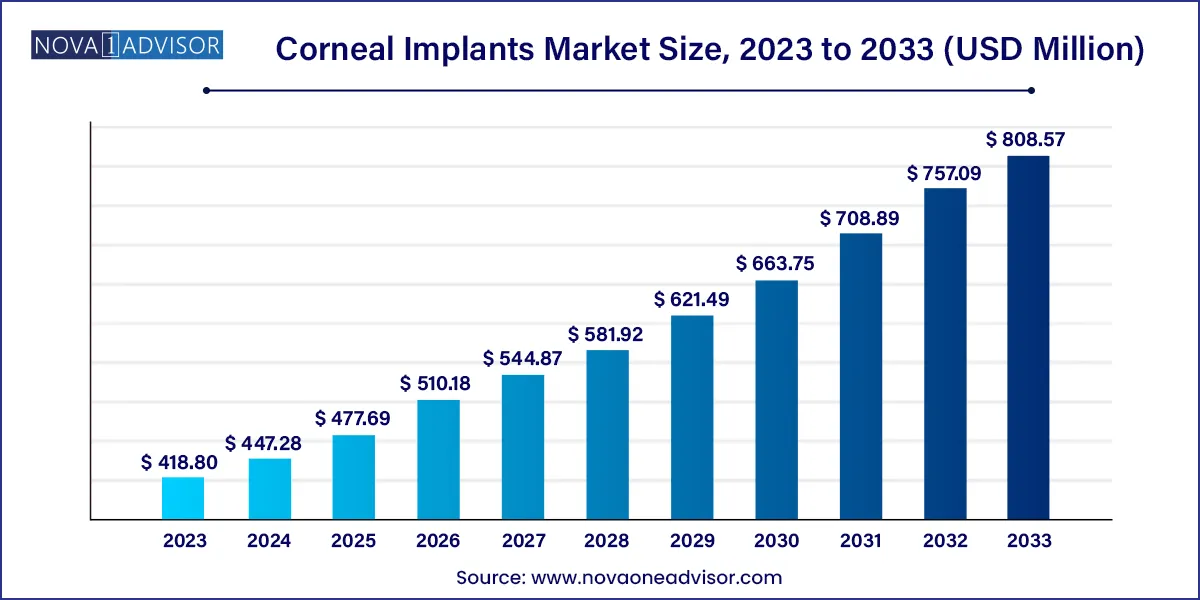
The global corneal implants market size was exhibited at USD 418.80 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 808.57 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market and accounted for the largest share of 59.0% in 2023.
- The human tissue segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 91.8% in 2023.
- The penetrating keratoplasty segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 53.3% in 2023.
- The Fuchs dystrophy segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 52.8% in 2023
- The hospital's end-use segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 59.0% in 2023.
Market Overview
The global corneal implants market plays a critical role in modern ophthalmology by addressing visual impairment and blindness caused by corneal damage or degeneration. The cornea, the eye's outermost transparent layer, is essential for focusing vision. Damage to this structure whether from trauma, infections, degenerative conditions, or hereditary diseases can lead to partial or complete vision loss. Corneal implants, also known as corneal grafts or corneal transplants, restore visual function by replacing damaged tissue with either donor tissue (human cornea) or synthetic alternatives.
Globally, millions suffer from corneal blindness, and in many regions, it ranks as the second leading cause of blindness after cataracts. While penetrating keratoplasty has been the traditional approach to full-thickness corneal replacement, newer, more targeted methods like endothelial keratoplasty are gaining popularity for their faster recovery and reduced complication risks.
A growing demand for corneal implants stems from increasing awareness about eye health, the expansion of advanced eye care infrastructure in emerging economies, and innovations in synthetic implants. Despite challenges in donor tissue availability, advances in preservation techniques, bioengineering, and polymer-based synthetic corneas are helping to address the demand-supply gap.
In parallel, government and NGO-driven efforts to reduce avoidable blindness—particularly in developing nations—are catalyzing access to corneal transplantation services. Organizations such as SightLife, Orbis, and the Eye Bank Association of America (EBAA) are driving eye donation campaigns and improving surgical capacities. With an aging global population and rising incidence of corneal disorders like keratoconus and Fuchs dystrophy, the market for corneal implants is poised for sustained growth.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Lamellar and Endothelial Keratoplasty: Partial-thickness transplantation techniques are gaining favor due to better outcomes and reduced rejection rates.
-
Development of Bioengineered and Synthetic Corneas: Innovations in artificial corneal implants aim to address the global shortage of donor tissue.
-
Rising Prevalence of Keratoconus Among Youth: Increasing diagnoses and early interventions are fueling demand for corneal implants and cross-linking therapies.
-
Integration of Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Surgery: Enhanced precision in corneal surgery is reducing complications and expanding eligibility for advanced implants.
-
Teleophthalmology and AI in Screening: Remote diagnostics and artificial intelligence tools are accelerating early detection and surgical planning in rural areas.
-
Government and NGO Initiatives: Global collaborations to promote eye donation and corneal transplant access are expanding patient pools in under-served regions.
-
Advanced Preservation and Transport Techniques: Improved tissue banking and cold storage solutions are extending graft viability and geographical reach.
-
Growing Use of Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs): Faster recovery and lower costs are shifting simple corneal surgeries away from hospitals.
Corneal Implants Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 418.80 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 808.57 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 6.8% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Surgery, Application, End use, And Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Florida Lions Eye Bank; Alcon Inc.; Aurolab; CorneaGen; AJL Ophthalmic S.A.; DIOPTEX; Massachusetts Eye and Ear; San Diego Eye Bank; KeraMed, Inc.; Presbia PLC. |
Key Market Driver: Rising Global Prevalence of Corneal Diseases
A fundamental driver of the corneal implants market is the escalating burden of corneal diseases, particularly among aging populations and in areas with poor access to preventive eye care. Conditions such as keratoconus, infectious keratitis, corneal ulcers, and Fuchs endothelial dystrophy are on the rise due to increased exposure to environmental risk factors, contact lens misuse, and diabetes.
For instance, keratoconus a progressive thinning and cone-shaped distortion of the cornea affects nearly 1 in 2,000 individuals globally, with higher incidence rates in some Middle Eastern and Asian populations. In many cases, surgical implantation of a corneal graft is the only viable solution to restore vision. Similarly, Fuchs dystrophy, characterized by endothelial cell loss, often necessitates endothelial keratoplasty, especially in patients over 60.
The surge in corneal infections, particularly in tropical and under-resourced settings, is also pushing up the number of emergency grafts. According to the WHO, over 10 million people worldwide require corneal transplantation annually, but only a small fraction currently receive it highlighting a large, unmet demand.
Key Market Restraint: Shortage of Donor Corneal Tissue
Despite increasing demand, one of the most significant constraints in the corneal implants market is the limited availability of donor tissue, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Unlike cataract surgeries, which rely on artificial lenses, corneal transplants traditionally require viable human tissue sourced from eye banks.
Several countries face cultural, religious, and logistical barriers to eye donation. A study from the EBAA reported that while the U.S. manages to meet its domestic needs and even exports corneal tissue, many countries, including those in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, suffer from chronic shortages. Moreover, preservation, transportation, and matching tissue viability timelines further complicate availability.
This imbalance not only leads to long waiting times but also hinders timely intervention in acute cases, increasing the risk of irreversible vision loss. The shortage continues to drive demand for synthetic alternatives, but current artificial corneas still have limitations in biointegration and immune response modulation.
Key Market Opportunity: Technological Advancements in Synthetic and Bioengineered Corneas
The most promising opportunity in the corneal implants market lies in the development of synthetic and bioengineered corneal substitutes. As researchers aim to overcome the donor shortage challenge, tissue-engineered corneas made from collagen matrices, hydrogels, and polymeric materials are being tested in clinical trials. These innovations aim to replicate the structure and function of natural corneal tissue while reducing rejection risks.
Recent breakthroughs have included the use of decellularized porcine corneas, cross-linked collagen scaffolds, and stem-cell-infused implants that promote host cell migration and integration. One notable example is the 2022 pilot study in India and Iran involving a bioengineered implant developed by Linköping University and startup company LinkoCare Life Sciences, which restored vision in over 75% of blind patients.
As these technologies progress through regulatory pathways and gain surgical acceptance, they could radically transform access to vision restoration, especially in regions with limited donor availability.
Segments Insights:
Type Insights
Human cornea implants dominate the market, being the gold standard for corneal replacement. Derived from donated tissue, human corneas offer natural compatibility, reduced optical aberrations, and superior long-term outcomes. These implants are preferred in both full-thickness (penetrating) and partial-thickness (endothelial or anterior lamellar) surgeries. Regions with established eye banking systems such as the U.S., parts of Europe, and Australia primarily rely on human donor corneas for all transplant needs.
However, synthetic corneal implants are the fastest-growing segment, driven by the global donor shortage and advancements in biomaterials. Synthetic implants such as keratoprostheses and tissue-engineered scaffolds are gaining momentum in regions where eye donation is culturally limited or logistically challenging. They are particularly useful in patients who have undergone previous graft failure, chemical burns, or autoimmune keratitis. Continued investment in clinical research and material science is expected to further accelerate this segment’s adoption.
Surgery Method Insights
Penetrating keratoplasty currently holds the largest market share, as it is the most widely practiced and well-established corneal transplant technique. It involves the full-thickness replacement of the damaged cornea and is typically used in cases of advanced keratoconus, scarring, or trauma. Surgeons are well-trained in this method, and eye banks routinely prepare full-thickness grafts. While newer techniques are growing, penetrating keratoplasty remains a mainstay in both developed and developing markets.
Endothelial keratoplasty is the fastest-growing surgical method, particularly for indications like Fuchs dystrophy and bullous keratopathy. Techniques such as Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) and Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK) are gaining popularity due to faster visual recovery, reduced rejection rates, and smaller incision sizes. As surgical training and technology improve, this method is seeing increasing preference among ophthalmologists, particularly in North America, Europe, and Japan.
Application Insights
Keratoconus is the most dominant application area, primarily due to its high prevalence in adolescents and young adults. As the disease progresses, corneal thinning and irregular astigmatism can lead to significant visual impairment. While mild cases are managed with contact lenses and corneal cross-linking, advanced keratoconus often necessitates corneal implantation. Given its progressive nature, early surgical intervention through anterior lamellar keratoplasty or full transplantation is often recommended.
Fuchs dystrophy is the fastest-growing application, owing to an aging population and improved diagnostic capabilities. This condition involves degeneration of endothelial cells, leading to corneal edema and visual distortion. Endothelial keratoplasty is the preferred treatment, and rising awareness is pushing more patients toward surgical correction. Additionally, the trend toward bilateral sequential surgeries in Fuchs patients is expanding the procedural volume and creating demand for precise, pre-loaded endothelial grafts.
End-use Insights
Hospitals dominate the corneal implants market by virtue of their comprehensive surgical infrastructure, access to certified eye banks, and multidisciplinary care capabilities. Most corneal transplant surgeries especially those requiring general anesthesia, intensive postoperative monitoring, or complex intraocular procedures are performed in hospital settings. Teaching hospitals and academic centers also conduct research trials and often serve as regional hubs for referral cases.
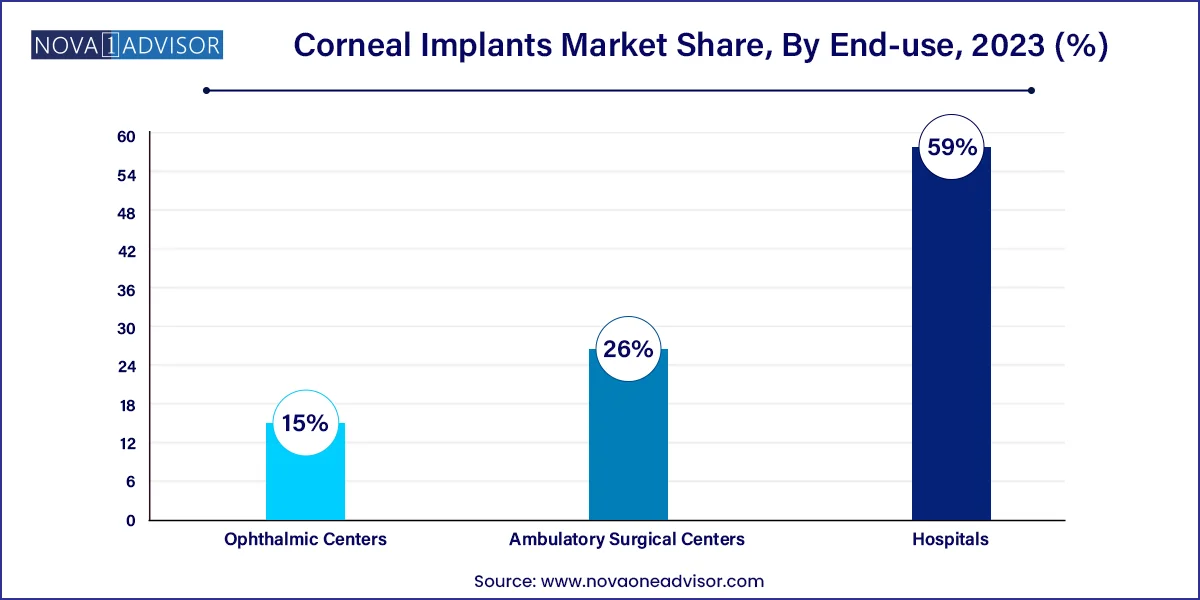
Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) are emerging as the fastest-growing end-use segment, especially in the United States and urban Asia. Many partial-thickness and straightforward corneal surgeries are now being performed in ASCs, benefiting from lower procedural costs, reduced patient waiting times, and same-day discharge. As ophthalmology increasingly adopts outpatient care models, ASCs will become integral to the delivery of routine corneal transplant services.
Regional Insights
North America is the dominant region in the global corneal implants market, due to its robust infrastructure for eye donation, presence of specialized ophthalmic centers, and high public awareness. The United States leads in eye bank operations, facilitated by the EBAA, which coordinates tissue availability and safety. Additionally, high adoption of endothelial keratoplasty and access to femtosecond laser-assisted surgeries place North America at the forefront of surgical innovation. Favorable reimbursement systems and advanced training programs further support this leadership.
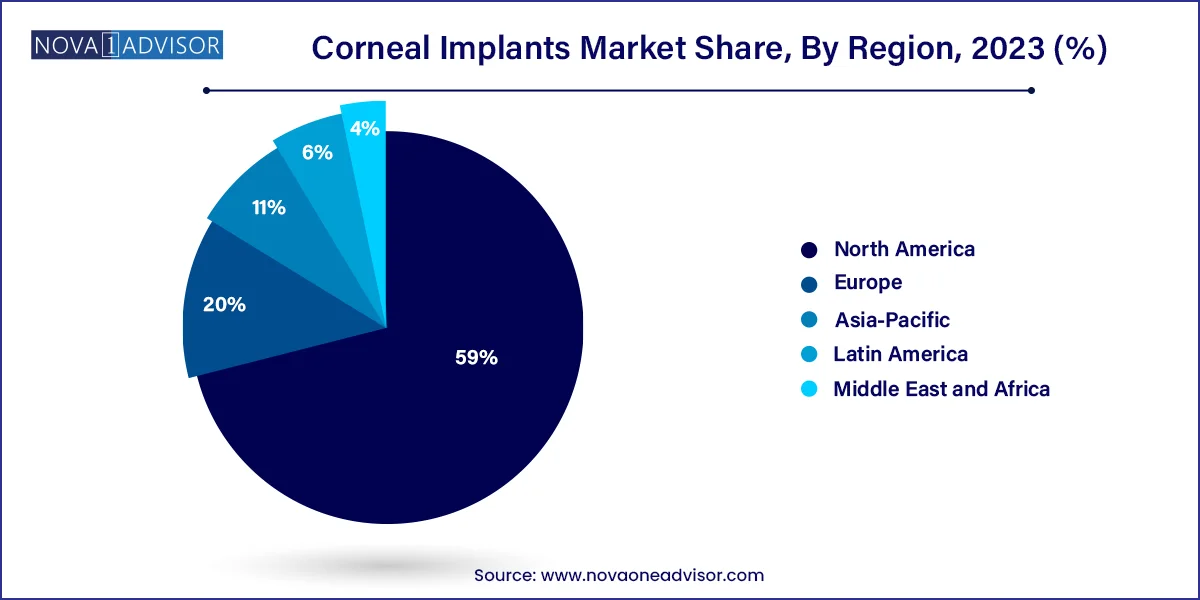
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by a combination of increasing corneal disease burden, public health initiatives, and growing surgical capabilities. Countries like India, China, and Indonesia are scaling up corneal blindness programs through public-private partnerships and international collaborations. India, for example, has seen a dramatic rise in both eye donations and corneal transplant surgeries in recent years, supported by entities like the National Programme for Control of Blindness (NPCB). While donor shortages persist, the emergence of low-cost synthetic alternatives and mobile surgical camps is expanding access.
Some of the prominent players in the corneal implants market include:
- Florida Lions Eye Bank
- Alcon Inc.
- Aurolab
- CorneaGen
- AJL Ophthalmic S.A.
- DIOPTEX
- Massachusetts Eye and Ear
- San Diego Eye Bank
- KeraMed, Inc.
- Presbia PLC
Recent Developments
-
LinkoCare Life Sciences (March 2025): Announced successful Phase II trials of its bioengineered corneal implant in Southeast Asia, showing promising results for restoring vision in non-infectious corneal blindness cases.
-
CorneaGen (January 2025): Launched a new pre-loaded DMEK graft system aimed at improving surgical efficiency and reducing endothelial cell loss during transplant.
-
SightLife Surgical (December 2024): Expanded its tissue recovery partnerships in Latin America to improve donor supply in underserved regions.
-
Presbia PLC (October 2024): Advanced its synthetic inlay lens for presbyopia treatment, with results showing improved long-term visual acuity.
-
San Diego Eye Bank (September 2024): Deployed AI-based tissue matching software to enhance corneal graft assignment and logistics.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global corneal implants market.
Type
Surgery Method
- Penetrating Keratoplasty
- Endothelial Keratoplasty
Application
- Keratoconus
- Fuchs Dystrophy
- Infectious Keratitis
- Corneal Ulcers
- Others
End-use
- Hospitals
- Ophthalmic Centers
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



