U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market Size and Growth
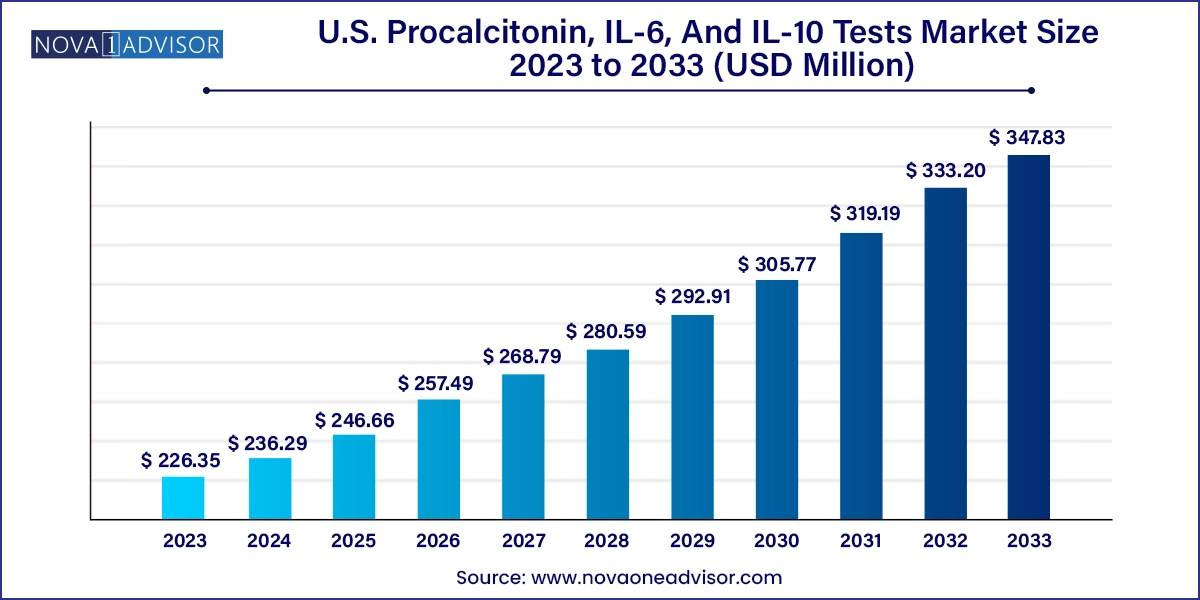
The U.S. procalcitonin, IL-6, and IL-10 tests market size was exhibited at USD 226.35 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 347.83 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.39% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market Key Takeaways:
- The inpatient patient type segment held the largest market share of 68.3% 2023 and is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 4.55% during the forecast period.
- The hospitals segment accounted for largest revenue share of 74.0% in 2023.
- The laboratories segment is expected to witness a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- The IL-6 segment accounted for largest revenue share of 59.34% in 2023.
- The insurance segment held the largest market share of 92.7% in 2023.
- The IL-6 segment accounted for largest revenue share of 59.3% in 2023.
Market Overview
The U.S. Procalcitonin (PCT), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and Interleukin-10 (IL-10) tests market represents a rapidly advancing niche within clinical diagnostics, playing a vital role in the early detection, monitoring, and management of inflammatory and infectious diseases. These biomarkers especially when used together offer crucial insights into the body’s immune response, helping differentiate between bacterial and viral infections, guiding antibiotic therapy, and predicting disease severity, especially in critical care settings.
Procalcitonin is widely regarded as a specific biomarker for bacterial infections and sepsis, while IL-6 and IL-10 provide complementary information on cytokine activity. IL-6 is associated with pro-inflammatory signaling and has become a cornerstone in sepsis, arthritis, and COVID-19 diagnostics. IL-10, on the other hand, is known for its anti-inflammatory roles and helps in understanding immune regulation, particularly in conditions like autoimmune disorders and allergies.
In the U.S., demand for these tests has surged due to heightened awareness around sepsis and antimicrobial stewardship, as well as lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic, during which IL-6 levels were critical in predicting cytokine storms. Hospitals and laboratories across the country are incorporating these tests into routine panels, and ongoing clinical trials continue to investigate their roles in conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), rheumatoid arthritis, and severe allergic responses.
As precision medicine becomes more mainstream, these biomarkers are integral to stratified patient care. Further, investments in immunodiagnostics and the expansion of molecular point-of-care platforms are making these tests more accessible outside tertiary care centers. Technological innovations, payer support, and growing clinical guidelines are setting the stage for robust market growth across the United States.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of Multiplex Immunoassay Platforms: Labs and hospitals are adopting multi-marker assays that include PCT, IL-6, and IL-10 in a single panel for efficient diagnostics.
-
Growing Role in Sepsis Management: These tests are increasingly embedded in sepsis protocols to support early detection and antibiotic stewardship.
-
Integration in COVID-19 Severity Assessments: IL-6 was prominently used during the pandemic to monitor inflammatory response and determine steroid or immunomodulator usage.
-
Increased Hospital-Based Usage: Hospitals with >250 beds are expanding in-house testing capabilities for faster turnaround and improved patient monitoring.
-
Expansion in Outpatient and Urgent Care Settings: Rapid immunochromatographic versions of PCT and IL-6 are being adopted in clinics and ambulatory care.
-
Insurance Reimbursement Improvements: CMS and private insurers are increasingly covering these tests when used for sepsis, bacterial infections, and immune disorders.
-
Research on New Clinical Applications: Studies are exploring IL-10’s utility in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), asthma, and organ transplantation tolerance.
Report Scope of U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 236.29 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 347.83 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 4.39% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Patient Type, Type, Application, End use, Payer Type, States |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
ARUP Laboratories; Promega Corporation; Quest Diagnostics Incorporated; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; BIOMÉRIEUX; Beckman Coulter, Inc.; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; QuidelOrtho Corporation |
Key Market Driver
Escalating Incidence of Sepsis and Hospital-Acquired Infections (HAIs)
One of the primary drivers fueling the U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, and IL-10 tests market is the rising incidence of sepsis and hospital-acquired infections, which are among the leading causes of mortality in critical care units. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates over 1.7 million Americans develop sepsis annually, leading to nearly 270,000 deaths. Early diagnosis is crucial, as every hour of delayed treatment significantly increases mortality risk.
Procalcitonin testing is increasingly being adopted to differentiate between bacterial and non-bacterial infections, allowing clinicians to prescribe antibiotics judiciously. IL-6 and IL-10 provide insights into cytokine activity and immune dysregulation, assisting in stratifying patient severity and monitoring response to therapies. These tests support real-time decision-making, aligning with national antimicrobial stewardship guidelines and helping reduce unnecessary antibiotic exposure, hospital stays, and healthcare costs.
Key Market Restraint
High Cost and Technical Complexity in Low-Volume Settings
Despite the clinical benefits, a notable restraint is the relatively high cost and technical demands of performing these tests, particularly in low-volume hospitals and outpatient labs. While larger hospitals can justify investments in immunoassay analyzers or multiplex platforms due to high patient throughput, smaller facilities may face challenges with capital expenses and reagent costs.
In addition, while immunochromatographic (rapid) tests for PCT exist, IL-6 and IL-10 assays often require centralized laboratory infrastructure with skilled personnel and cold-chain logistics for reagent handling. These limitations hinder adoption in community settings, especially in rural and underfunded regions, and may delay timely diagnostics. Reimbursement hurdles in some payer plans also affect utilization, although this is improving with newer clinical guidelines and CPT code expansions.
Key Market Opportunity
Expansion of Personalized Medicine and Immune Profiling
A compelling growth opportunity for this market lies in the expansion of personalized medicine and immune profiling strategies, where IL-6 and IL-10 are emerging as crucial biomarkers. These interleukins offer insights into individual immune responses, allowing physicians to tailor treatments in conditions such as autoimmune diseases, cancer, and transplant medicine.
For example, IL-6 inhibitors like tocilizumab are used in rheumatoid arthritis and COVID-19 treatment, with IL-6 tests guiding dosing and therapeutic decisions. IL-10 levels are being investigated as predictive biomarkers in allergy immunotherapy, asthma management, and even post-organ transplantation rejection monitoring. With the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and private institutions funding longitudinal biomarker studies, the incorporation of PCT, IL-6, and IL-10 into broader precision health frameworks is expected to expand, increasing demand in both clinical and research applications.
U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market By Patient Type Insights
Inpatient testing accounted for the dominant share of the market due to the critical nature of the conditions that necessitate PCT, IL-6, and IL-10 testing—primarily sepsis, bacterial infections, and inflammatory syndromes requiring ICU admission. Hospitals use these biomarkers for real-time clinical decision-making in emergency rooms, critical care units, and operating rooms. The necessity for rapid turnaround times in acutely ill patients, especially during post-operative infections or septic shock, drives high test volumes in hospital environments.
Outpatient testing, however, is the fastest-growing segment. With the growing emphasis on early diagnosis, point-of-care technologies, and the increasing burden of chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases, IL-6 and IL-10 are being considered in outpatient rheumatology, allergology, and pulmonary practices. Rapid testing kits for PCT are also making their way into urgent care centers to guide antibiotic usage, particularly for respiratory tract infections. As decentralized healthcare expands in the U.S., outpatient test adoption is poised to accelerate.
U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market By End Use Insights
Hospitals with >250 beds constituted the leading end-use category, given their capacity for advanced diagnostic infrastructure and the high volume of critically ill patients. These hospitals often maintain comprehensive cytokine panels in their internal labs and integrate PCT testing into antibiotic stewardship programs. Larger hospitals are also more likely to participate in biomarker-based clinical research, contributing to high PCT, IL-6, and IL-10 test volumes.
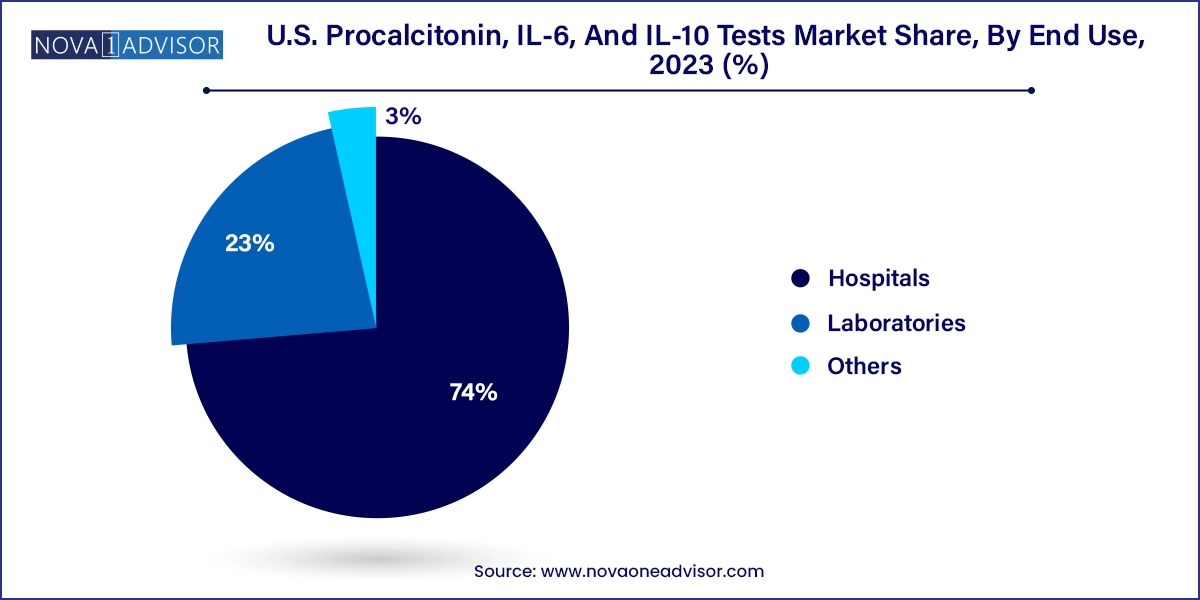
Diagnostic laboratories, both hospital-affiliated and independent, are the fastest-growing end use segment. Commercial labs are expanding their cytokine testing capabilities to cater to outpatient clinics, urgent care centers, and specialty practices. The rise of mail-in testing kits and the increased use of blood collection centers for immune profiling have further expanded testing accessibility. Labs like Quest Diagnostics and LabCorp are integrating multi-marker panels into their service offerings for infection and inflammation profiling.
U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market By Type Insights
Procalcitonin (PCT) tests led the market due to their well-established role in guiding antibiotic treatment for bacterial infections and sepsis. The immunoassay-based PCT tests are widely used in hospitals and labs, and the FDA has cleared several rapid immunochromatographic versions as well. Their specificity for bacterial infections makes them especially useful for differentiating viral from bacterial pneumonia, which gained attention during the COVID-19 pandemic. PCT has also been incorporated into clinical guidelines, making its use standard in many hospital sepsis protocols.
IL-10 tests, while newer and less widely used, are growing at the fastest pace. Their application in autoimmune disorders, allergies, and emerging areas like transplant immunology is gaining traction. Clinical trials and NIH-funded studies are exploring IL-10’s role in asthma severity, ulcerative colitis, and immunotherapy response prediction. As newer, more affordable IL-10 assay kits are launched and integrated into multiplex cytokine panels, their use is expanding across both clinical and research settings.
U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market By Payer Type Insights
Insurance coverage dominated the payer type segment, supported by Medicare, Medicaid, and private payer reimbursement policies for sepsis, infection-related hospitalization, and autoimmune diagnostics. As test utilization expands in evidence-backed settings, payers have broadened coverage, especially for PCT and IL-6 under FDA-cleared or CLIA-certified settings.
However, out-of-pocket payments are rising among outpatient users, especially in the self-pay diagnostic and wellness testing space. High-deductible plans and lack of coverage for some IL-10 and research-based IL-6 tests have prompted patients and providers to turn to direct-pay models. The growth of retail diagnostic networks and online lab portals is accelerating this trend.
U.S. Procalcitonin, IL-6, And IL-10 Tests Market By Application Insights
Sepsis-related testing dominates the application landscape for both Procalcitonin and IL-6. These tests are instrumental in detecting systemic infections and guiding early treatment, especially in critical care environments. PCT levels correlate with the presence and severity of bacterial infections, and IL-6 levels rise sharply in cytokine storm syndromes, making them valuable tools in triage and monitoring. Hospitals use serial measurements of these biomarkers to track treatment response and determine the need for escalation or de-escalation of therapy.
In the IL-10 segment, inflammatory and allergic disorders—particularly autoimmune diseases—are emerging as high-growth applications. IL-10 testing is gaining adoption in specialized centers managing conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and severe allergic asthma. Personalized immunology protocols increasingly include IL-10 profiling to assess disease severity and treatment outcomes, especially in patients on biologics or immunomodulators.
State-Level Analysis
California
California leads in overall test volumes due to its large population, advanced hospital systems, and presence of biotech hubs. Major health systems in San Francisco, Los Angeles, and San Diego offer cytokine testing routinely in infectious disease and oncology departments. The state also supports several research programs evaluating IL-6 and IL-10 in autoimmune disease and transplant tolerance.
New York
New York state, particularly through academic medical centers in NYC, is a high adopter of multiplex cytokine testing. During the COVID-19 peak, IL-6 was widely used in patient management, and since then, hospitals have continued to invest in immunodiagnostics.
Texas and Florida
Texas and Florida are emerging markets for PCT and IL-6 testing, especially in their extensive hospital networks and rural hospital expansions. Sepsis initiatives supported by Medicaid expansion in Florida have encouraged test use.
Midwest and South
States like Ohio, Illinois, and Georgia are increasingly incorporating IL-6 and IL-10 into rheumatology and pediatric allergy clinics. Hospital networks are expanding in-house testing capabilities, aided by federal grants and state-level healthcare initiatives.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. procalcitonin, IL-6, and IL-10 tests market include:
- ARUP Laboratories
- Promega Corporation
- Quest Diagnostics Incorporated
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- BIOMÉRIEUX
- Beckman Coulter, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- QuidelOrtho Corporation
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. procalcitonin, IL-6, and IL-10 tests market
Patient Type
Type
-
- Immunoassay
- Immunochromatography
- Others
Application
-
- Bacterial Infection
- Sepsis
- COPD
- Arthritis
- Others
-
- Bacterial Infection
- Sepsis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Others
-
- Bacterial Infection
- Allergies
- Inflammatory Disorders
- Others
End Use
-
- 1-100
- 101-250
- 251-500
- 500 and above
Payer Type
State
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming


