insufficient transparency around privacy practices. These factors collectively slow adoption rates and create barriers to market expansion.
Regulatory Complexity and Interoperability Challenges
Regulatory complexity and interoperability challenges restrain the growth of the U.S. mHealth apps market by creating significant hurdles for developers and healthcare providers. Navigating stringent regulations such as HIPAA and FDA guidelines requires substantial time and resources, increasing development costs and slowing product launches. Additionally, the lack of standardized interoperability across various electronic health record (EHR) systems and healthcare platforms limits seamless data exchange, reducing the effectiveness and appeal of many mHealth apps. This fragmentation complicates integration into existing clinical workflows, discouraging healthcare organizations from adopting new digital tools. As a result, these regulatory and technical barriers slow market growth and innovation.
Opportunities
Demand for Personalized Care
The growing demand for personalized care creates significant opportunities in the market by driving the development of tailored health solutions that address individual patient needs. mHealth apps can leverage data from wearables, health records, and user inputs to offer customized recommendations, treatment plans, and real-time monitoring. This personalized approach improves patient engagement, adherence to therapies, and overall health outcomes, making these apps highly valuable to both consumers and healthcare providers. Moreover, advances in AI and machine learning enable increasingly sophisticated personalization, opening new avenues for innovation and differentiation in a competitive market. As patients seek more control and relevance in their healthcare, personalized mHealth apps are poised for rapid adoption and growth.
- In June 2025, Welldoc announced it will power the new Lilly Health app with its cardiometabolic digital platform to support patients using Eli Lilly’s incretin-based therapies for conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes. The app, initially available for users of Zepbound® or Mounjaro®, offers medication logging, reminders, device connectivity, and health tracking. Lilly and Welldoc aim to enhance the patient experience with personalized support and educational resources.
Telemedicine Integration
Telemedicine integration creates significant opportunities in the U.S. mHealth apps market by enabling seamless virtual consultations and continuous remote patient monitoring, which improve access to care and convenience for patients. By combining telehealth services with mHealth apps, healthcare providers can offer more comprehensive, real-time care outside traditional clinical settings. This integration helps reduce healthcare costs, minimize hospital visits, and enhance chronic disease management by maintaining constant patient-provider communication. The post-pandemic surge in telemedicine adoption has accelerated demand for integrated digital health platforms, making mHealth apps an essential tool in modern care delivery. As telemedicine continues to expand, apps that support this ecosystem are well-positioned for strong growth.
What Macroeconomic Factors are Impacting the Growth of the U.S. mHealth Apps Market?
Economic Growth and GDP
Economic growth and rising GDP primarily drive the growth of the market by increasing overall healthcare spending and enabling both consumers and providers to invest more in digital health solutions. A strong economy boosts disposable income and healthcare budgets, facilitating greater adoption of innovative technologies like mHealth apps. Conversely, slower economic growth could limit these investments, potentially restraining market expansion.
Inflation and Disposable Income
Rising inflation can restrain the growth of the market by reducing consumers’ disposable income, making them less likely to spend on non-essential health apps or devices. Higher costs of living may lead users and healthcare providers to prioritize essential expenses over digital health solutions. However, in some cases, inflation-driven healthcare cost pressures can also drive demand for affordable remote care options like mHealth apps to help manage expenses.
U.S. Tariffs
U.S. tariffs generally restrain the growth of the market by increasing the cost of imported hardware components like smartphones, wearables, and medical devices that integrate with these apps. Higher tariffs can lead to increased prices for consumers and healthcare providers, potentially limiting adoption rates. However, since mHealth apps are primarily software-based, the overall impact is more indirect and less pronounced compared to hardware-dependent sectors.
Segment Outlook
Type Insights
Why Did the Medical Apps Segment Dominate the U.S. mHealth Apps Market?
The medical apps segment dominated the market while holding the largest share in 2024 and is expected to sustain its dominance throughout the forecast period. This is primarily due to the increasing demand for remote patient monitoring, disease management, and personalized healthcare solutions. With rising cases of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and mental health disorders, patients and providers are increasingly turning to mobile apps for continuous health tracking and care coordination. These apps enable real-time data sharing, medication reminders, and virtual consultations, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing hospital visits. Moreover, healthcare providers and payers in the U.S. are increasingly integrating medical apps into digital health ecosystems, which has further boosted their adoption.
Another major contributor to the segment’s dominance is the growing investment in digital health infrastructure and the favorable regulatory environment supporting telehealth and digital therapeutics. Medical apps that manage specific conditions, like diabetes management, mental health support, and cardiac monitoring, have become essential tools in value-based care models. Additionally, innovations in AI and data analytics embedded within these apps have improved diagnostic accuracy and treatment personalization. The increasing collaboration between app developers, healthcare providers, and insurers has also created a robust ecosystem that continues to fuel the growth of the segment.
The fitness apps segment is expected to expand at a significant rate in the upcoming period, driven by surging health consciousness and shifting lifestyle preferences. As Americans increasingly prioritize preventive wellness over reactive care, fitness apps offering personalized workout plans, nutritional guidance, and real-time activity tracking are gaining widespread appeal. This momentum is further amplified by deep integration with wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness bands, which enable seamless monitoring of metrics such as heart rate, steps, calories burned, and sleep patterns. The post-pandemic shift toward home-based and hybrid fitness models also contributes to growth, as users seek digital alternatives to gyms for convenience, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness
U.S. mHealth Apps Market Size 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Medical Apps |
7.4 |
8.31 |
9.33 |
10.49 |
11.78 |
13.23 |
14.87 |
16.7 |
18.75 |
21.06 |
23.64 |
| Fitness Apps |
5.36 |
5.89 |
6.49 |
7.14 |
7.86 |
8.64 |
9.5 |
10.45 |
11.49 |
12.63 |
13.89 |
What Made iOS the Dominant Segment in the Market in 2024?
The iOS segment dominated the U.S. mHealth apps market, capturing the largest share in 2024. This dominance stems largely from Apple’s strong foothold in the U.S., where iPhones and the Apple ecosystem enjoy widespread adoption, particularly among healthcare professionals and tech-savvy users. iOS’s tight integration with health-focused tools such as HealthKit, the Apple Watch, and support for Health Records API, allows seamless syncing of critical health data and enriches app functionality. Additionally, Apple’s stringent App Store quality, security, and privacy standards foster trust among users and developers, especially important for sensitive health applications, solidifying iOS’s leadership in the mHealth space.
The android segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the projection period. This is mainly due to the broad affordability and widespread accessibility of Android devices across varying income levels expand the potential user base, particularly among diverse and lower-income demographics such as Medicaid users. Android’s open ecosystem encourages developers to build customizable and scalable mHealth solutions, which are especially effective in public health initiatives, chronic disease management, and personalized wellness offerings. Additionally, Android apps benefit from seamless integration with Google Fit and a wide range of wearable devices, enhancing user experience and encouraging adoption among health-conscious consumers.
U.S. mHealth Apps Market Size 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Android |
5.1 |
5.65 |
6.26 |
6.95 |
7.7 |
8.53 |
9.46 |
10.48 |
11.61 |
12.87 |
14.26 |
| iOS |
7.01 |
7.84 |
8.76 |
9.8 |
10.96 |
12.25 |
13.7 |
15.31 |
17.12 |
19.14 |
21.39 |
| Others |
0.64 |
0.71 |
0.79 |
0.88 |
0.98 |
1.09 |
1.22 |
1.36 |
1.51 |
1.68 |
1.88 |
U.S. mHealth Apps Market Value Chain Analysis
1. Research & Development (R&D)
This stage involves conceptualizing, designing, and developing mHealth applications based on medical needs, user demand, and regulatory compliance. It includes collaboration between software developers, healthcare professionals, and data scientists to build evidence-based, secure, and user-friendly solutions tailored to fitness, chronic disease management, mental health, or telemedicine services.
2. Regulatory Compliance & Approval
Before launch, mHealth apps, especially those classified as medical devices or handling protected health information (PHI), must comply with U.S. regulations like HIPAA, FDA guidelines, and HHS interoperability rules. This stage ensures that the app meets safety, privacy, and interoperability standards, reducing legal risk and building trust with users and providers.
3. Platform Development & Integration
Developers integrate mHealth apps with operating systems (iOS, Android), wearable devices, and third-party services like Apple HealthKit, Google Fit, and electronic health records (EHRs). Strong backend infrastructure and API compatibility are essential here to ensure seamless performance, scalability, and user data synchronization across healthcare systems and personal devices.
4. Marketing & Distribution
This stage includes launching the app on platforms such as the Apple App Store or Google Play, along with digital marketing, partnerships with healthcare providers, insurers, and wellness platforms. Marketing efforts focus on educating users about the app’s value, driving downloads, and encouraging retention through targeted campaigns and community engagement.
5. End-User Adoption & Engagement
Patients, caregivers, fitness users, and healthcare providers interact with the app, using it for health tracking, virtual consultations, reminders, or remote monitoring. Success at this stage depends on the app's usability, personalization, engagement features, and the perceived value it provides in improving health outcomes or convenience.
6. Data Management & Analytics
Apps collect and analyze user data to offer personalized insights, improve app performance, and support clinical decision-making. This stage is increasingly powered by AI and machine learning, transforming raw health data into actionable intelligence while ensuring secure data storage and adherence to privacy laws.
7. Feedback & Continuous Improvement
User reviews, clinical feedback, and performance analytics inform ongoing updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements. Continuous improvement ensures the app remains competitive, relevant to evolving healthcare needs, and compliant with changing regulations and user expectations.
Top Companies in the U.S. mHealth Apps Market
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Garnet Health launched its redesigned mobile app, optimized for iOS 18 and Android 15, enhancing digital access for patients and providers. The app improves the patient experience by offering healthcare resources anytime, anywhere.
- In September 2024, Magellan Health, a U.S.-based healthcare company, launched a Teen Mental Wellbeing app for ages 13-22, powered by BeMe Health’s digital platform. The app promotes self-understanding, builds resilience, and supports mental wellbeing using science-backed tools and evidence-based methods.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- Medical Apps
- Women's Health
- Fitness & Nutrition
- Menstrual Health
- Pregnancy Tracking & Postpartum Care
- Disease Management
- Menopause
- Others
- Chronic Disease Management Apps
- Obesity Management Apps
- Mental Health Management Apps
- Diabetes Management Apps
- Blood Pressure and ECG Monitoring Apps
- Cancer Management Apps
- Other Chronic Disease Management Apps
- Personal Health Record Apps
- Medication Management Apps
- Diagnostic Apps
- Remote Monitoring Apps
- Others (Pill Reminder, Medical Reference, Professional Networking, Healthcare Education)
- Fitness Apps
By Platform

