Diagnostic Testing Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
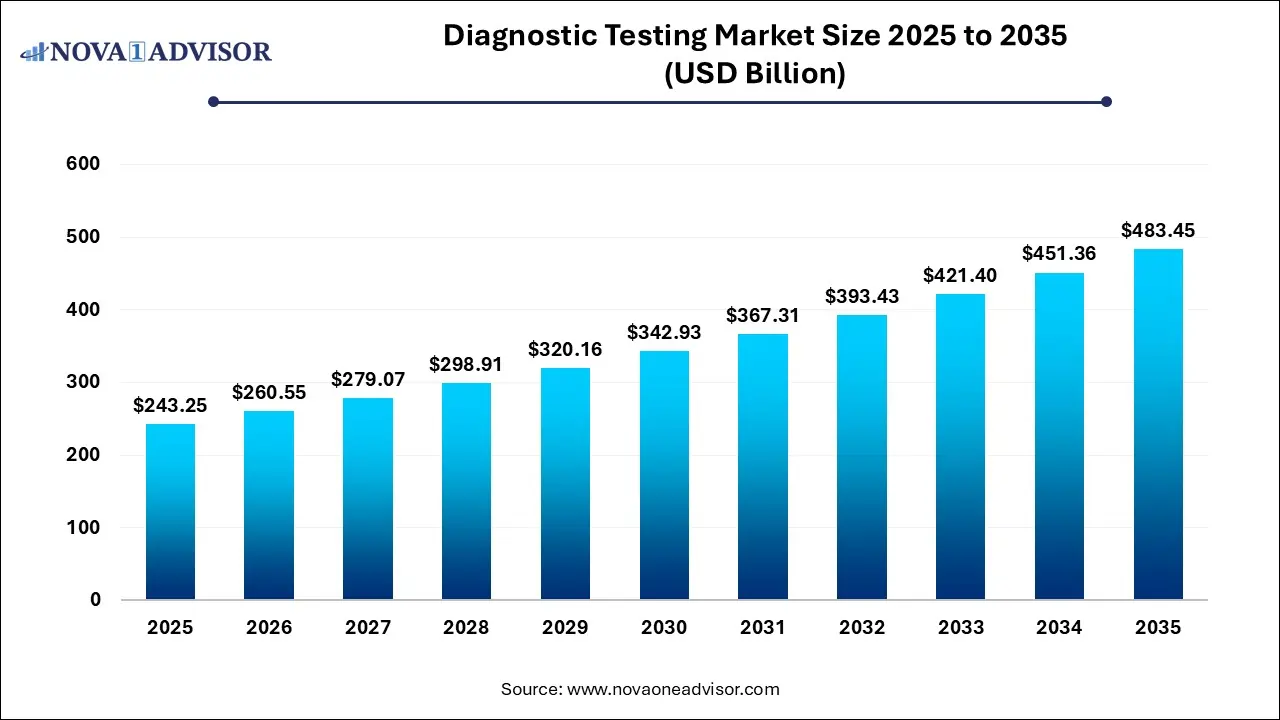
The global diagnostic testing market size was estimated at USD 243.25 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 483.45 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 7.11% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
Market Overview
The diagnostic testing market plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare systems, facilitating early disease detection, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. This expansive sector spans clinical laboratory services, home diagnostic kits, advanced imaging modalities, and molecular testing technologies. As healthcare becomes increasingly personalized and data-driven, diagnostic tools are evolving rapidly to meet demands for speed, accuracy, and patient convenience.
The market is experiencing robust growth due to rising incidences of chronic diseases, growing geriatric population, heightened awareness about preventive health, and advancements in diagnostic technologies. The COVID-19 pandemic further highlighted the importance of diagnostic infrastructure and propelled public and private investments into expanding testing capabilities. From infectious disease testing to genetic screening, the range of diagnostics has significantly widened, catering to both clinical and at-home segments.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Surge in Home-Based Testing: Increasing consumer preference for privacy and convenience is driving the popularity of home diagnostics, especially for pregnancy, glucose, and COVID-19 testing.
-
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being incorporated to analyze complex diagnostic data, especially in imaging, genomics, and pathology, enhancing diagnostic speed and accuracy.
-
Growth in Molecular Diagnostics: Techniques such as PCR and NGS are being widely adopted for infectious disease testing, cancer screening, and genetic disorders.
-
Telehealth Integration: Diagnostics are increasingly being linked with telemedicine services, offering patients end-to-end care from testing to treatment.
-
Expansion of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT): POCT enables faster diagnosis at or near the patient site, making it a preferred option in emergency and remote settings.
-
Miniaturization and Microfluidics: Portable diagnostic tools are being developed using microfluidic platforms, enabling complex assays to be conducted with minimal resources.
-
Direct-to-Consumer Testing Models: Companies are offering diagnostic test kits directly to consumers, bypassing traditional healthcare providers.
-
Rise in Companion Diagnostics: These are used alongside targeted therapies in oncology, helping to identify patients most likely to benefit from specific treatments.
Diagnostic Testing Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 260.55 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 483.45 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 7.11% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Application, Approach, Solution, Technology, Mode of Testing, Sample Type, Testing Type, Age, Distribution Channel, End User, Geography |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
F-Hoffman La-Rcohe Ltd. (Switzerland), Danaher (US), BD (US), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (US), ACON Laboratories Inc. (US), Hemosure, Inc. (US), MicroGen Diagnostics (US), Grifols, S.A (Spain), BODITECH MED INC. (South Korea), Chembio Diagnostic Systems, Inc. (US), Nanoentek (South Korea), DiaSorin S.p.A. (Italy), Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (US), BIOMEDOMICS INC (US), EKF Diagnostics Holdings plc (UK), Siemens Healthcare GmbH (Germany), PerkinElmer Inc. (US), bioMérieux SA (France), ARKRAY USA, Inc. (US), Biohit Oyj (Finland), Quidel Corporation (US), Illumina, Inc. (US) |
Market Driver: Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The increasing global burden of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and respiratory illnesses is a significant driver of the diagnostic testing market. According to WHO, non-communicable diseases account for over 70% of all global deaths. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential to effectively manage these conditions, improve outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs. As patients shift toward preventive care models, regular diagnostic monitoring becomes central to disease management. Innovations such as continuous glucose monitoring for diabetics or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin tests for cardiac events underscore the critical role diagnostics play in improving patient quality of life.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Advanced Diagnostic Technologies
While diagnostic innovations promise accuracy and rapidity, their high cost remains a barrier, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Advanced imaging equipment, NGS platforms, and AI-integrated diagnostic tools require significant capital investment and technical expertise, limiting widespread adoption. Additionally, disparities in healthcare infrastructure and reimbursement policies affect access to these technologies. For instance, a full genetic panel test may cost hundreds of dollars and is often not covered under basic health insurance, discouraging usage despite clinical need.
Market Opportunity: Integration of Wearable Devices and Diagnostics
The merging of wearable technologies with diagnostic platforms offers immense growth potential. Devices such as smartwatches, biosensors, and fitness bands can now track vital health metrics and serve as preliminary screening tools for conditions like atrial fibrillation, sleep apnea, or even glucose levels. When integrated with cloud-based diagnostic algorithms, these wearables can trigger alerts for further lab testing, creating a continuum of care. Companies investing in interoperable ecosystems stand to capture a broad consumer base focused on wellness and proactive health management.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Clinical diagnostics remain the cornerstone of the diagnostic testing market. Hospitals and laboratories perform a vast majority of diagnostic procedures, including blood panels, histopathology, and infectious disease testing. Their accuracy, credibility, and regulatory compliance ensure continued dominance. High patient volumes and complex testing requirements such as cancer biopsies or autoimmune panel screenings necessitate specialized laboratory environments and professional interpretation.
In contrast, home diagnostics are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, propelled by innovations in self-testing kits and increasing consumer health awareness. The COVID-19 pandemic normalized self-swabbing and home antigen testing. Similar trends are now visible for chronic disease monitoring, fertility tracking, and genetic testing, aided by smartphon e-compatible devices and easy online ordering.
By Application
Oncology holds the largest share within diagnostic applications. The necessity for early cancer detection and the rise of targeted therapies have fueled demand for imaging diagnostics, tumor markers, and genomic profiling. Diagnostic companies are developing liquid biopsy tools and circulating tumor DNA tests to identify cancers in early, more treatable stages. Breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers see significant test volume.
Neurology-related diagnostics are gaining ground as neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy rise with aging populations. Advanced imaging, cerebrospinal fluid markers, and genetic screenings are being used more frequently. AI-driven neuroimaging analysis is also improving diagnostic accuracy, propelling growth in this segment.
By Approach
In-vitro diagnostic (IVD) instruments dominate due to their ability to deliver high-throughput, laboratory-grade results across a wide range of conditions. Automated platforms and multiplex assays are common in hospital labs and diagnostic chains. These include immunoassays, hematology analyzers, and molecular diagnostic systems.
Point-of-care testing (POCT), however, is rapidly gaining traction for its ability to deliver immediate results in clinics, ambulances, and even homes. Glucose meters, rapid antigen tests, and portable blood analyzers enhance access to diagnostics, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
By Solution
Diagnostic products, such as test kits, reagents, instruments, and software, dominate the market due to their one-time or consumable-based sales model. Companies invest heavily in proprietary platforms, such as Roche’s Cobas systems or Abbott’s ID NOW, to lock customers into recurring reagent sales.
Meanwhile, diagnostic services are becoming an essential revenue stream, particularly in specialized and genetic testing. Companies like Labcorp and Quest Diagnostics offer full-service lab testing with physician reporting, driving long-term value through partnerships with hospitals and research institutes.
By Technology
PCR-based technology is the most widely used due to its accuracy and speed, especially in infectious disease diagnostics such as COVID-19, HIV, and influenza. PCR is a gold standard for molecular diagnostics and remains integral for high-sensitivity applications.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS), although still relatively niche, is the fastest-growing technology segment. It enables comprehensive genomic profiling, making it indispensable in oncology, rare diseases, and personalized medicine. Companies like Illumina and Thermo Fisher Scientific are investing heavily in miniaturized, cost-effective NGS platforms for broader clinical use.
By Mode of Testing
Prescription-based testing remains dominant due to its integration within hospital and physician-led care models. Tests for cholesterol, kidney function, or autoimmune diseases typically require clinical supervision.
However, over-the-counter (OTC) testing is gaining popularity among health-conscious consumers. Examples include home pregnancy tests, allergy panels, and food intolerance kits. E-commerce platforms and social media campaigns are promoting direct-to-consumer diagnostics, lowering entry barriers.
By Sample Type
Blood remains the primary sample type for most diagnostic tests due to its ability to provide comprehensive information on a wide range of diseases. It is standard for hematology, biochemistry, and serology-based diagnostics.
Saliva is gaining popularity as a non-invasive sample type, particularly in genetic testing and hormone level analysis. Companies like 23andMe and AncestryDNA have built entire testing models around saliva samples, demonstrating its viability and consumer acceptance.
By Testing Type
Biochemistry tests dominate due to their broad use in liver, kidney, and metabolic panel assessments. These are essential for routine health checkups and chronic disease management.
Microbiology is expanding as awareness about antimicrobial resistance and infectious diseases grows. Cultures, sensitivity testing, and pathogen identification remain crucial, particularly in hospital-acquired infection settings.
By Age
The adult and geriatric segment dominates the diagnostic testing market due to the higher prevalence of chronic illnesses, cancer, and neurodegenerative conditions in older adults. Regular screenings and preventive health checks are more common in this age group.
Pediatrics, though a smaller segment, is crucial for early detection of congenital diseases, allergies, and developmental conditions. Newborn screening programs are expanding globally, especially in developed countries.
By Distribution Channel
Direct tenders to government and large hospital networks dominate, especially for equipment and reagents used in centralized labs. Bulk procurement and long-term contracts provide vendors with stability and scale.
Online sales are rapidly rising, especially for OTC diagnostics and home test kits. Consumers can order kits through company websites or platforms like Amazon, with results accessible via mobile apps.
By End User
Hospitals and diagnostic centers remain the largest end-users due to infrastructure, specialist availability, and high patient footfall. These institutions use complex diagnostic systems and serve as referral centers.
Homecare and ambulatory surgical centers are growing due to shifts in healthcare delivery models. Minimally invasive procedures and remote monitoring tools are making it easier to manage patients outside traditional hospital settings.
By Regional
North America, particularly the United States, dominates the diagnostic testing market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare spending, and significant investment in R&D. The region is home to leading diagnostic companies such as Abbott, Thermo Fisher, and Labcorp. Favorable reimbursement policies, regulatory support, and public-private partnerships, especially during the pandemic, have further strengthened the diagnostic landscape.
Asia-Pacific is witnessing rapid growth due to rising healthcare awareness, growing middle-class population, and government initiatives to improve diagnostic capabilities. Countries like India and China are investing in expanding diagnostic labs, and private players are launching home-testing kits to cater to the tech-savvy population. Moreover, regional medical tourism is boosting demand for high-quality diagnostics at competitive prices.
Key Market Developments
-
March 2025: Abbott launched its new wearable glucose monitoring system, Libre 4, with real-time diagnostic capabilities and mobile integration.
-
January 2025: Labcorp expanded its genetic testing services by acquiring a genomics firm focused on oncology.
-
November 2024: Siemens Healthineers unveiled a compact POCT device for cardiovascular diagnostics at MEDICA.
-
August 2024: Thermo Fisher Scientific introduced an AI-powered pathology imaging platform for cancer diagnostics.
-
June 2024: Roche Diagnostics received CE-IVD approval for its COVID-19 and influenza combo test kit.
Diagnostic Testing Market Players
- F-Hoffman La-Rcohe Ltd. (Switzerland)
- Danaher (US)
- BD (US)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (US)
- ACON Laboratories Inc. (US)
- Hemosure, Inc. (US)
- MicroGen Diagnostics (US)
- Grifols, S.A (Spain)
- BODITECH MED INC. (South Korea)
- Chembio Diagnostic Systems, Inc. (US)
- Nanoentek (South Korea)
- DiaSorin S.p.A. (Italy)
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (US)
- BIOMEDOMICS INC (US)
- EKF Diagnostics Holdings plc (UK)
- Siemens Healthcare GmbH (Germany)
- PerkinElmer Inc. (US)
- bioMérieux SA (France)
- ARKRAY USA, Inc. (US)
- Biohit Oyj (Finland)
- Quidel Corporation (US)
- Illumina, Inc. (US)
- Lamdagen Corporation (US)
- LifeSign LLC. (US)
- Medixbiochemica (Finaland)
- Nova Biomedical (US)
- Ortho Clinical Diagnostics (US)
- Sannuo Biosensing Co., Ltd. (US)
- STRECK (US)
- Sysmex Corporation (Japan)
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Diagnostic Testing market.
By Type
- Clinical Diagnostic
- Home Diagnostic
By Application
- Cardiology
- Oncology
- Neurology
- Orthopedics
- Gastroenterology
- Gynecology
- Odontology
- Others
By Approach
- Molecular Diagnostic Instrument
- In-Vitro Diagnostic Instrument
- Point Of Care Testing Instrument
By Solution
By Technology
- Immunoassay-Based
- PCR-Based
- Next-generation Sequencing
- Spectroscopy-Based
- Chromatography-Based
- Microfluidics
- Substrate Technology
- Others
By Mode of Testing
- Prescription Based Testing
- OTC Testing
By Sample Type
- Urine
- Saliva
- Blood
- Hair
- Sweat
- Others
By Testing Type
- Biochemistry
- Hematology
- Microbiology
- Histopathology
- Others
By Age
- Pediatric
- Adult & Geriatric
By Distribution Channel
- Direct Tenders
- Retail Sales
- Online Sales
By End User
- Hospitals, Diagnostic Center
- Research Labs and Institutes
- Research Institute
- Homecare
- Blood Banks
- Specialty Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

