U.S. Teleradiology Market Size and Growth
The U.S. teleradiology market size was exhibited at USD 957.69 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 3,055.09 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.3% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
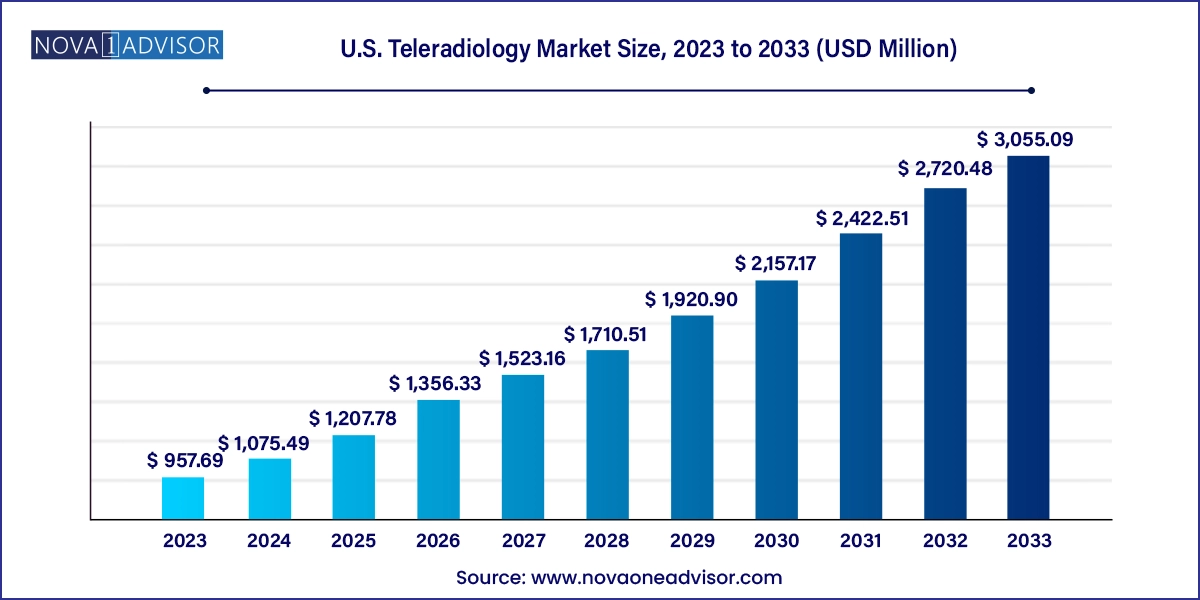
U.S. Teleradiology Market Key Takeaways:
- The X-rays segment held the largest revenue share of 28.93% in 2023.
- The market for CT scans is expected to expand at the highest CAGR of 12.8% during the forecast period.
- The preliminary tests segment held the largest revenue share above 63.26% in 2023.
- The final tests segment is anticipated to exhibit the fastest CAGR of 13.2% from 2024 to 2033.
- The hospitals segment held the largest market share of approximately 52.68% in 2023.
- The radiology clinics segment is anticipated to exhibit a CAGR of 12.5% from 2024 to 2033.
Market Overview
The U.S. teleradiology market has witnessed significant transformation over the past decade, driven by the digitization of healthcare, rapid advancements in medical imaging technologies, and increasing demand for radiology services amid a shortage of radiologists. Teleradiology involves the transmission of radiological images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs from one location to another for diagnostic and consultative purposes. This technology plays a vital role in improving access to timely and expert radiology interpretations, particularly for rural or underserved hospitals and emergency departments.
The market in the U.S. has expanded as healthcare institutions seek to optimize workflows, reduce turnaround times, and manage imaging backlogs. With growing patient volumes and the rising complexity of imaging studies, teleradiology offers a cost-effective and efficient solution. The increasing integration of PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), AI-enabled diagnostics, and cloud-based image management platforms has strengthened the infrastructure supporting remote radiology. Post-pandemic shifts toward telemedicine and remote diagnostics have further normalized the acceptance of teleradiology across hospitals, radiology groups, and outpatient imaging centers.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising adoption of AI-powered teleradiology platforms for diagnostic accuracy and speed
-
Increased demand for after-hours and subspecialty reads by remote radiologists
-
Integration of teleradiology with electronic health records (EHR) and PACS systems
-
Growth in cloud-based image sharing and diagnostic collaboration tools
-
Expansion of teleradiology services to rural and critical access hospitals
-
Consolidation in the radiology services industry through mergers and partnerships
-
Focus on compliance with HIPAA and data security in image transmission
-
Rise in cross-state radiology licensure and interstate telehealth policies
Report Scope of U.S. Teleradiology Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1,075.49 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 3,055.09 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 12.3% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Type, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Virtual Radiologic (vRad); Agfa-Gevaert Group; ONRAD, Inc.; Everlight Radiology; 4ways Healthcare Ltd.; RamSoft, Inc.; USARAD Holdings, Inc.; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Matrix (Teleradiology Division of Radiology Partners); Medica Group PLC |
Key Market Driver: Shortage of Radiologists and Subspecialists
A critical driver for the U.S. teleradiology market is the growing shortage of radiologists and subspecialists, particularly in non-urban regions. While demand for imaging services continues to rise due to an aging population and increased chronic disease prevalence, the number of radiologists entering the workforce has not kept pace. Many hospitals struggle to offer 24/7 radiology coverage, and access to subspecialty expertise in areas like neuroradiology or pediatric imaging is especially limited.
Teleradiology bridges this gap by enabling hospitals and imaging centers to outsource their radiology reads to board-certified professionals located across the country. These services ensure timely interpretations during night shifts, holidays, or peak times, reducing diagnostic delays and improving patient outcomes. The flexibility to tap into a national talent pool is particularly beneficial for small or rural hospitals that cannot afford in-house radiologists around the clock.
Key Market Restraint: Regulatory and Reimbursement Challenges
Despite its growth potential, the U.S. teleradiology market faces challenges related to regulatory complexity and reimbursement uncertainties. Teleradiology providers must navigate varying state licensure laws, credentialing requirements, and malpractice regulations, which can limit the scalability of operations across state lines. Additionally, reimbursement rates for teleradiology services are often inconsistent and may differ from traditional in-person interpretations.
Medicare and private payers have specific guidelines for reimbursing remote radiology services, and lack of standardization creates ambiguity for both providers and billing departments. Furthermore, achieving compliance with data privacy regulations such as HIPAA requires substantial investment in secure transmission systems and administrative oversight, which can pose operational burdens for smaller practices or startups.
Key Market Opportunity: AI Integration for Workflow Optimization
An emerging opportunity in the U.S. teleradiology market lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to optimize workflows and enhance diagnostic capabilities. AI algorithms are increasingly being employed for image triaging, automated anomaly detection, report generation, and clinical prioritization. These capabilities help radiologists manage large volumes of scans more efficiently, reducing burnout and improving accuracy.
AI also supports clinical decision-making by flagging critical findings such as brain hemorrhages or pulmonary embolisms, prompting immediate review. Teleradiology platforms integrating AI can offer value-added services to hospitals and clinics, improving turnaround time and diagnostic precision. Companies investing in AI-enabled platforms stand to gain a competitive edge by offering faster, more reliable, and scalable radiology services
U.S. Teleradiology Market By Product Insights
X-rays dominated the U.S. teleradiology market, owing to their widespread use across emergency departments, outpatient clinics, and trauma centers. X-ray imaging remains the most commonly performed diagnostic test due to its affordability, speed, and utility in diagnosing fractures, infections, and thoracic conditions. Teleradiology platforms are increasingly used for preliminary and final interpretation of chest X-rays, especially during off-hours and in critical access hospitals.
However, CT scans are the fastest-growing segment, driven by their expanding application in stroke assessment, cancer diagnosis, and trauma care. The ability to provide high-resolution, cross-sectional images makes CT indispensable in emergency radiology. With increasing demand for subspecialty reads and rapid interpretation of complex scans, teleradiology services for CT imaging are in high demand across U.S. hospitals.
U.S. Teleradiology Market By Type Insights
Preliminary tests account for the majority of teleradiology interpretations, especially during night shifts and weekends. Hospitals often rely on teleradiologists to provide preliminary readings that inform immediate patient management decisions. These preliminary reports are subsequently reviewed and finalized by in-house radiologists during regular hours.
In contrast, final tests are experiencing rapid growth, particularly in standalone radiology groups and outpatient imaging centers. As trust in the accuracy and reliability of remote interpretations grows, more institutions are outsourcing complete diagnostic workflows, including final reads. This shift is fueled by efficiency demands, cost savings, and access to subspecialty expertise.
U.S. Teleradiology Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals remain the largest end-users of teleradiology services, especially tertiary care institutions and emergency departments. Hospitals benefit from around-the-clock coverage and improved patient throughput by leveraging remote radiologists. Additionally, teleradiology allows hospitals to optimize staffing levels and manage peak workloads without compromising care quality.
Radiology clinics are the fastest-growing end-use segment, as independent imaging centers expand their service offerings and geographic reach. Teleradiology enables clinics to tap into subspecialty expertise, accelerate report turnaround times, and provide competitive diagnostic services to referring physicians. With the growing demand for outpatient imaging and cost-efficient diagnostics, clinics are increasingly investing in teleradiology partnerships and platforms.
Country-Level Analysis (United States)
In the United States, teleradiology has become an integral part of modern radiology practices. The country’s advanced healthcare IT infrastructure, wide adoption of digital imaging, and established regulatory frameworks make it fertile ground for teleradiology expansion. Urban hospitals rely on it to manage imaging overflow, while rural hospitals depend on it for continuous access to specialists.
Federal initiatives promoting telehealth adoption and cross-state practice, such as the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (IMLC), have further facilitated the growth of teleradiology. In addition, states with large rural populations like Texas, Montana, and North Carolina have seen higher adoption due to acute needs in access to radiology expertise. The presence of leading teleradiology providers, academic institutions, and health-tech innovators positions the U.S. as a global leader in this domain.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. teleradiology market include:
- Virtual Radiologic (vRad)
- Agfa-Gevaert Group
- ONRAD, Inc.
- Everlight Radiology;
- 4ways Healthcare Ltd.
- RamSoft, Inc.
- USARAD Holdings, Inc.
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- Matrix (Teleradiology Division of Radiology Partners)
- Medica Group PLC
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: vRad (Virtual Radiologic) expanded its AI-enhanced platform for triaging emergency cases, reducing report turnaround times by 25%.
-
January 2025: Nines Inc. announced a strategic partnership with a major hospital chain to provide 24/7 final reads across 12 states.
-
November 2024: Radiology Partners launched a teleradiology fellowship program to train radiologists in remote workflows and AI-assisted reporting.
-
September 2024: Teleradiology Solutions introduced a new HIPAA-compliant cloud platform for seamless image sharing among multi-state providers.
-
August 2024: USARAD Holdings Inc. announced the expansion of their subspecialty teleradiology services in oncology and pediatric imaging.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. teleradiology market
Product
- X-rays
- CT Scans
- MRI Scans
- Ultrasound
- Nuclear Imaging
Type
- Preliminary Tests
- Final Tests
End-use
- Hospitals
- Radiology Clinic

