U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
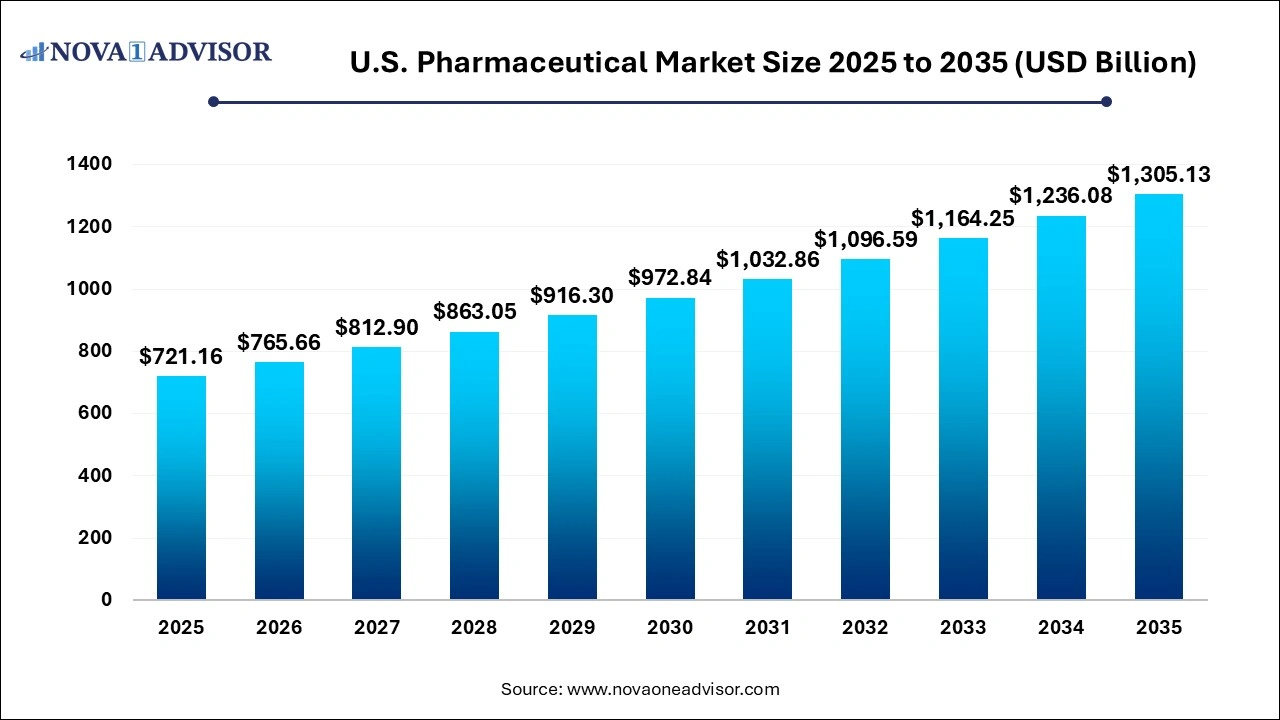
The U.S. pharmaceutical market size was valued at USD 721.16 billion in 2025 and is projected to surpass around USD 1,305.13 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 6.11% over the forecast period of 2026 to 2035.
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Key Takeaways
- Based on molecule type, the market for conventional drugs (small molecules) dominated the market with a revenue share of 57% in 2025.
- The biologics& biosimilar segment is expected to witness growth with the fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2035.
- The branded segment dominated the pharmaceutical market with a revenue share of 69% in 2025.
- The prescription segment held a dominant revenue share of 89% in 2024 in the market
- Based on disease, the cancer segment dominated the overall market with share of 16.79% in 2025.
- The neurological disorders segment is expected to witness growth with fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2035.
- Based on the route of administration, the oral route dominated the market with a revenue share of 60 % in 2025.
- The parenteral route of administration is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- Tablets held the largest market share in 2024 in the pharmaceuticals market.
- The sprays segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
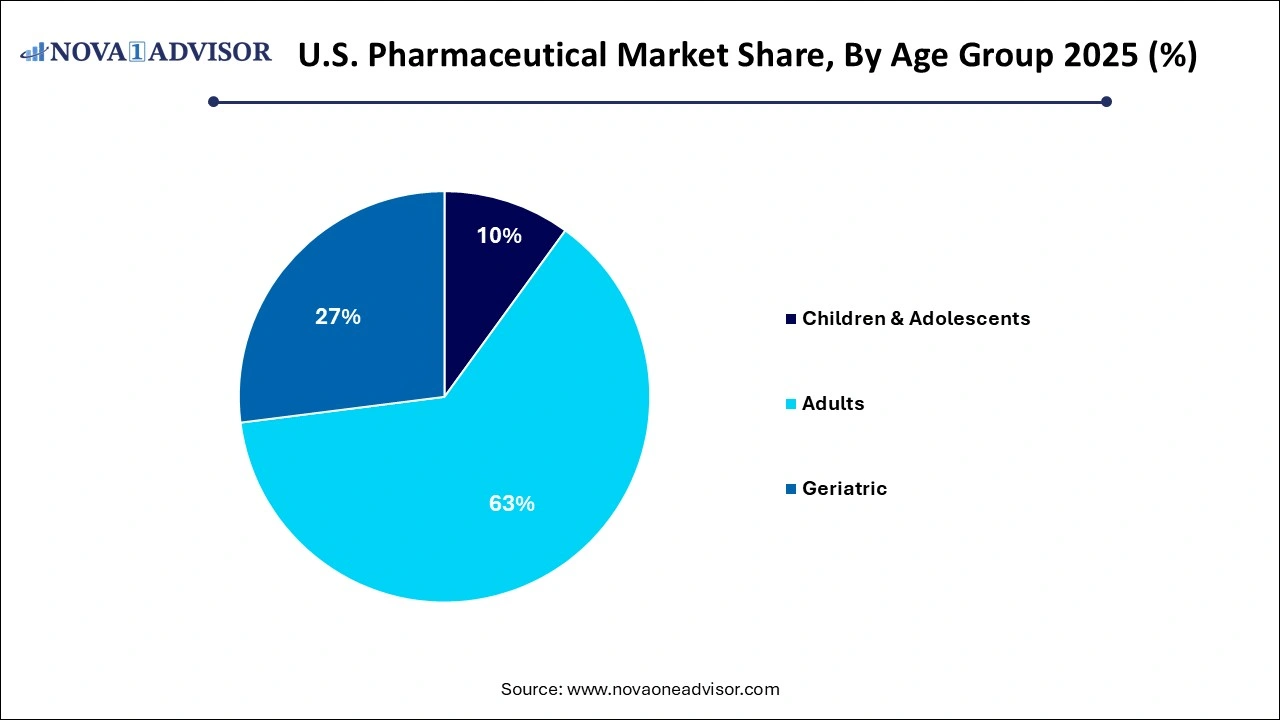
- The adult segment held the largest share of 63.00% in the pharmaceuticals market in 2025 and is further expected to advance at the fastest growth rate over the forecast period.
- The children & adolescent segment is expected to witness steady growth from 2026 to 2035.
- Based on the end market, the hospitals segment dominated the pharmaceuticals market, with a revenue share of 51.66% in 2025.
- Clinics are estimated to expand at the fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2035.
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Overview
The U.S. pharmaceutical market is the largest and most influential pharmaceutical ecosystem in the world, contributing significantly to the global healthcare sector. In 2025, the market was estimated to be worth over $600 billion, driven by a combination of cutting-edge R&D, robust healthcare infrastructure, and the presence of leading pharmaceutical giants. With an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and a steady demand for innovative therapies, the U.S. pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve rapidly.
The pharmaceutical sector in the United States encompasses a wide spectrum, ranging from small molecule drugs to large molecule biologics, covering everything from mass-produced generics to highly specialized gene therapies. Federal regulations, particularly from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), play a pivotal role in shaping product pipelines, clinical trial protocols, and approval timelines. While the U.S. maintains a premium pricing model for drugs, insurance schemes like Medicare and Medicaid, and recent policy pushes for drug pricing reforms, continue to shape the competitive dynamics.
In recent years, the country has witnessed a transformative shift toward personalized medicine, driven by genomics and AI-assisted drug development. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated innovation in mRNA platforms, vaccine production, and remote healthcare solutions, setting the stage for continued digital and biological convergence in pharmaceutical R&D.
Major Trends in the U.S. Pharmaceutical Market
-
Acceleration of Biologics and Gene Therapy: Advanced therapies such as monoclonal antibodies and cell-based interventions are gaining regulatory traction and market demand.
-
Digital Therapeutics Integration: Growing adoption of AI, wearables, and digital apps to supplement or enhance pharmacological treatment plans.
-
Rising Popularity of Specialty Pharmaceuticals: High-cost, high-impact drugs designed for niche conditions like multiple sclerosis, hemophilia, or certain cancers are driving revenue.
-
Patent Expiries and Biosimilar Growth: A wave of blockbuster biologics losing exclusivity is opening the door for biosimilars.
-
Consolidation through M&A Activity: Pharmaceutical majors are acquiring smaller biotech firms to expand pipelines and accelerate innovation.
-
Telepharmacy and Online Dispensing Models: The rise of Amazon Pharmacy and other digital platforms is redefining drug distribution.
-
Increased FDA Fast-track Approvals: Especially for oncology and rare disease therapies, leading to quicker time-to-market.
-
Pressure on Drug Pricing Transparency: Legislative efforts like the Inflation Reduction Act are forcing companies to rethink pricing strategies.
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 765.66 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 1,305.13 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 6.11% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Molecule Type, Product, Type, Disease, Route of Administration, Formulation, Age Group, End market |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbvie; Astrazeneca; Bristrol Myers Squibb; GSK Johnson & Johnson; Merck & Co; Novartis Pfizer; Roche HoldingSanofi |
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Segment Insights
By Molecule Type Insights
Biologics & Biosimilars dominated the U.S. pharmaceutical market in 2025, thanks to a surge in monoclonal antibody approvals and high demand for biologics in treating cancer and autoimmune diseases. Biologics are not only more effective in targeting complex molecular pathways but also tend to command premium prices. AbbVie's Humira and Merck’s Keytruda are prime examples of blockbuster biologics that have reshaped therapeutic strategies and revenue models. The increasing availability of biosimilars is driving market competition while making biologics more accessible.
Within this segment, Cell & Gene Therapy is experiencing the fastest growth. The FDA approved over 20 gene and cell therapies in 2023, marking a new era of regenerative medicine. These therapies offer potentially curative outcomes for diseases previously considered untreatable, such as spinal muscular atrophy and inherited retinal disorders. Companies like Novartis and bluebird bio are expanding their pipelines aggressively, and new startups are gaining VC interest at a rapid pace.
By Product Insights
Branded drugs account for the largest share of the U.S. pharmaceutical market due to their continued dominance in specialized therapy areas like oncology, immunology, and rare diseases. These products command high prices and generate substantial revenue during their exclusivity period. Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck continue to rely heavily on their branded portfolios to maintain leadership.
On the other hand, generics are witnessing renewed growth, particularly after the expiration of patents for several high-revenue drugs like Revlimid and Tecfidera. Generic manufacturers like Teva, Mylan, and Sandoz are capitalizing on these openings while improving manufacturing technologies and compliance systems. Government incentives to reduce healthcare costs have also made generics a favorable option for Medicaid and Medicare programs.
By Type Insights
Prescription medications dominate the U.S. pharmaceutical market due to the complexity and specialization of treatments, especially in chronic and life-threatening diseases. FDA-regulated prescription drugs are the mainstay for managing cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological disorders, requiring physician oversight and controlled dispensation.
However, Over-the-Counter (OTC) drugs are expanding, particularly in preventive and lifestyle-related categories. Companies are launching OTC formulations for allergies, heartburn, and minor mental health concerns like mild anxiety. In 2024, Perrigo received FDA approval to convert a popular contraceptive to OTC status, reflecting a broader trend towards empowering patients through self-medication for certain conditions.
By Disease Insights
Cancer treatment dominates the U.S. pharmaceutical landscape, both in R&D funding and market revenue. Immunotherapies, targeted small molecules, and combination regimens have transformed cancer into a more manageable disease in many cases. Drugs like Opdivo, Keytruda, and Lynparza are being increasingly used in earlier lines of therapy, thereby expanding their patient base and market size.
Meanwhile, neurological disorders are witnessing accelerated growth in drug development. The FDA's conditional approval of Biogen’s Aduhelm (for Alzheimer’s) in 2022, and Eisai’s Leqembi in 2023, signaled a resurgence of interest in neurological therapeutics. Ongoing research into Parkinson’s, ALS, and rare pediatric neurodegenerative diseases reflects a growing demand and investor confidence in this area.
By Route of Administration Insights
Oral formulations remain the most preferred and widely used route of drug administration in the U.S. They offer ease of use, better patient compliance, and are suitable for both acute and chronic treatments. The majority of generic drugs are formulated as oral tablets or capsules.
In contrast, Parenteral routes, especially intravenous (IV) and intramuscular (IM), are gaining ground due to the rise in biologics, which often require injection or infusion. With the increasing use of monoclonal antibodies, mRNA vaccines, and gene therapies, injectable formulations are seeing double-digit growth. Pharma companies are investing in wearable injectors and auto-injector pens to make administration more patient-friendly.
By Formulation Insights
Tablets dominate the pharmaceutical market owing to their affordability, stability, and ease of mass production. This trend holds strong across both branded and generic sectors. Even for complex therapies like diabetes or hypertension, tablets remain the most common format due to daily dosing requirements.
However, injectables are rising quickly, driven by the need for targeted delivery and rapid therapeutic action. Auto-injectors and pre-filled syringes are seeing increased adoption in rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and COVID-19 vaccination efforts. Companies are innovating in drug delivery mechanisms, including nanoparticle-based injectable suspensions, to improve bioavailability.
By Age Group Insights
Adults constitute the largest user base for pharmaceuticals in the U.S., reflecting the burden of lifestyle diseases, mental health conditions, and acute infections. Working-age individuals are frequent consumers of medications for stress, cardiovascular health, diabetes, and dermatological conditions.
Nevertheless, the geriatric population is growing rapidly as life expectancy increases and baby boomers age into higher-risk health categories. The elderly are more likely to suffer from polypharmacy requiring multiple prescriptions concurrently. This demographic shift is driving demand for customized geriatric formulations, extended-release products, and drug-drug interaction management solutions.
By End Market Insights
Hospitals continue to dominate as the primary dispensing points for high-cost, high-risk medications, including cancer therapies, gene therapies, and complex antibiotics. Most parenteral drugs and therapies requiring close monitoring are administered in a hospital setting, particularly during initial treatment cycles.
However, clinics are becoming increasingly important, particularly with the growth of specialty care centers and infusion clinics. For instance, outpatient oncology centers are handling an increasing share of cancer treatments. The push toward value-based care and outpatient management is encouraging pharmaceutical firms to engage more closely with clinic networks and telehealth platforms.
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Top Key Companies:
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Recent Developments
-
Pfizer (March 2024): Announced a $43 billion acquisition of Seagen Inc. to strengthen its oncology pipeline, particularly in antibody-drug conjugates.
-
Moderna (April 2024): Launched clinical trials for its personalized cancer vaccine in collaboration with Merck, using mRNA technology.
-
Johnson & Johnson (January 2024): Received FDA approval for its CAR-T cell therapy for relapsed multiple myeloma patients.
-
Eli Lilly (February 2024): Gained FDA fast-track status for its Alzheimer’s candidate donanemab, boosting its neurology portfolio.
-
AbbVie (March 2024): Announced a biosimilar version of Humira priced at 85% of the originator to address affordability concerns post-patent expiry.
U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. pharmaceutical market.
By Molecule Type
- Biologics & Biosimilars (Large Molecules)
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Vaccines
- Cell & Gene Therapy
- Others
- Conventional Drugs (Small Molecules)
By Product
By Type
By Disease
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Infectious diseases
- Neurological disorders
- Respiratory diseases
- Autoimmune diseases
- Mental health disorders
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Women’s health diseases
- Genetic and rare genetic diseases
- Dermatological conditions
- Obesity
- Renal diseases
- Liver conditions
- Hematological disorders
- Eye conditions
- Infertility conditions
- Endocrine disorders
- Allergies
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Topical
- Parenteral
- Intravenous
- Intramuscular
- Inhalations
- Other Route of Administration
By Formulation
- Tablets
- Capsules
- Injectable
- Sprays
- Suspensions
- Powders
- Other Formulations
By Age Group
- Children & Adolescents
- Adults
- Geriatric
By End Market
By Regional
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada