Wound Dressing Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
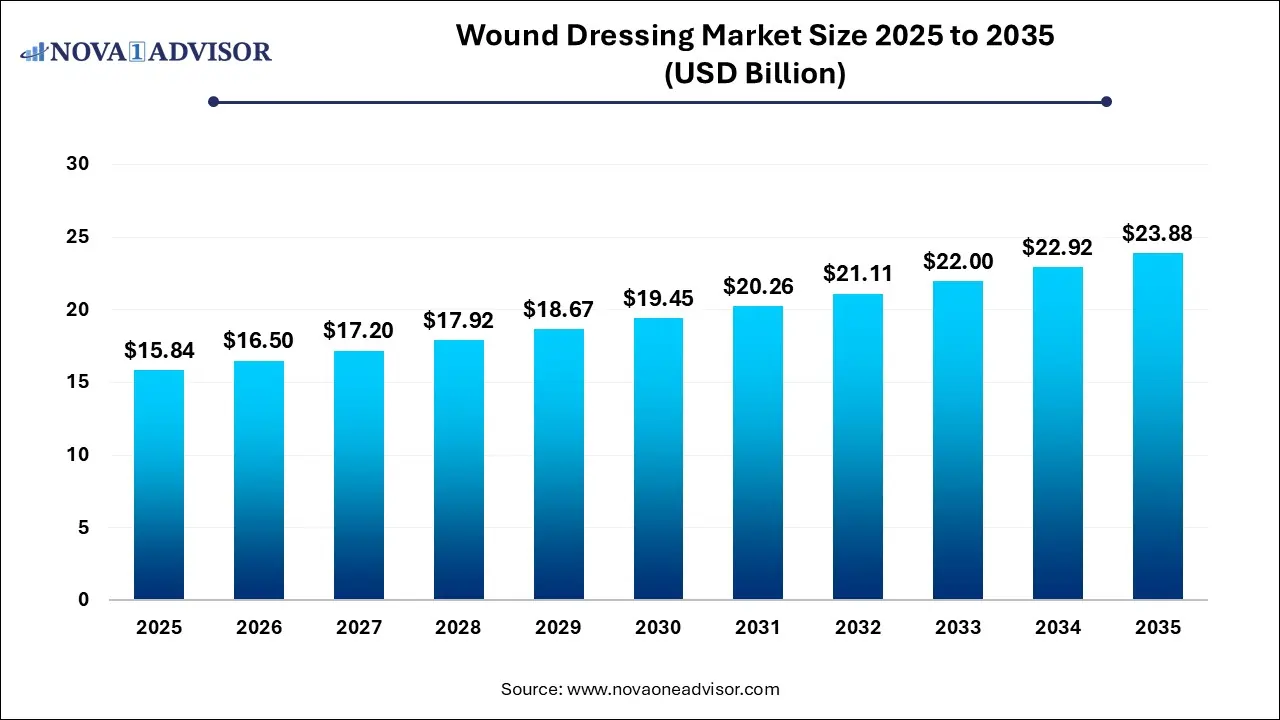
The global wound dressing market size was exhibited at USD 15.84 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 23.88 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 4.19% during the forecast period of 2026 to 2035.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market with a revenue share of 46.0% in 2025.
- Advanced dressing led the market and accounted for a revenue share of 55.0% in 2025.
- The chronic wounds segment dominated the market in 2025.
- The hospital segment dominated the market in 2025.
Market Overview
The wound dressing market has evolved significantly from traditional materials like cotton and gauze to sophisticated, bioactive products tailored to specific wound types and healing stages. Wound dressings are critical components in wound management, designed not only to protect the wound but also to facilitate faster healing, reduce pain, and prevent infections. They are used across a broad spectrum of clinical scenarios, including surgical interventions, trauma cases, chronic wound management, and burn care.
Aging populations, rising surgical procedures, and the increasing prevalence of lifestyle-related chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers are major contributors to market demand. Additionally, advancements in material sciences and biomedical engineering have led to the development of dressings that maintain optimal moisture balance, deliver drugs locally, and even integrate antimicrobial or oxygen-enhancing capabilities.
As the burden of chronic wounds grows worldwide and healthcare systems seek cost-effective yet high-performance solutions, the wound dressing market is gaining prominence. Globally, health organizations are emphasizing early wound care, and public-private collaborations are funding innovations in wound management technologies, boosting market expansion.
Market Outlook
- Market Growth Overview: The wound dressing market is expected to grow significantly between 2026 and 2035, driven by the high prevalence of diabetes, aging population, and rising road accidents and workplace injuries, increasing demand for effective wound care.
- Sustainability Trends: Sustainability trends involve material innovation, green manufacturing, and technological integration for efficiency.
- Major Investors: Major investors in the market include Smith+Nephew, 3M, Convatec, Mölnlycke Health Care, Coloplast, Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon), Integra LifeSciences, Medtronic, and B. Braun
- Startup Economy: The startup economy is focused on advanced solutions, agility, R&D intensity, and strategic exits and investment.
Impact of AI on the Wound Dressing Market?
AI is transforming the wound dressing industry by shifting from passive care to proactive, data-driven wound management. AI-powered systems, particularly those using computer vision and machine learning, can objectively assess, measure, and monitor wounds via smartphone apps, providing more accurate diagnoses and tracking healing progress over time. This technology also plays a crucial role in the development of "smart dressings" embedded with biosensors (e.g., pH, temperature, moisture) that provide real-time data, allowing for timely interventions and personalized treatment plans.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Preference for Moist and Advanced Dressings: Foam, hydrocolloid, and hydrogel dressings are gaining traction due to their superior healing properties.
-
Integration of Antimicrobial Agents: Silver-based and non-silver antimicrobial dressings are being adopted to reduce infection risks, particularly in chronic wounds.
-
Shift Toward Bioactive and Skin-Substitute Dressings: Innovations in active dressings support tissue regeneration and wound closure.
-
Growing Use of Smart and Oxygen-Releasing Dressings: Technologies offering pH monitoring or micro-oxygenation are entering the market.
-
Increased Demand in Home Healthcare: The rise in home-based care is driving demand for easy-to-apply and longer-wear dressings.
-
Eco-Friendly and Biodegradable Products: Sustainable materials are being explored to reduce clinical waste and environmental impact.
-
Digital Tracking and e-Wound Platforms: Clinical use of mobile apps for dressing change schedules and wound documentation is rising.
-
Strong Growth in Emerging Economies: Governments are funding wound care access through universal health schemes and rural outreach.
Wound Dressing Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 16.50 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 23.88 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 4.19% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
3M; Coloplast Corp.; Medline Industries; Smith & Nephew; ConvaTec Group PLC; Derma Sciences (Integra LifeSciences); Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson); Baxter International; Molnlycke Health Care AB |
Market Driver: Increasing Burden of Chronic Wounds and Surgeries
One of the most significant drivers of the wound dressing market is the global rise in chronic wounds, particularly driven by conditions like diabetes, vascular disease, and immobility-related pressure ulcers. Diabetic foot ulcers alone affect over 15% of diabetics globally and are associated with high morbidity and healthcare costs.
Simultaneously, an increase in the volume of surgical procedures due to growing life expectancy and medical accessibility has expanded the need for post-operative wound care. Proper dressing is essential to prevent infection and complications, ensuring faster recovery and shorter hospital stays. Advanced wound dressings are being increasingly adopted in surgical units for their ability to create a moist healing environment, which accelerates tissue repair.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Advanced Wound Dressings
Despite their clinical benefits, the high cost of advanced and active wound dressings is a notable barrier to wider adoption, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Advanced dressings can be several times more expensive than traditional gauze or cotton, and in many healthcare systems, they are not fully reimbursed.
This cost barrier limits the use of advanced products in outpatient or primary care settings where budgets are constrained. Additionally, in homecare environments, patients may default to cheaper alternatives due to affordability issues, even when clinical guidance favors advanced solutions. This cost-benefit mismatch affects market penetration and remains a concern for both manufacturers and healthcare policymakers.
Market Opportunity: Expansion into Home Healthcare and Remote Wound Management
With the shift toward value-based and patient-centric care, home-based wound management is emerging as a high-growth opportunity. Aging populations, rising demand for convenience, and post-COVID-19 emphasis on decentralized care have driven the need for wound dressing solutions that are easy to apply, monitor, and manage outside of clinical settings.
This is particularly relevant for patients with chronic wounds requiring long-term dressing. Companies are responding with adhesive foam dressings, antimicrobial sheets, and hydrocolloid plasters that require less frequent changes and can be used by non-clinicians. Furthermore, digital platforms are now being used to enable remote wound monitoring, where patients can upload images for clinical review creating a robust ecosystem for homecare wound management.
Segments Insights:
By Product Insights
Advanced wound dressings dominate the market, offering superior functionality such as moisture retention, antimicrobial protection, and autolytic debridement. Foam dressings, in particular, are widely used for both acute and chronic wounds due to their high absorbency and gentle contact layers. Hydrocolloid and hydrogel dressings are also gaining popularity, especially in pressure ulcers and burns, where maintaining a moist wound environment is essential.
Active dressings are the fastest-growing segment, led by biomaterial-based products and skin substitutes that actively promote healing. These include collagen-infused dressings and regenerative matrices used in complex wound scenarios such as diabetic foot ulcers and surgical wounds that fail to close. Demand for skin-substitutes is especially strong in burn centers and trauma units where full-thickness wounds are common.
By Application Insights
Chronic wounds dominate the market, with diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure sores contributing a substantial share. These conditions often require prolonged and complex treatment protocols, where advanced dressings play a critical role. Silver dressings, alginates, and collagen-based products are frequently used in chronic cases to manage infection, exudate, and delayed granulation.
Acute wounds are witnessing faster growth, particularly driven by trauma cases, surgical site management, and burn injuries. As the global volume of surgeries rises—especially in orthopedic and cardiovascular domains—acute post-operative wound care has become more sophisticated. Single-use, long-wear foam and antimicrobial dressings are being adopted in operating rooms to reduce infection risk and improve healing outcomes.
By End-use Insights
Hospitals account for the largest market share, given their role in treating complex and surgical wounds. Hospital-based wound care units and surgical departments are significant consumers of advanced dressing products. Reimbursement coverage and bulk procurement models support adoption even for costlier dressings in these settings.
Home healthcare is the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by long-term care of chronic wounds and palliative scenarios. Foam and hydrocolloid dressings designed for ease of application and extended wear time are well-suited for home use. Patients with mobility issues, the elderly, and those recovering post-surgery increasingly rely on homecare kits and telehealth support for wound care, accelerating this segment’s growth.
By Regional Insights
North America leads the global wound dressing market, fueled by a high prevalence of chronic diseases, robust healthcare infrastructure, and strong presence of key players. The U.S. is particularly active in wound care innovation and is supported by reimbursement systems that cover many advanced wound products. Clinical awareness and availability of homecare services further bolster demand.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by rising healthcare expenditure, expanding hospital networks, and increasing surgical volumes. Countries such as China and India are witnessing rapid growth in diabetic populations, which is directly influencing the incidence of foot ulcers and skin lesions. Moreover, government healthcare schemes are beginning to cover advanced wound care, opening up opportunities for both local and global manufacturers.
U.S. Wound Dressing Market Trends
The U.S. region's market growth is driven by the rising global prevalence of diabetes, obesity, and vascular diseases, which necessitate sophisticated solutions for chronic ulcers. This demand is further amplified by a rapidly aging population and a high volume of traumatic injuries, pushing the industry toward a technological shift focused on smart, bioactive, and interactive dressings infused with silver or growth factors.
China Wound Dressing Market Trends
China has an advanced dressing, films, and led market share, rising adoption of smart, interactive, and biologic dressings, notes, and mobility forecasts. Rising demand in home healthcare alongside hospitals/clinics, according to Mordor Intelligence, and a boom in retail.
How Did Europe Notably Grow in the Wound Dressing Market?
Europe's advanced wound care market is fundamentally driven by its aging demographic and the rising incidence of diabetes, which necessitate sophisticated solutions for chronic and geriatric-related ulcers. The region's robust healthcare infrastructure and favorable reimbursement policies in nations like Germany and the UK accelerate the adoption of high-tech innovations, including smart dressings with biosensors and portable NPWT devices.
Germany Wound Dressing Market Trends
Germaine’s advanced wound care market is expanding rapidly as aging populations and rising diabetes rates drive a critical need for specialized treatments like diabetic foot ulcer therapies. The industry is moving away from traditional methods toward high-tech bioactive dressings and smart materials that significantly improve healing outcomes and reduce infection risks.
Value Chain Analysis of the Wound Dressing Market
Research & Development (R&D) and Raw Material Sourcing
This foundational stage involves the discovery of new materials and technologies to improve wound healing and prevent infection.
- Key Players: 3M Company, Smith+Nephew, and Organogenesis
Manufacturing and Production
Raw materials are transformed into finished wound dressing products in this stage, adhering to strict quality control and regulatory standards.
- Key Players: Mölnlycke Health Care AB, ConvaTec Group PLC, and Cardinal Health
Distribution and Logistics
Products are moved from manufacturing facilities to various healthcare settings, which requires an efficient and wide-reaching supply chain.
- Key Players: Cardinal Health, Medline Industries, and Owens & Minor
Marketing and Sales
Activities in this stage focus on promoting product benefits, increasing brand awareness, and providing education to healthcare professionals on proper wound care management.
- Key Players: Johnson & Johnson, Coloplast A/S, and PAUL HARTMANN AG
Recent Developments
-
Smith & Nephew (April 2025): Launched the PICO 7Y single-use negative pressure dressing with an integrated canister for managing high-exudate wounds.
-
3M Health Care (March 2025): Announced FDA clearance for its Tegaderm™ CHG antimicrobial film dressing for use in post-surgical wounds.
-
Mölnlycke Health Care (February 2025): Expanded its Avance® Solo platform to include foam dressings with integrated oxygenation capabilities.
-
Convatec (January 2025): Partnered with an AI health tech company to develop a smart wound dressing sensor that monitors pH and exudate levels.
-
Coloplast (December 2024): Released biodegradable foam dressings made from plant-based polymers to reduce environmental impact in large hospital chains.
Wound Dressing Market Companies
- Smith+Nephew As a major global player in advanced wound management, Smith+Nephew offers a comprehensive portfolio including innovative foam dressings (ALLEVYN) and negative pressure wound therapy (PICO, RENASYS).
- Mölnlycke Health Care AB Mölnlycke specializes in innovative solutions for wound care and surgical procedures, emphasizing patient comfort and sustainability in its product portfolio.
- Convatec Group PLC Convatec develops advanced solutions for managing chronic conditions, with leading positions in advanced wound care and technologies like their unique Hydrofiber® (AQUACEL) dressings.
- Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson) Operating as Johnson & Johnson's surgical technologies arm, Ethicon focuses on advanced wound closure solutions used extensively in surgical and acute care environments.
- Coloplast Corp. Coloplast manufactures and sells products for ostomy, urology, and skin/wound care, including advanced foam and hydrocolloid dressings designed for skin protection and pressure injuries.
- URGO Medical specializes in advanced wound healing and is recognized for its expertise in an array of advanced dressings, including hydrocolloids and hydrogels.
- 3M 3M, through its former Health Care business, now part of Solventum, has a substantial role in comprehensive wound care provision through its health division.
- Integra LifeSciences Integra LifeSciences provides surgical instruments, neurosurgery products, and a wide array of regenerative tissue technologies and biologic products for critical wounds and burns.
- PAUL HARTMANN AG provides a wide range of medical and healthcare products, including solutions for wound care management and infection prevention. Their contributions to the wound dressing market include both traditional and advanced wound care products to support various treatment needs.
- DR. AUSBÜTTEL (DRACO) As part of the PAUL HARTMANN AG group, DR. AUSBÜTTEL (DRACO) focuses on developing effective and high-quality wound care products.
- Medline Industries, Inc. Medline is a major manufacturer and distributor of healthcare supplies, offering a diverse range of wound care products, including skin care and advanced wound dressings.
- Brightwake Ltd. Brightwake is an innovator in the medical textiles field, known for developing unique fiber technologies for advanced wound care applications.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global wound dressing market.
Product
-
- Gauze
- Tape
- Bandages
- Cotton
- Others
-
-
- Foam Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Film Dressing
- Alginate Dressing
- Hydrogel Dressing
- Collagen Dressing
- Other Advanced Dressing
-
-
- Silver Dressing
- Non-silver Dressing
-
-
- Biomaterials
- Skin-substitute
Application
-
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Pressure Ulcers
- Venous Leg Ulcers
- Other Chronic Wounds
-
- Surgical & Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
End-use
- Hospitals
- Outpatient Facilities
- Home Healthcare
- Research & Manufacturing
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

