Teleneurology Market Size, Share, Growth, Report 2025 to 2034
The global teleneurology market size was estimated at USD 6.75 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 20.30 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 11.64% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2034. The growth of the market is attributed to the rising prevalence of neurological disorders, a shortage of specialists, expanding telemedicine adoption, and increased demand for remote patient care solutions.
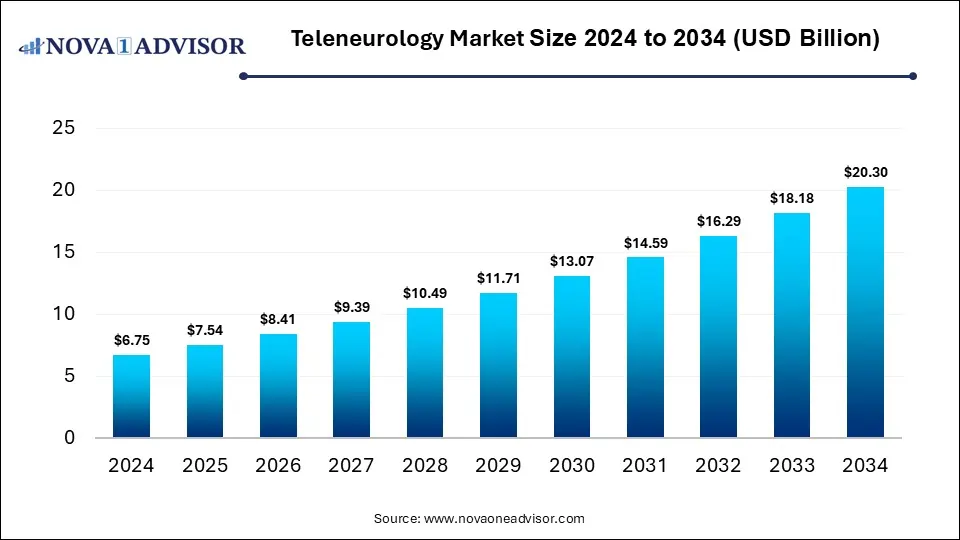
Teleneurology Market Key Takeaways
- By region, North America held the largest share of the teleneurology market in 2024.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to experience the fastest growth between 2025 and 2034.
- By application, the stroke segment led the market in 2024.
- By application, the dementia segment is expected to expand at a significant rate during the forecast period.
- By service, the tele-consulting segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By service, the tele-monitoring segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR over the projection period.
- By end use, the providers segment contributed the largest market share in 2024.
- By end use, the patients segment is likely to expand at the fastest rate in the upcoming period.
Impact of AI on the Teleneurology Market
AI is significantly transforming the teleneurology market by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, enabling faster clinical decision-making and supporting remote patient monitoring. Advanced algorithms can analyze neurological imaging, detect early signs of disorders like stroke or dementia, and assist in triaging patients more efficiently. AI-powered tools also facilitate personalized treatment plans and continuous assessment of neurological conditions through wearable devices and digital biomarkers. Moreover, AI streamlines administrative workflows and reduces the burden on neurologists by automating documentation and data analysis. These innovations are making teleneurology more scalable, accessible, and efficient, particularly in underserved areas.
Market Overview
The teleneurology market involves the use of telecommunication technologies to deliver neurological care remotely, enabling consultations, diagnoses, and monitoring of patients with neurological disorders. Teleneurology offers significant advantages, including faster access to specialist care, especially for time-sensitive conditions like stroke, and ongoing management of chronic diseases such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s, and dementia. It reduces the need for hospital visits, enhances care in rural or underserved areas, and improves patient outcomes through timely intervention. The market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing adoption of telemedicine platforms and advancements in digital health technologies. As healthcare systems worldwide embrace remote care, teleneurology is becoming a critical component of modern neurology practice.
What are the Major Trends in the Teleneurology Market?
- Expansion of Telestroke Programs: Hospitals and health systems are rapidly adopting telestroke services to provide urgent stroke care, especially in rural and underserved areas. These programs enable real-time neurologist consultations to accelerate treatment decisions during the critical "golden hour."
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: AI is being used to enhance diagnostic accuracy, interpret neuroimaging, and predict disease progression. Machine learning models help in early detection of conditions like Alzheimer’s and improve clinical decision-making.
- Growth of Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable devices and mobile health tools are increasingly used to track patients with chronic neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s and epilepsy. This enables continuous care and timely interventions without in-person visits.
- Rising Demand for Geriatric Neurology Services: With the global aging population, there is a growing need for remote care for age-related neurological disorders like dementia and Alzheimer’s. Teleneurology allows elderly patients to receive care from home, improving convenience and safety.
- Increasing Public and Private Investments: Governments and healthcare providers are investing in telehealth infrastructure, while startups and tech companies are developing specialized teleneurology platforms. These investments are accelerating the market’s growth and technological innovation.
Navigating Macroeconomic Influences on the Teleneurology Industry
GDP Growth
GDP growth generally drives the growth of the market, as higher economic output enables greater investment in healthcare infrastructure, digital technologies, and public health initiatives. Countries with rising GDP are more likely to allocate funds toward improving access to specialized care, including remote neurological services. Moreover, stronger economies attract private investments and support the expansion of telemedicine platforms, further accelerating teleneurology adoption.
Inflation Rates
High inflation rates restrain the growth of the market by increasing operational costs for healthcare providers and reducing consumer spending power. Inflation can lead to budget constraints in both public and private healthcare sectors, delaying investments in digital health infrastructure and technology adoption. Additionally, rising costs may make telehealth services less affordable or deprioritized, particularly in low- and middle-income regions.
Report Scope of Teleneurology Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 7.54 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 20.30 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 11.64% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Application, Service, End use, and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Shortage of Neurologists
The shortage of neurologists is a key factor driving the growth of the teleneurology market, as it creates a critical gap in access to timely neurological care, especially in rural and underserved areas. Teleneurology helps bridge this gap by enabling remote consultations, allowing patients to connect with specialists without the need for physical travel. This is particularly vital for acute conditions like stroke, where timely intervention can significantly impact outcomes. Healthcare systems are increasingly adopting teleneurology to optimize specialist resources, reduce patient wait times, and improve overall care delivery. As the demand for neurological services continues to outpace supply, teleneurology is becoming an essential solution to address workforce limitations.
There is a global shortage of neurologists, with low-income countries averaging just 0.1 neurologists per 100,000 people compared to 7.1 in high-income nations and 9.2 in Europe. Several Asian countries have fewer than one neurologist per million people, and while some regions like Latin America have seen growth, others, including Africa, continue to lag behind. Even in well-resourced regions like North America and Europe, neurologist distribution is uneven, and burnout, growing treatment complexity, and reduced confidence among general practitioners worsen the gap. Additionally, the number of general neurologists is declining in high-income countries, with the U.S. and Australia both projecting significant workforce shortages in the coming years.
Increasing Incidence of Neurological Disorders
The increasing incidence of neurological disorders such as stroke, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy is significantly driving the growth of the market. As the global population ages and lifestyle-related risk factors rise, the demand for specialized neurological care continues to grow. Teleneurology offers a scalable solution to manage this surge by enabling remote diagnosis, treatment, and long-term monitoring of patients. It ensures faster access to care, especially in areas lacking neurology specialists, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital admissions. This rising burden of neurological diseases is pushing healthcare providers to adopt teleneurology as a cost-effective and efficient care delivery model.
A major study published in The Lancet Neurology reveals that over 3 billion people worldwide were living with a neurological condition in 2021. Neurological disorders are now the leading cause of ill health and disability globally, with a 18% rise in disease burden since 1990. Over 80% of related deaths and health loss occur in low- and middle-income countries, where access to care remains limited.
Government Support
Government support is playing a crucial role in driving the growth of the teleneurology market by promoting telehealth adoption through funding, favorable regulations, and policy initiatives. Many countries have introduced reimbursement models and telemedicine-friendly laws that encourage healthcare providers to implement remote neurology services. Public health agencies are also investing in digital infrastructure to expand access to specialist care in rural and underserved regions. These efforts help reduce barriers to implementation and increase the scalability of teleneurology solutions. As a result, government backing is accelerating the integration of teleneurology into mainstream healthcare systems.
Restraints
High Costs and Complex Integration
Implementing teleneurology systems often requires substantial investment in advanced technology, secure communication networks, and training for healthcare providers. Additionally, integrating these systems with existing healthcare infrastructure and electronic health records can be technically complex and time-consuming. These factors can deter smaller healthcare facilities and limit widespread adoption, particularly in resource-constrained settings. As a result, high upfront costs and integration difficulties slow down the market’s expansion despite growing demand.
Technical Issues and Regulatory & Reimbursement Challenges
Technical issues such as poor internet connectivity, data security concerns, and lack of standardized platforms pose significant challenges to the growth of the teleneurology market. These technical barriers can affect the quality and reliability of remote neurological consultations, limiting patient and provider adoption. Additionally, regulatory uncertainties and inconsistent reimbursement policies across regions create hurdles for widespread implementation. Without clear guidelines and adequate financial incentives, healthcare providers may be reluctant to invest in teleneurology services.
Opportunities
Development of Specialized Teleneurology Platforms
The development of specialized teleneurology platforms is creating significant opportunities by offering tailored solutions that address the unique needs of neurological care. These platforms integrate advanced features such as real-time video consultations, AI-powered diagnostic tools, and seamless data sharing, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of remote assessments. By providing user-friendly interfaces and customizable workflows, they improve both patient and provider experiences, encouraging wider adoption. Furthermore, specialized platforms enable better management of chronic neurological conditions through continuous monitoring and personalized care plans. This innovation is expanding the scope and effectiveness of teleneurology.
- In July 2025, British health tech startup Neu Health has launched its specialized smartphone-based platform in the U.S. for detecting and managing Parkinson’s and dementia. The platform, now FDA-cleared for tremor measurement, uses smartphone sensors to assess motor and cognitive functions without wearables or special hardware. Patients complete simple tasks at home, enabling early detection through AI-analyzed digital biomarkers and predictive scores.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Expansion into emerging markets creates immense opportunities for the teleneurology market by addressing the significant gaps in neurological care access in these regions. Many emerging economies face a shortage of specialists and limited healthcare infrastructure, making remote neurology services highly valuable. Increasing internet penetration and government initiatives to improve digital health further support the adoption of teleneurology. Additionally, the growing burden of neurological disorders in emerging economies drives demand for scalable and cost-effective solutions. As a result, entering these markets offers substantial growth potential and the chance to improve healthcare outcomes on a large scale.
Segment Outlook
Application Insights
Why Did the Stroke Segment Lead the Teleneurology Market in 2024?
The stroke segment led the market while holding the largest share in 2024 due to the critical need for rapid diagnosis and treatment to improve patient outcomes. Teleneurology enables timely access to neurologists, especially in remote or underserved areas where stroke specialists are scarce. The widespread adoption of telestroke programs has proven effective in reducing treatment delays and improving survival rates. Additionally, increasing awareness of stroke symptoms and the urgency of care has driven healthcare providers to invest heavily in teleneurology solutions.
The dementia segment is expected to grow at a significant rate during the projection period. The growth of the segment is attributed to the rapidly aging global population and the rising prevalence of dementia-related disorders. As dementia requires ongoing monitoring and management, teleneurology offers a convenient way for patients and caregivers to access specialist care without frequent hospital visits. Advances in remote cognitive assessment tools and digital monitoring technologies are enhancing early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Additionally, increasing awareness about dementia and the need for continuous care is driving demand for telehealth solutions tailored to this condition.
Teleneurology Market Size 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Stroke |
1.89 |
2.1 |
2.34 |
2.6 |
2.9 |
3.22 |
3.58 |
3.98 |
4.43 |
4.93 |
5.48 |
| Parkinson |
0.68 |
0.76 |
0.85 |
0.95 |
1.07 |
1.2 |
1.35 |
1.51 |
1.69 |
1.9 |
2.13 |
| Epilepsy |
0.94 |
1.06 |
1.19 |
1.34 |
1.51 |
1.7 |
1.91 |
2.14 |
2.41 |
2.71 |
3.04 |
| Headache |
1.21 |
1.35 |
1.5 |
1.66 |
1.85 |
2.05 |
2.27 |
2.52 |
2.8 |
3.11 |
3.45 |
| Multiple sclerosis |
0.54 |
0.61 |
0.68 |
0.77 |
0.86 |
0.97 |
1.08 |
1.22 |
1.37 |
1.54 |
1.73 |
| Dementia |
0.81 |
0.91 |
1.02 |
1.14 |
1.28 |
1.43 |
1.61 |
1.8 |
2.02 |
2.26 |
2.54 |
| Others |
0.68 |
0.75 |
0.83 |
0.92 |
1.03 |
1.14 |
1.27 |
1.41 |
1.56 |
1.74 |
1.93 |
Service Insights
What Made Tele-Consulting the Dominant Segment in the Market in 2024?
The tele-consulting segment dominated the teleneurology market in 2024 due to its critical role in providing immediate, real-time access to neurologists, especially for urgent conditions like stroke and epilepsy. It bridges the gap between patients and specialists, particularly in rural or underserved regions where neurological expertise is limited. Tele-consulting enables faster diagnosis and treatment decisions, which are crucial for improving patient outcomes in time-sensitive neurological disorders.
Additionally, the widespread adoption of smartphones, tablets, and video conferencing technology has made tele-consulting more accessible and user-friendly. Healthcare providers and systems have increasingly integrated tele-consulting into standard care protocols, driven by favorable reimbursement policies and growing patient acceptance.
The tele-monitoring segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR in the upcoming period, owing to the rising demand for continuous, real-time management of chronic neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Advances in wearable devices and remote monitoring technologies allow healthcare providers to track patient health metrics outside of clinical settings, enabling proactive interventions. This approach improves patient outcomes while reducing hospital visits and healthcare costs. Growing patient preference for convenient, home-based care and increasing integration of AI and data analytics further drive the adoption of tele-monitoring services.
- In April 2025, Nihon Kohden launched its second-generation Live View Panel Pro™, a virtual health system for advanced remote neurophysiological assessment and care. The upgraded platform features real-time viewing, two-way intercom, and centralized data management to address staffing shortages and rising patient volumes. It streamlines decision-making, reduces unnecessary transfers, and enables neurology teams to deliver expert care across multiple locations.
Teleneurology Market Size 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Tele-Consulting |
4.18 |
4.63 |
5.11 |
5.65 |
6.25 |
6.91 |
7.63 |
8.43 |
9.32 |
10.29 |
11.37 |
| Tele-Monitoring |
2.02 |
2.32 |
2.66 |
3.04 |
3.48 |
3.98 |
4.55 |
5.19 |
5.93 |
6.76 |
7.71 |
| Tele-Education |
0.54 |
0.59 |
0.64 |
0.69 |
0.76 |
0.82 |
0.89 |
0.96 |
1.04 |
1.13 |
1.22 |
End Use Insights
How Does Providers Hold the Largest Share of the Teleneurology Market in 2024?
The providers segment dominated the market by holding the largest share in 2024. This is because healthcare institutions such as hospitals, clinics, and specialized neurological centers are the primary implementers of teleneurology services. Providers have increasingly adopted these solutions to address the shortage of neurologists and to expand access to expert care, especially in remote and underserved areas. Integrating teleneurology into their care models allows providers to improve patient outcomes through timely diagnosis and treatment while optimizing resource use.
Additionally, favorable reimbursement policies and government initiatives have encouraged providers to invest in telehealth infrastructure. Providers also benefit from improved workflow efficiency and the ability to serve a larger patient base without geographic limitations.
The patients segment is likely to expand at the fastest rate over the forecast period due to increasing patient awareness and demand for convenient, accessible neurological care from home. Advances in user-friendly telehealth technologies and mobile health apps empower patients to actively participate in managing their neurological conditions remotely. Additionally, the rising prevalence of chronic neurological disorders and an aging population are driving more patients to seek ongoing monitoring and consultations without frequent hospital visits. Growing acceptance of telemedicine, coupled with improved internet access, especially in rural areas, further accelerates patient adoption.
Teleneurology Market Size 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Patients |
2.36 |
2.66 |
2.99 |
3.37 |
3.8 |
4.27 |
4.81 |
5.41 |
6.09 |
6.85 |
7.71 |
| Providers |
3.38 |
3.75 |
4.15 |
4.61 |
5.12 |
5.68 |
6.3 |
6.99 |
7.75 |
8.6 |
9.54 |
| Payers |
1.01 |
1.13 |
1.26 |
1.41 |
1.57 |
1.76 |
1.96 |
2.19 |
2.44 |
2.73 |
3.04 |
Real-World Impact of Teleneurology
1. Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital
Challenge: Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital faced delays in stroke care due to limited neurologist access, leading to slow Alteplase administration and frequent patient transfers, causing treatment delays and revenue loss.
Solution: Partnering with Access TeleCare, the hospital launched a 24/7 teleneurology program that sped up stroke evaluations, reduced transfers, and improved Alteplase use. A dedicated neurologist team collaborated with on-site staff for rapid response, treatment, and seamless care transitions.
Result: The hospital achieved Primary Stroke Center certification, reduced transfers, and gained a 98% ROI. The program’s success led to system-wide expansion across four more hospitals.
2. Access TeleCare
The Challenge: An 86-year-old woman arrived at a crowded emergency department alone, confused, and unable to speak, with no access to her medical history, making neurological assessment difficult and risking delayed stroke diagnosis.
The Solution: A teleNeurologist from Access TeleCare quickly connected, conducted a focused exam, an, with support from the on-site team, accurately diagnosed a stroke and recommended IV thrombolytics. The medication was administered in just 34 minutes, 11 minutes faster than the national average.
The Result: This case demonstrates how teleNeurology enabled rapid, expert care despite communication and logistical barriers. The program ensured timely treatment, family involvement, seamless documentation, and improved patient outcomes through 24/7 remote neurologist access.
Regional Insights
What Made North America the Dominant Region in the Market?
North America dominated the teleneurology market by capturing the largest share in 2024. This is primarily due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and widespread adoption of telemedicine technologies. Supportive government policies, favorable reimbursement frameworks, and strong investments in digital health have further accelerated market growth. Additionally, widespread internet penetration and high digital literacy enable easy access to teleneurology services across urban and rural areas. The presence of key market players and ongoing innovations in telehealth platforms also contribute to North America’s leadership. The region also benefits from a high prevalence of neurological disorders and a significant shortage of neurologists, driving demand for remote care solutions.
- A comprehensive analysis combining data from five cohort studies across the U.S. and Canada estimates the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in North America at 572 per 100,000 among individuals aged 45 and older. Based on these findings and U.S. Census projections, the number of Americans with PD was about 680,000 in 2010, rising to 930,000 in 2020 and projected to reach 1.24 million by 2030.
The U.S. is the major contributor to the North America teleneurology market due to its advanced healthcare system and early adoption of telemedicine technologies. The high prevalence of neurological disorders, coupled with a shortage of specialists, has increased the demand for remote neurological care across the country. Supportive regulatory frameworks and reimbursement policies have encouraged widespread integration of teleneurology services in hospitals and clinics. Additionally, significant investments in digital health infrastructure and ongoing innovation by key market players further bolster the U.S.'s leading position in the market.
What Makes Asia Pacific the Fastest-Growing Market for Teleneurology?
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for teleneurology due to increasing healthcare digitization and rising awareness of neurological disorders across the region. Rapid urbanization and growing internet penetration are improving access to telehealth services, especially in remote and underserved areas. Additionally, many countries in the region are investing in healthcare infrastructure and adopting supportive policies to encourage telemedicine adoption. The large patient population coupled with a shortage of neurologists further fuels demand for remote neurological care.
India is a major contributor to the Asia Pacific teleneurology market due to its large population and growing burden of neurological disorders. The country faces a significant shortage of neurologists, especially in rural areas, which drives demand for remote neurological consultations and monitoring. Rapid improvements in internet connectivity and smartphone penetration have made telehealth more accessible to a wider population. Additionally, supportive government initiatives promoting digital healthcare and telemedicine are accelerating market growth.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, is leveraging digital health to transform healthcare delivery and empower citizens through platforms like eSanjeevani. As a cloud-based telemedicine solution, eSanjeevani enables remote consultations across geographic boundaries and serves as the National Telemedicine Service. With over 311 million patients served as of November 2024, it has significantly improved access to healthcare, demonstrating its role as a transformative force in India’s public health system.
Region-Wise Breakdown of the Teleneurology Market
|
Region
|
Market Size (2024)
|
Projected CAGR (2025-2034)
|
Key Growth Factors
|
Key Challenges
|
Market Outlook
|
|
North America
|
USD 2.8 Bn
|
5.97%
|
Strong telemedicine infrastructure, supportive reimbursement policies, high digital health adoption
|
Regulatory complexity, digital divide in rural areas
|
Dominant market with robust growth
|
|
Asia Pacific
|
USD 2.0 Bn
|
6.98%
|
Rapid healthcare digitization, improving connectivity, large underserved populations
|
Limited digital literacy, rural infrastructure challenges
|
Fastest-growing region
|
|
Europe
|
USD 1.6 Bn
|
9.86%
|
Growing investments in digital health, aging population, increasing neurological disorder prevalence
|
Varying national regulations, uneven infrastructure across countries
|
Steady growth
|
|
Latin America
|
USD 0.5 Bn
|
5.49%
|
Growing telemedicine adoption, digital health integration in neurology, increasing healthcare accessibility
|
Infrastructure limitations, inconsistent telehealth policy frameworks
|
Developing market with steady growth
|
|
MEA
|
USD 0.3 Bn
|
4.75%
|
Expanding telemedicine infrastructure, regulatory support, and pilot telestroke programs in some countries
|
Limited coverage, technology access barriers, regional disparities
|
Emerging market
|
Teleneurology Market Value Chain Analysis
1. Technology Development
This stage involves the research, design, and development of software platforms, diagnostic tools, and communication technologies tailored to neurology. Companies invest in AI, cloud computing, and telecommunication advancements to ensure secure, real-time, and accurate remote neurological consultations.
2. Platform & Service Integration
In this stage, developed technologies are integrated into healthcare systems, including EHR (Electronic Health Records), imaging systems, and patient portals. The goal is to create seamless workflows for neurologists and healthcare staff, improving operational efficiency and enabling better clinical decision-making.
3. Regulatory Compliance & Certification
Before deployment, teleneurology platforms must comply with regional healthcare regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in the EU. This ensures patient data privacy, secure transmission of medical information, and standardized practices across providers, building trust among users.
4. Service Delivery (Healthcare Providers)
Healthcare providers, including hospitals, neurology clinics, and telemedicine networks, use the integrated systems to deliver consultations, follow-ups, and remote monitoring. This is the most visible part of the value chain, directly impacting patient care and outcomes, especially for time-sensitive conditions like stroke.
5. Patient Interaction & Monitoring
Patients engage with teleneurology platforms through mobile apps, video consultations, or wearable devices for real-time monitoring and communication. This stage emphasizes patient experience, adherence to treatment plans, and ongoing management of chronic neurological conditions from the comfort of home.
6. Reimbursement & Feedback Loop
After service delivery, providers seek reimbursement through insurance or government healthcare programs, depending on regional frameworks. Feedback from both clinicians and patients is collected to enhance platform usability, improve care protocols, and guide future technological developments.
Teleneurology Market Companies
1. Providence
Providence offers a comprehensive TeleNeurology suite, including Emergent TeleNeurology, TeleNeuroHospitalist, and TeleEEG services, to provide rapid specialist consultations and follow up care across its network. Its decentralized virtual neurology model improves access, reduces unnecessary transfers, and supports continuous coverage even in small and rural hospitals.
2. Teladoc Health, Inc.
Teladoc Health is a global leader in telemedicine, offering AI-driven virtual care platforms and services across more than 130 countries. Through strategic partnerships with health systems and continuous expansion, such as the acquisition of InTouch Health, it delivers scalable teleneurology solutions and acute stroke consultations that significantly reduce treatment delays.
3. Eagle Telemedicine
Eagle Telemedicine has expanded its specialty offerings to include Pediatric TeleNeurology, improving access for children with neurological conditions, especially in underserved areas. Its Virtual Partnership model delivers timely neurology consultations to community hospitals, reducing patient transfers and enhancing care quality close to home.
4. Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC)
MUSC’s Telestroke Program brings high-quality stroke care, including teleneurology consultations, to rural hospitals, helping combat the stark neurologist-to-patient ratio in South Carolina. By collaborating with community hospitals, MUSC improves access to timely neurological assessments and treatment in the “Stroke Belt” region.
5. Blue Sky Telehealth
Blue Sky Telehealth operates one of the largest teleneurology networks, delivering 24/7 access to neurologists across more than 300 hospitals in 26 states with under one-minute response times. Its Teleneurohospitalist and remote EEG services enhance inpatient neurological care and diagnostic capacity in partnering hospitals.
6. American Well (Amwell)
Amwell provides a robust telehealth platform that integrates seamlessly with EHR systems and supports tele-consulting for neurological care, including stroke and chronic condition management. Its widespread presence across the U.S., strong tech integrations, and partnerships (e.g., with Epic and Philips) make it a pivotal player in advancing teleneurology.
7. Sevaro Health, Inc.
Sevaro Health delivers rapid-response teleneurology and neurocritical care services, offering stroke alert response times as fast as 45 seconds, and seamless EMR integration. Its hybrid tele-on-site model supports hospitals with urgent neurological needs and streamlines layered care delivery.
8. Access TeleCare, LLC
Access TeleCare connects expert neurologists to hospitals lacking in-house neurology resources, enabling swift and reliable care for acute neurological needs. The company’s decentralized model and data-driven support enhance care accessibility particularly in underserved regions.
9. TeleSpecialists
TeleSpecialists provides 24/7 TeleStroke and TeleNeuroHospitalist services to hospitals nationwide, delivering rapid emergency consultation and structured inpatient rounding via telemedicine. Its services are enhanced by a robust quality management framework, delegated credentialing, and seamless EMR workflow integration, ensuring high-standard, on-demand neurological care.
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, TeleSpecialists, LLC launched its EMS Integration service to enhance stroke care by enabling real-time collaboration between neurologists, EMS teams, and hospitals during patient transport. This early teleneurology involvement accelerates stroke evaluations and reduces door-to-needle times. Patients benefit from faster treatment, including immediate CT scans upon hospital arrival.
- In November 2023, Sevaro Health Inc. launched Nirvana Notes, an intuitive teleneurology documentation app designed by neurologists for teleneurology practice. Part of the Synapse AI platform, it enables streamlined, consistent documentation of H&P, imaging review, and consult notes within minutes. Accessible via mobile or web, it enhances clinical decision-making and supports higher-quality remote neurological care.
- On March 7, 2023, NIMHANS and the Department of Health launched two key initiatives in neurology: the NEPSIG survey in Gowribidanur and a teleneurology program in Chikkaballapur. Implemented under the Karnataka Brain Health Initiative (KaBHI), these aim to improve understanding and accessibility of neurological care in the community.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Application
- Dementia
- Epilipesy
- Headache
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson
- Stroke
- Others
By Service
- Tele-Consulting
- Tele-Education
- Tele-Monitoring
By End Use
- Patients
- Payers
- Providers
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa

