Spheroids Market Size and Growth
The Spheroids market size was exhibited at USD 922.25 million in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 6,797.68 million by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 22.11% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
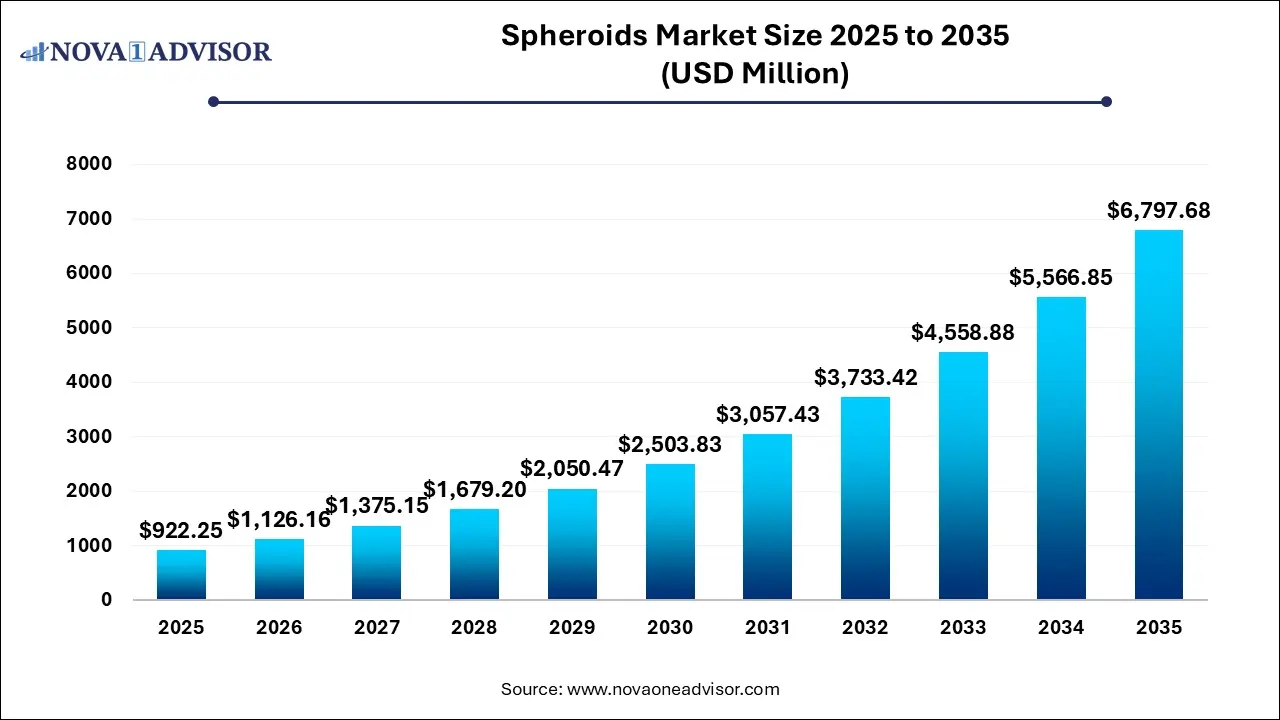
Key Takeaways:
- The multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS) segment accounted for a larger revenue share of 29% in 2025
- The hanging drop method segment accounted for a larger revenue share of 32% in 2025 and is expected to have a fastest growth rate over the forecast period.
- The cell line segment accounted for a larger revenue share of 57% in 2025.
- The developmental biology segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 31% in 2025.
- The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 48% in 2025.
- North America accounted for the largest revenue share of 37% in 2025.
Market Overview
The spheroids market has experienced significant expansion over the last decade, driven by the growing applications of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture techniques across pharmaceutical research, regenerative medicine, and personalized therapeutics. Spheroids multicellular aggregates that mimic the complex in vivo microenvironment of tissues offer several advantages over traditional 2D cell cultures. These advantages include improved cell-cell interactions, more accurate modeling of physiological conditions, and enhanced predictability of drug responses. The market's rapid acceleration is a testament to the rising demand for more realistic preclinical testing models and advancements in cell culture technologies.
As biopharmaceutical companies increasingly rely on 3D models for drug efficacy and toxicity screening, spheroids have become critical tools. They are also extensively utilized in cancer research, as multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS) provide a more relevant model of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Furthermore, government and private funding in stem cell research and tissue engineering are fueling the development of innovative spheroid-based products and protocols. With the market evolving quickly, companies are collaborating with academic institutions and research centers to enhance the reliability and scalability of spheroid models.
Major Trends in the Market
- Increased Adoption of 3D Cell Culture in Drug Discovery: Pharmaceutical companies are moving away from 2D cultures toward 3D spheroids to improve preclinical accuracy.
- Rise in Personalized Medicine Applications: Patient-derived spheroids are gaining popularity in tailoring treatment plans for cancer and chronic diseases.
- Integration with Organoids and Organ-on-a-Chip Technologies: Combining spheroids with microfluidic platforms enhances physiological relevance.
- Automation and High-Throughput Screening (HTS): Automated systems for generating and analyzing spheroids are reducing labor and enhancing scalability.
- Shift Toward Stem Cell-Based Spheroids: iPSC-derived spheroids are providing promising platforms for developmental biology and regenerative medicine.
- Academic-Industry Collaborations: Growing partnerships between biotech firms and universities are fostering innovations in spheroid methodologies.
- Increased Funding in Regenerative Medicine: Government investments are enabling the exploration of spheroids in tissue repair and organ regeneration.
Report Scope of Spheroids Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 1,126.16 Million |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 6,797.68 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 22.11% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Method, Source, Application, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; Corning Incorporated; Merck KGaA; Lonza Group AG; InSphero AG; Greiner Bio-One International GmbH; 3D Biotek LLC; CN Bio Innovations; Kuraray Co., Ltd.; Tecan Group Ltd. |
Key Market Driver
Rising Demand for Advanced In Vitro Models in Drug Testing
One of the most powerful drivers of the spheroids market is the increasing demand for predictive and physiologically relevant in vitro models in drug discovery and toxicology screening. Traditional 2D cultures often fail to replicate the complexities of human tissues, leading to high attrition rates during clinical trials. Spheroids, especially tumor spheroids, offer superior modeling of tissue architecture, gradients of oxygen and nutrients, and drug penetration. These advantages lead to better correlation with in vivo results and more informed go/no-go decisions during drug development. This demand is further intensified by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA encouraging the use of alternative models that reduce animal testing.
Key Market Restraint
High Cost and Technical Complexity of Spheroid Culture Techniques
Despite their benefits, the implementation of spheroid technologies remains limited in some settings due to high costs and technical hurdles. Culturing spheroids often requires specialized plates, media, and imaging equipment. Moreover, maintaining uniformity and reproducibility across batches remains a challenge, especially in high-throughput environments. Researchers must undergo rigorous training, and protocol optimization is often needed based on cell type and application. These limitations deter smaller laboratories and institutions with limited budgets from adopting spheroid-based approaches widely, posing a restraint to overall market penetration.
Key Market Opportunity
Emergence of Personalized Spheroids for Tailored Therapeutics
The emergence of personalized medicine presents a promising opportunity for the spheroids market. Patient-derived spheroids, especially from tumor biopsies, can be cultured and tested with multiple drug combinations to predict therapeutic outcomes. This ex vivo testing can help oncologists make informed decisions about treatment regimens, thereby improving survival rates and reducing unnecessary side effects. Personalized spheroid models are also useful in genetic and rare diseases where conventional treatment data is lacking. As sequencing technologies and single-cell analysis become more affordable, the integration of patient data with spheroid testing is poised to revolutionize individualized healthcare.
Segmental Analysis
By Type Outlook
Multicellular Tumor Spheroids (MCTS) dominated the market in 2025, and this segment continues to hold the lion’s share.
MCTS remain the most extensively used spheroid type, particularly in oncology drug development. Their structural similarity to in vivo tumors makes them ideal for modeling cancer cell behavior, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance mechanisms. MCTS have been pivotal in anti-cancer compound screening and understanding tumor microenvironments. They are also extensively utilized by biotech firms to identify immunotherapeutic targets and simulate drug penetration barriers. As cancer remains a leading global burden, the dominance of MCTS is expected to continue in both academic and commercial settings.
Embryoid Bodies are projected to be the fastest-growing segment.
Embryoid bodies, which arise from pluripotent stem cells, are gaining momentum in developmental biology and tissue engineering. They mimic early embryonic development and can differentiate into all three germ layers. With the boom in stem cell research and the application of iPSCs, embryoid bodies are increasingly used for modeling diseases, organogenesis, and cell lineage specification. Their versatility and ability to mimic embryonic conditions make them valuable for understanding developmental disorders and screening teratogenic drugs, contributing to their rapid growth in the market.
By Method Outlook
Low Cell Attachment Plates were the most widely adopted method for spheroid generation.
These plates facilitate spontaneous aggregation of cells into spheroids without the need for additional scaffolding or matrices. Their simplicity, reproducibility, and compatibility with automated systems make them attractive for high-throughput drug screening. Pharmaceutical companies rely heavily on this method for generating consistent tumor spheroids, enabling large-scale compound testing with minimal variability. The design of the plates also supports scalability, essential for commercial research settings.
Hanging Drop Method is emerging as the fastest-growing technique.
Despite being more labor-intensive, the hanging drop method offers high control over spheroid size and homogeneity, crucial for experimental reproducibility. It is particularly useful in academic and specialized research settings, where precision and spheroid customization are essential. Its application in developmental biology and stem cell studies is expanding, and recent innovations have allowed semi-automated versions to bridge the scalability gap, propelling growth in this segment.
By Source Outlook
Cell Line-based spheroids accounted for the largest share of the market.
Readily available and easy to culture, cell line-based spheroids are the go-to choice for most research labs and pharmaceutical companies. Their stable genetic makeup, cost-effectiveness, and repeatability make them ideal for protocol standardization and early-phase screening. Common cell lines like HeLa, MCF-7, and HepG2 are routinely used in cancer, hepatotoxicity, and neurological studies, offering a reliable platform for proof-of-concept research.
iPSCs Derived Cells are witnessing the fastest growth.
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived spheroids have opened new avenues for personalized disease modeling and regenerative medicine. They can be generated from patient-specific cells, offering unmatched genetic relevance and disease specificity. iPSC-derived spheroids are particularly useful in neurodegenerative and cardiovascular disease research, where animal models often fail. As protocols become more refined and scalable, this segment is experiencing exponential growth.
By Application Outlook
Drug Toxicity & Efficacy Testing was the dominant application segment.
Spheroids are revolutionizing preclinical testing by providing more accurate, predictive models for drug responses. Their 3D structure allows for better simulation of pharmacokinetics and drug diffusion, which is critical for assessing cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and therapeutic efficacy. Major pharmaceutical companies have adopted spheroids into their compound screening pipelines to reduce clinical trial failures, improve safety profiles, and enhance lead optimization.
Regenerative Medicine is the fastest-growing application segment.
Spheroids composed of stem cells or progenitor cells are being explored for tissue regeneration in orthopedic, cardiac, and neural applications. Their ability to secrete extracellular matrices and growth factors makes them suitable for scaffolding or direct implantation in injured tissues. The promise of reduced immune rejection and better integration is driving investment in regenerative therapies using spheroids, particularly in the Asia Pacific and North America.
By End Use Outlook
Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industries led the end-use segment.
These industries rely on spheroids for lead identification, toxicity profiling, and validating drug candidates under near-physiological conditions. The growing need for predictive testing and alternative models has made spheroids a staple in preclinical R&D. Integration with robotic systems and image-based analytics has also made these models more amenable to industrial environments, enhancing their appeal.
Academic & Research Institutes are the fastest-growing end users.
With increased funding from government and private institutions, academic labs are expanding their use of spheroids for both basic and translational research. Their ability to generate customized, disease-specific spheroids makes them ideal for niche research. The academic sector also plays a crucial role in developing novel spheroid methodologies and validating them through peer-reviewed studies, contributing significantly to market expansion.
By Regional Analysis
North America dominated the spheroids market in 2025.
The region benefits from a robust biopharmaceutical industry, strong research infrastructure, and high investment in advanced therapeutics. The U.S., in particular, has seen a surge in spheroid adoption due to its emphasis on reducing animal testing and enhancing clinical predictability. Government agencies like the NIH and FDA continue to support 3D model development through grants and regulatory incentives. Moreover, partnerships between leading biotech firms and academic institutions have led to the rapid commercialization of spheroid-based platforms.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing regional market
Countries like China, Japan, and India are investing heavily in biotechnology, stem cell research, and personalized medicine. Government-backed research initiatives, rising healthcare expenditures, and the establishment of translational medicine hubs have propelled the adoption of spheroid technologies. The region also benefits from a large patient population for clinical trials and cost advantages for outsourcing R&D. The increasing collaboration between global pharmaceutical companies and local CROs is further accelerating spheroid utilization.
Some of The Prominent Players in The Spheroids market Include:
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Thermo Fisher Scientific expanded its Gibco™ 3D cell culture product line with new spheroid-optimized media to support scalable production of tumor spheroids for high-throughput applications.
- In February 2025, Corning Inc. introduced an advanced low-attachment plate design with improved well geometry for enhanced uniformity of spheroid formation.
- In January 2025, Lonza Group AG announced a strategic collaboration with a leading academic center in Switzerland to explore iPSC-derived spheroids for cardiac regeneration.
- In November 2024, 3D Biotek launched a customizable spheroid generation kit aimed at academic researchers and small biotech firms focusing on cancer and neural studies.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Spheroids market
Type
- Multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS)
- Neurospheres
- Mammospheres
- Hepatospheres
- Embryoid bodies
Method
- Micropatterned Plates
- Low Cell Attachment Plates
- Hanging Drop Method
- Others
Source
- Cell Line
- Primary Cell
- iPSCs Derived Cells
Application
- Developmental Biology
- Personalized Medicine
- Regenerative Medicine
- Disease Pathology Studies
- Drug Toxicity & Efficacy Testing
End Use
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical industries
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Hospitals and Diagnostic centers
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

