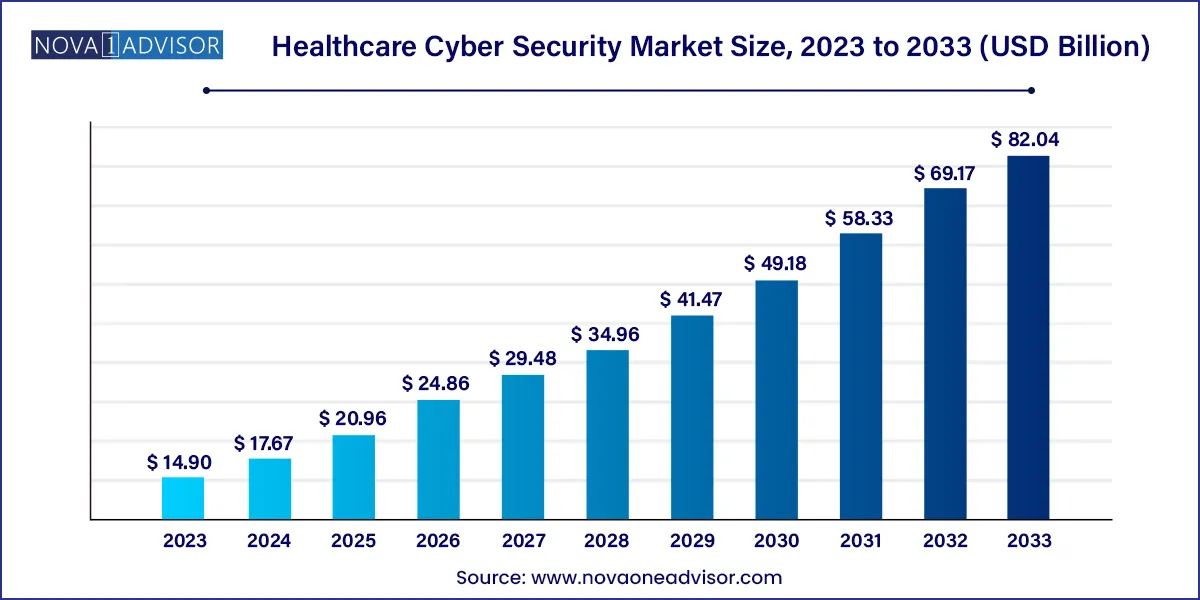
The global healthcare cyber security market size was exhibited at USD 14.90 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 82.04 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 18.6% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market for healthcare cyber security and accounted for the largest revenue share of around 42%.
- ntivirus and Antimalware segment dominated the market with 25.6% share in 2023.
- Malware segment dominated the market with 25.4% share in 2023.
- The hospital segment held the largest revenue share of around 63.0%.
Market Overview
The healthcare cyber security market has emerged as a critical pillar safeguarding sensitive patient data, protecting hospital operations, and ensuring regulatory compliance. The healthcare industry, traditionally slow in adopting advanced IT practices, has been increasingly targeted by cyberattacks, ransomware, and sophisticated phishing campaigns. With the healthcare sector handling massive volumes of personal health information (PHI), electronic health records (EHR), and insurance data, cybersecurity is no longer a choice but a necessity.
Healthcare cyber security encompasses a wide range of protective measures against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other forms of cyber threats. From protecting networks, devices, and applications to securing internal systems against espionage and sabotage, the industry demands tailored solutions that address its complex ecosystem. With the global digitization of healthcare records and the rising trend of telemedicine post-pandemic, the demand for healthcare cybersecurity solutions is experiencing unprecedented growth.
According to internal estimates and market evaluations, the healthcare cyber security market size is projected to experience a substantial growth rate over the next decade. This growth is propelled by the increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks, stringent regulatory environments like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S., GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, and growing investments by healthcare institutions to fortify their defenses.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Proliferation of IoT and Connected Medical Devices: Medical devices like insulin pumps, MRI machines, and heart monitors are increasingly connected to hospital networks, creating new vulnerabilities.
-
Rise in Ransomware Attacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting hospitals with ransomware attacks that paralyze systems until a ransom is paid.
-
Cloud Adoption in Healthcare: Cloud-based storage and services are rapidly being adopted, requiring enhanced cloud security solutions.
-
Blockchain for Healthcare Data Security: Blockchain technology is gaining attention for its potential to secure patient data and ensure transparency.
-
Growing Demand for Endpoint Security: As remote working and telehealth become standard, securing endpoints like smartphones, tablets, and laptops is paramount.
-
Zero Trust Architecture Implementation: Organizations are moving towards Zero Trust Security models to ensure no implicit trust is granted to assets or user accounts.
-
Increased Focus on Compliance and Risk Management Solutions: Regulatory fines and reputational damage drive healthcare providers to prioritize compliance solutions.
Healthcare Cyber Security Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 14.90 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 82.04 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 18.6% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type Of Solution, Type Of Threat, End use, Type Of Security, Deployment, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Cisco; IBM; FireEye; Symantec; Trend Micro; MacAfee; Intel; Kaspersky; Lockheed Martin; Northrop Grumman, Imperva Inc., Fortinet Inc., Medigate Ltd |
Driver: Surge in Healthcare Data Breaches
One of the prime drivers fueling the healthcare cyber security market is the surge in healthcare data breaches. Patient information is highly valuable on the black market, sometimes fetching higher prices than credit card information. With digital health records becoming standard, the volume of data at risk has expanded exponentially. High-profile breaches, like the ransomware attack on Ireland's Health Service Executive in 2021, exposed the vulnerabilities within even state-run healthcare organizations. The repercussions of these breaches—including financial loss, operational disruption, and erosion of patient trust—have made cyber security investments a strategic priority for healthcare providers globally.
Restraint: High Cost of Cyber Security Solutions
Despite the evident need, the high cost of implementing robust cybersecurity measures acts as a major restraint. Healthcare providers, particularly small and mid-sized hospitals, often operate under strict budget constraints. Advanced solutions involving artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technology come with significant upfront and maintenance costs. Additionally, cybersecurity is an ongoing commitment, requiring constant updates, employee training, and system audits, which strain financial resources. Consequently, many smaller institutions defer or limit their cybersecurity investments, leaving them vulnerable to cyber threats.
Opportunity: Rise of Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare Services
The explosion of telemedicine and remote healthcare services presents a lucrative opportunity for the healthcare cybersecurity market. Telehealth consultations, wearable health devices, and mobile health applications rely on internet connections, making data transmission vulnerable to interception. Protecting these new digital avenues demands innovative cybersecurity solutions tailored to mobile and decentralized systems. Companies specializing in securing telemedicine platforms and remote patient monitoring systems have a massive, untapped market to serve. This opportunity is particularly potent in emerging economies where telemedicine is helping bridge the healthcare access gap.
Segments Insights:
Type of Solutions Insights
Identity and Access Management dominated the market. Healthcare organizations must control who has access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access patient records and internal systems. Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions are the first line of defense against insider threats and unauthorized data breaches. As healthcare networks expand with new devices and remote workers, IAM systems ensure a secure, seamless user experience while maintaining compliance with stringent healthcare regulations. Companies such as Okta and Imprivata are leading the charge, offering advanced multi-factor authentication and role-based access control solutions.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is the fastest-growing segment. SIEM solutions provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, and response capabilities crucial for healthcare providers under constant threat from cyberattacks. The increase in sophisticated ransomware attacks has made continuous system monitoring a necessity. Solutions like IBM QRadar and Splunk are gaining traction among healthcare providers aiming to strengthen their security posture proactively. The integration of AI and machine learning with SIEM platforms further enhances their effectiveness, driving rapid adoption across the sector.
Type of Threat Insights
Malware dominated the market. Malware remains the most common and devastating form of cyberattack in healthcare. Malware can encrypt files, steal sensitive data, or even disrupt life-saving equipment. Instances like the WannaCry attack on the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) in 2017, which caused widespread disruption, highlight the grave threat malware poses to healthcare systems. Organizations are investing heavily in antivirus, anti-malware, and advanced threat detection systems to counter this persistent threat.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are the fastest-growing threat category. APTs involve long-term targeted attacks often orchestrated by organized cybercrime groups or nation-states. These threats are particularly dangerous in healthcare as they can go undetected for months, siphoning sensitive data. The sophistication and patience involved in APT attacks have led healthcare organizations to deploy advanced behavioral analytics and threat intelligence solutions, fueling this segment’s rapid growth.
End-use Insights
Hospitals dominated the end-use segment. Hospitals are the most critical and vulnerable healthcare facilities when it comes to cybersecurity. With thousands of patient records, financial information, and connected medical devices, hospitals present a lucrative target for cybercriminals. Attacks on hospitals, such as the 2020 ransomware attack on Universal Health Services in the U.S., which affected 400 facilities, showcase the necessity for robust cyber security protocols in hospitals.
Health Insurance providers are the fastest-growing end-users. With vast databases containing personally identifiable information (PII) and financial records, health insurance companies are prime targets. Regulatory demands like HIPAA, PCI DSS compliance, and growing consumer awareness around data privacy are forcing insurers to heavily invest in cybersecurity infrastructure.
Regional Insights
North America dominated the healthcare cybersecurity market. The region’s leadership is driven by high healthcare IT spending, stringent data protection regulations like HIPAA, and a high rate of cyberattacks targeting U.S. healthcare facilities. The U.S. houses several cybersecurity vendors offering cutting-edge solutions tailored for healthcare, including IBM Security and Palo Alto Networks. Moreover, government initiatives like the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act promote the adoption of cybersecurity standards among healthcare providers.
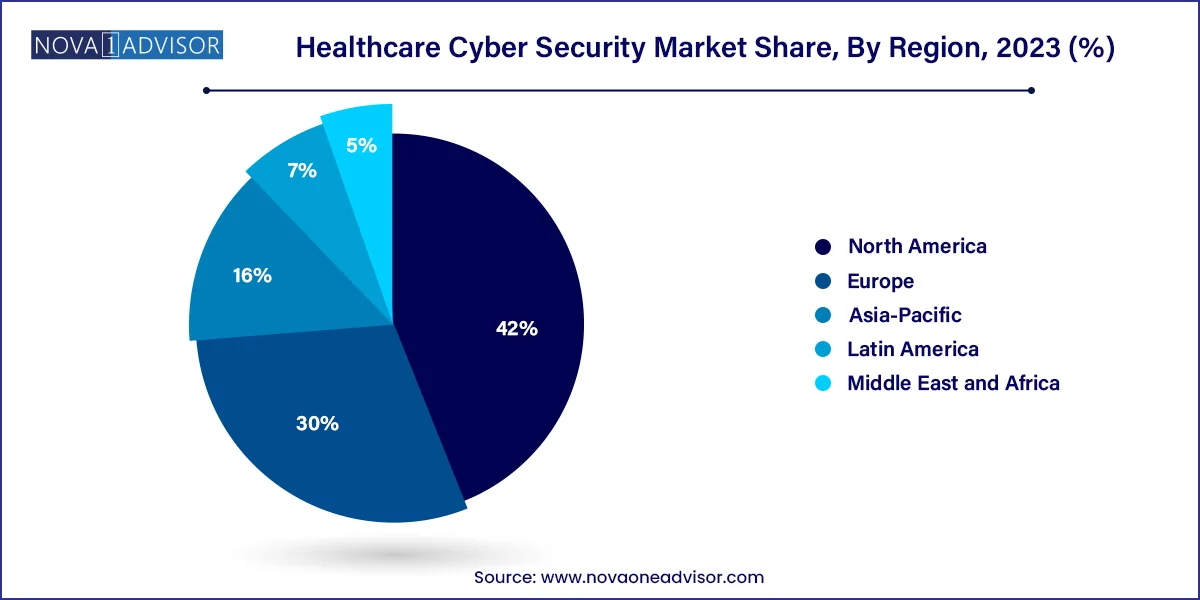
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region. Countries like China, India, and Japan are witnessing a healthcare digitization boom, making cybersecurity a pressing concern. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated telehealth adoption, making healthcare systems more vulnerable to attacks. Governments are rolling out regulations to mandate cybersecurity measures, and investments in AI-based threat detection solutions are rising. For example, India's Personal Data Protection Bill, expected to be implemented soon, will further drive healthcare organizations to bolster cybersecurity defenses.
Some of the prominent players in the healthcare cyber security market include:
- Cisco
- IBM
- FireEye
- Symantec
- Trend Micro
- MacAfee
- Intel
- Kaspersky
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Imperva Inc
- Fortinet Inc
- Medigate Ltd
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Palo Alto Networks launched "Prisma Cloud for Healthcare," a cloud-native security platform specifically designed for healthcare providers adopting cloud infrastructures.
-
February 2025: IBM Security announced the acquisition of a cybersecurity startup "HealthLock," which specializes in advanced threat detection for healthcare environments.
-
January 2025: McAfee collaborated with Epic Systems to integrate its cybersecurity solutions directly into electronic health record platforms.
-
December 2024: Cisco Systems announced new cybersecurity tools targeted at protecting telemedicine and remote patient monitoring systems.
-
November 2024: Fortinet expanded its healthcare-specific cybersecurity solutions, introducing AI-driven threat analytics for hospitals.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global healthcare cyber security market.
Type of Solution
- Identity and Access Management
- Risk and Compliance Management
- Antivirus and Antimalware
- DDoS Mitigation
- Security Information and Event Management
- Intrusion Detection System/ Intrusion Prevention System
- Others
Type of Threat
- Malware
- DDoS
- Advanced Persistent Threat
- Spyware
- Lost or Stolen Devices
- Others
End-Use
- Pharma & Chemicals
- Medical Devices
- Health Insurance
- Hospitals
- Others
Type of Security
- Network Security
- Endpoint Security
- Application Security
- Content Security
Deployment
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


