U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
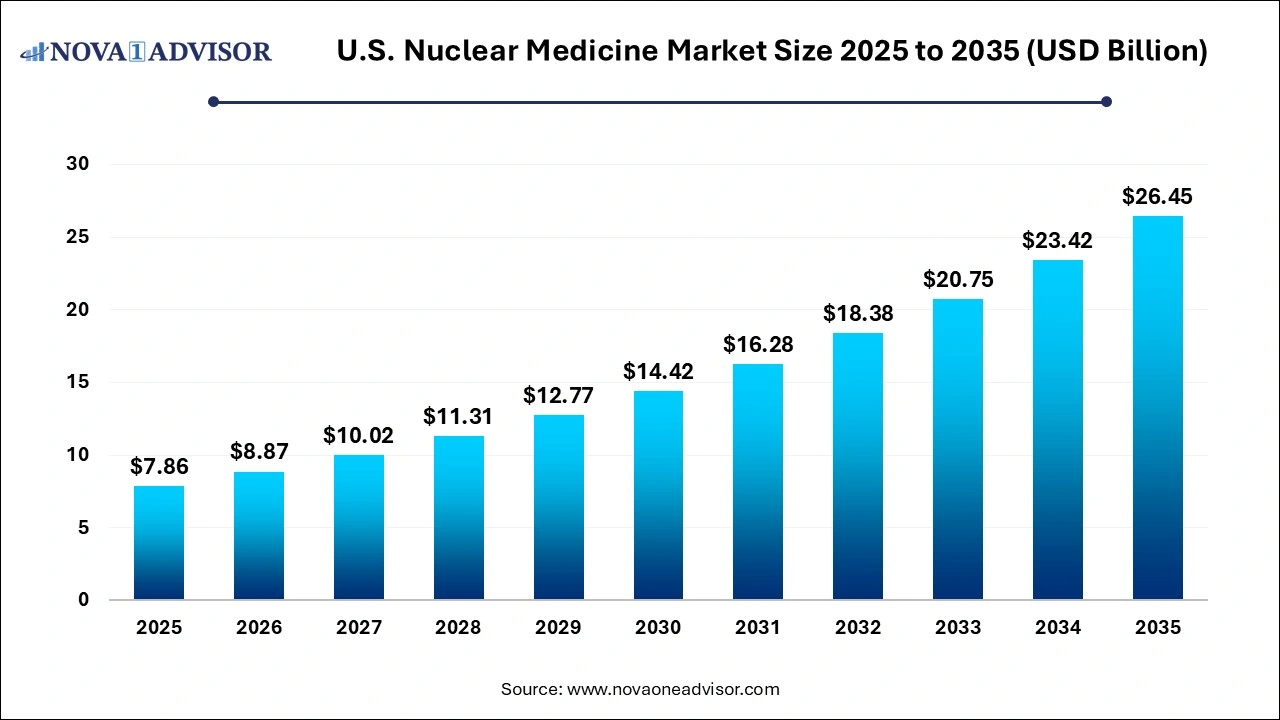
The U.S. nuclear medicine market size was valued at USD 7.86 billion in 2025 and is projected to surpass around USD 26.45 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 12.9% over the forecast period of 2026 to 2035.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Key Takeaways
- The diagnostic products segment dominated the market and accounted for 72% of the global revenue in 2025.
- The therapeutic products segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- Hospitals & clinics dominated the market with the largest share in 2025.
- The diagnostic centers segment is projected to witness significant growth rate over the forecast period.
- The oncology segment dominated the market with the largest share 25.85% in 2025.
- The endocrine tumor segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Artificial Intelligence: The Next Growth Catalyst in U.S. Nuclear Medicine
AI is profoundly reshaping the U.S. nuclear medicine industry by enhancing image reconstruction and quality in PET/CT, allowing for higher resolution and reduced noise. AI-powered software is streamlining workflows by automating tasks like lesion segmentation and reporting, which significantly reduces the workload on clinicians. The technology is crucial for advancing theranostics and personalized medicine, with AI enabling precise dosimetry and predictive modeling of patient response to radiopharmaceutical therapies.
Value Chain Analysis of the U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market
- Raw Material Sourcing & Upstream Supply: This stage involves sourcing raw materials like molybdenum-99 (Mo-99), Iodine-131, and Actinium-225, which are often produced in nuclear research reactors or high-energy accelerators.
Key Players: Nordion Inc., NTP Radioisotopes, Eckert & Ziegler, and NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes.
- Manufacturing & Radiopharmaceutical Synthesis (Midstream): Radioisotopes are processed, purified, and chemically labeled with targeting molecules in specialized "hot cells" to create ready-to-administer diagnostic or therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals.
Key Players: Cardinal Health, Curium Pharma, Novartis, Lantheus Holdings, and Jubilant Life Sciences.
- Distribution & Logistics: Due to the short half-lives, this stage requires a highly specialized, time-critical logistics network that delivers radiopharmaceuticals directly from manufacturers to hospitals and imaging centers.
Key Players: Cardinal Health and RLS Radiopharmacies.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Overview
The U.S. nuclear medicine market is undergoing a robust transformation, fueled by advancements in molecular imaging, increasing demand for targeted radiotherapies, and the rising burden of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological disorders. Nuclear medicine, which utilizes small amounts of radioactive material (radiopharmaceuticals) to diagnose and treat disease, is a cornerstone of personalized medicine in the United States.
This field comprises two primary components: diagnostic imaging such as Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and therapeutic nuclear medicine, including targeted alpha therapy, beta-emitting isotopes, and brachytherapy. With a growing emphasis on precision diagnostics and minimally invasive therapies, the nuclear medicine ecosystem is witnessing a surge in R&D activities, FDA approvals, and strategic collaborations.
The U.S. holds a dominant global position due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong academic research environment, and early adoption of next-generation isotopes and delivery platforms. Furthermore, initiatives by the Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to expand domestic radioisotope production, reduce reliance on foreign supply, and promote theranostics (therapeutics + diagnostics) are shaping the future of nuclear medicine.
In recent years, nuclear medicine has gained prominence in oncology for early tumor detection, staging, and treatment response monitoring. Agents such as 18F-FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose) and lutetium-177-based therapies are changing clinical paradigms. As the market evolves, radiopharmaceuticals are being paired with artificial intelligence (AI), hybrid imaging modalities, and digital health platforms heralding a new era in precision medicine.
Major Trends in the U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market
-
Theranostics Expansion: Dual-purpose agents combining diagnostics and therapeutics are gaining clinical traction, especially in prostate and neuroendocrine tumors.
-
Domestic Radioisotope Production Initiatives: The U.S. government is investing in local Tc-99m and Lu-177 production to secure supply chains.
-
Alpha Emitters Gaining Momentum: New clinical trials using RA-223 and other alpha-emitting isotopes are expanding therapeutic frontiers.
-
Growth in Outpatient Nuclear Imaging Centers: Decentralized diagnostic services are driving access to advanced imaging tools across urban and suburban areas.
-
AI and Image Processing Integration: AI-driven image analysis is improving detection accuracy and interpretation speed in nuclear imaging.
-
Increasing Use of PET Imaging in Cardiology and Neurology: F-18 and RB-82 are increasingly used for myocardial perfusion and brain metabolism mapping.
-
Personalized Cancer Radiotherapy: Tailored treatment protocols using molecular markers and radioisotopes are becoming standard practice.
-
Brachytherapy Renaissance: Brachytherapy sees renewed interest due to precise tumor targeting with reduced systemic side effects.
-
Mini Cyclotron and Generator Innovations: Portable and on-site production technologies are addressing isotope half-life limitations.
-
Clinical Trials Boom: A wave of clinical research is validating nuclear agents for liver, pancreatic, endocrine, and breast cancers.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 8.87 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 26.45 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 12.9% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, application, end-use, country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Eckert & Ziegler; Curium; GE Healthcare; Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd.; Bracco Imaging S.P.A ; Nordion (Canada), Inc.; The Institute For Radioelements (IRE); NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd.; Eczacıbaşı-Monrol; Lantheus Medical Imaging; Inc.; The Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization; Novartis (Advanced Accelerator Applications); Siemens Healthineers AG. |
Market Driver: Rising Incidence of Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases
A major growth driver for the U.S. nuclear medicine market is the rising incidence of cancer and cardiovascular diseases, both of which are leading causes of mortality in the country. According to the American Cancer Society, over 1.9 million new cancer cases were diagnosed in the U.S. in 2024, and heart disease remains the number one cause of death.
Nuclear imaging, particularly PET and SPECT, enables early detection, functional evaluation, and monitoring of these diseases. In oncology, radiopharmaceuticals such as 18F-FDG help detect metabolic activity in tumors well before anatomical changes are visible on CT or MRI. This facilitates early diagnosis, accurate staging, and real-time monitoring of therapy responses.
In cardiology, Tc-99m and RB-82-based myocardial perfusion imaging is widely used to evaluate coronary artery disease. The availability of high-sensitivity imaging tools improves clinical decision-making and patient outcomes, particularly in high-risk populations. With aging demographics and increasing comorbidity rates, the demand for nuclear medicine-based diagnostics and therapeutics continues to surge.
Market Restraint: Short Half-life of Isotopes and Supply Chain Challenges
One of the persistent restraints in the U.S. nuclear medicine market is the short half-life of many radioisotopes and the logistical complexities associated with their production and transport. Isotopes like Tc-99m, F-18, and RB-82 have half-lives ranging from minutes to hours, requiring highly coordinated manufacturing and distribution systems.
Most radiopharmaceuticals must be produced in cyclotrons or nuclear reactors and delivered to imaging centers within a narrow time window. Any delays or disruptions due to equipment failure, regulatory issues, or transportation bottlenecks—can result in canceled diagnostic procedures, delayed treatments, and significant cost burdens for healthcare providers.
Additionally, until recently, the U.S. heavily relied on imported molybdenum-99 (the precursor of Tc-99m), raising concerns about supply chain security. While domestic production efforts are ramping up, the infrastructure gap remains a limiting factor for widespread market scalability, especially in rural and underserved regions.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Theranostics in Prostate and Neuroendocrine Cancers
A game-changing opportunity in the market lies in the expansion of theranostic approaches using the same or similar agents for both imaging and therapy in prostate and neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). FDA approvals of Lutathera (Lu-177-DOTATATE) for NETs and Pluvicto (Lu-177-PSMA-617) for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) have validated this approach.
In theranostics, a diagnostic scan is first performed using a PET agent such as 68Ga-DOTATATE or 68Ga-PSMA to identify eligible patients. If the target is confirmed, the patient is treated with a similar therapeutic isotope conjugate, such as Lu-177-DOTATATE or Lu-177-PSMA. This ensures personalized and highly targeted treatment with minimal systemic toxicity.
The success of this model is prompting investment in new theranostic agents, clinical trials, and infrastructure upgrades in nuclear medicine departments. As research expands into other tumor types like breast, liver, and brain cancers, the theranostics wave is expected to reshape the therapeutic landscape in the U.S.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market by Product Insights
Diagnostic products dominate the U.S. nuclear medicine market, particularly SPECT and PET agents. Tc-99m remains the most widely used radioisotope in SPECT imaging due to its ideal half-life and gamma-ray emission properties. It is used extensively in bone scans, myocardial perfusion imaging, and thyroid scans. PET products like F-18 FDG and RB-82 are experiencing high adoption in oncology and cardiology, respectively. The F-18 isotope has become a gold standard for metabolic imaging in cancer care.
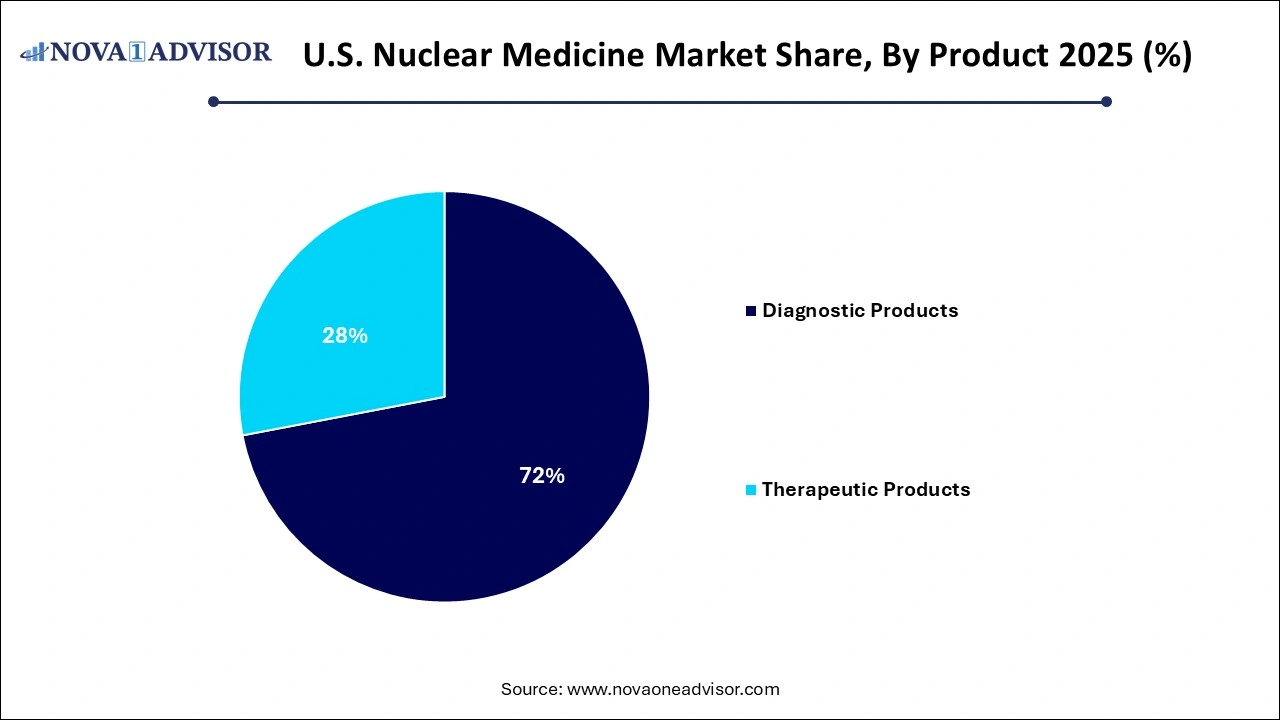 Therapeutic products are the fastest-growing segment, with Lu-177, I-131, and RA-223 at the forefront of clinical use. Beta emitters dominate therapeutic applications for thyroid cancer, bone metastasis, and neuroendocrine tumors. Alpha emitters like RA-223 are gaining interest due to their potent cytotoxicity over short distances, making them ideal for bone metastasis. Brachytherapy products such as Cesium-131 and Iodine-125 are also experiencing renewed application in prostate and brain cancers, especially with image-guided systems.
Therapeutic products are the fastest-growing segment, with Lu-177, I-131, and RA-223 at the forefront of clinical use. Beta emitters dominate therapeutic applications for thyroid cancer, bone metastasis, and neuroendocrine tumors. Alpha emitters like RA-223 are gaining interest due to their potent cytotoxicity over short distances, making them ideal for bone metastasis. Brachytherapy products such as Cesium-131 and Iodine-125 are also experiencing renewed application in prostate and brain cancers, especially with image-guided systems.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market by End-use Insights
Hospitals and clinics are the dominant end-users, benefiting from in-house radiopharmacies, SPECT/PET scanners, and specialist teams. These facilities perform a high volume of nuclear imaging and therapeutic procedures, particularly for cancer, cardiac, and thyroid patients. Academic medical centers often serve as hubs for nuclear medicine research and clinical trials.
Diagnostic centers are the fastest-growing end-user category, owing to the decentralization of imaging services. Independent and outpatient imaging facilities are investing in compact SPECT/CT and PET/CT systems, driven by increasing referrals, cost-efficiency, and rapid turnaround. These centers are improving access to nuclear medicine in non-urban settings and contributing to broader adoption.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market by Application Insights
Oncology remains the largest application area, accounting for the majority of both diagnostic and therapeutic nuclear medicine procedures. PET/CT scans using F-18 FDG are widely employed for staging cancers, assessing treatment efficacy, and detecting metastasis. The rise of PSMA and DOTATATE-targeted agents has further solidified nuclear medicine’s role in cancer care. Moreover, Lu-177-based radiotherapeutics have demonstrated excellent outcomes in patients with metastatic tumors.
Cardiology is another major and growing application, particularly due to the prevalence of coronary artery disease. Tc-99m SPECT is widely used for stress testing, while RB-82 PET imaging is gaining preference for myocardial perfusion studies due to higher image resolution. The ability of nuclear imaging to evaluate myocardial viability and perfusion in real-time makes it critical in cardiac patient management and revascularization decisions.
Country-Level Analysis
The United States holds a leadership position in the global nuclear medicine market, backed by a strong regulatory framework, robust R&D pipeline, and established nuclear infrastructure. The FDA has approved multiple radiopharmaceuticals and maintains active engagement with developers through the Drug Development Tool (DDT) program and expedited approval pathways.
In recent years, the U.S. Department of Energy has prioritized domestic production of Mo-99 and Lu-177 isotopes, reducing reliance on foreign suppliers. National labs and private firms are collaborating to develop cyclotron and reactor-independent technologies. Moreover, the American College of Nuclear Medicine and the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) are playing vital roles in standardizing protocols and training.
Academic institutions, including MD Anderson Cancer Center, Mayo Clinic, and Memorial Sloan Kettering, are pioneering clinical applications and trials of novel nuclear agents. In parallel, the rise of commercial imaging chains and contract radiopharmacies is boosting access and scalability. The U.S. market is poised for long-term growth as new therapeutic isotopes and delivery systems enter the clinic.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Novartis received FDA approval for Pluvicto (Lu-177-PSMA-617) for PSMA-positive metastatic prostate cancer following successful Phase 3 trial results.
-
February 2025: Bracco Imaging launched a new F-18 labeled brain imaging agent targeting beta-amyloid plaques, with clinical use in early Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
-
January 2025: Curium Pharma expanded its U.S. radiopharmacy network to increase regional production and delivery capacity for Tc-99m and Lu-177-based products.
-
December 2024: Actinium Pharmaceuticals initiated a Phase 1 trial for an alpha-emitting radiotherapeutic in relapsed lymphoma, marking the company's expansion into solid tumors.
-
November 2024: Telix Pharmaceuticals partnered with a major U.S. hospital network to deploy 68Ga-PSMA PET imaging agents for prostate cancer diagnostics across 30 centers.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Top Key Companies:
- Eckert & Ziegler: Eckert & Ziegler is a primary global provider of isotope technology, specializing in the development and manufacturing of radiopharmaceuticals for cancer therapy and nuclear-medical imaging.
- Curium: Curium operates as a vertically integrated world leader in radiopharmaceuticals, supplying approximately 47% of its global revenue through its extensive U.S. operations.
- GE HealthCare: GE HealthCare holds a leading position by integrating AI-powered PET/CT and SPECT/CT imaging systems with a robust network of domestic nuclear pharmacies.
- Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd. (Jubilant Radiopharma): Jubilant Radiopharma maintains the second-largest radiopharmacy network in the U.S., serving over 1,800 healthcare providers and delivering more than 3 million doses annually.
- Bracco Imaging S.p.A.: Bracco Imaging contributes as a critical provider of diagnostic imaging agents and medical devices used across multiple modalities, including nuclear medicine.
- Nordion (Canada), Inc.: A division of Sotera Health, Nordion is a leading global supplier of medical isotopes, specifically focusing on the reliable production of Cobalt-60 and other critical radioactive materials.
- The Institute For Radioelements (IRE): The Institute for Radioelements (IRE) is a major global producer of molybdenum-99 (Mo-99) and iodine-131, which are essential precursors for the majority of diagnostic scans in the U.S.
U.S. Nuclear Medicine Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Nuclear Medicine market.
By Product
- Diagnostic Products
- SPECT
- TC-99m
- TL-201
- GA-67
- I-123
- Other SPECT Products
- PET
- F-18
- SR-82/RB-82
- Other PET products
- Therapeutic Products
- Alpha Emitters
- Beta Emitters
- I-131
- Y-90
- SM-153
- Re-186
- Lu-117
- Other Beta Emitters
- Brachytherapy
- Cesium-131
- Iodine-125
- Palladium-103
- Iridium-192
- Other Brachytherapy Products
By Application
- Cardiology
- SPECT
- PET
- Therapeutic Applications
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Thyroid
- SPECT
- Therapeutic Applications
- Lymphoma
- Bone Metastasis
- Therapeutic Applications
- Endocrine Tumor
- Pulmonary Scans
- Others
By End-use
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others


 Therapeutic products are the fastest-growing segment, with Lu-177, I-131, and RA-223 at the forefront of clinical use. Beta emitters dominate therapeutic applications for thyroid cancer, bone metastasis, and neuroendocrine tumors. Alpha emitters like RA-223 are gaining interest due to their potent cytotoxicity over short distances, making them ideal for bone metastasis. Brachytherapy products such as Cesium-131 and Iodine-125 are also experiencing renewed application in prostate and brain cancers, especially with image-guided systems.
Therapeutic products are the fastest-growing segment, with Lu-177, I-131, and RA-223 at the forefront of clinical use. Beta emitters dominate therapeutic applications for thyroid cancer, bone metastasis, and neuroendocrine tumors. Alpha emitters like RA-223 are gaining interest due to their potent cytotoxicity over short distances, making them ideal for bone metastasis. Brachytherapy products such as Cesium-131 and Iodine-125 are also experiencing renewed application in prostate and brain cancers, especially with image-guided systems.