Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Size & Share Report, 2034
The global therapeutic drug monitoring market size was valued at USD 3.15 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 4.28 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.11% from 2025 to 2034. The growth of the therapeutic drug monitoring market is driven by the increasing chronic disease burden, rising emphasis on personalized medicine and precision dosing, focus on patient safety and the surge in investments for adopting advanced TDM systems.
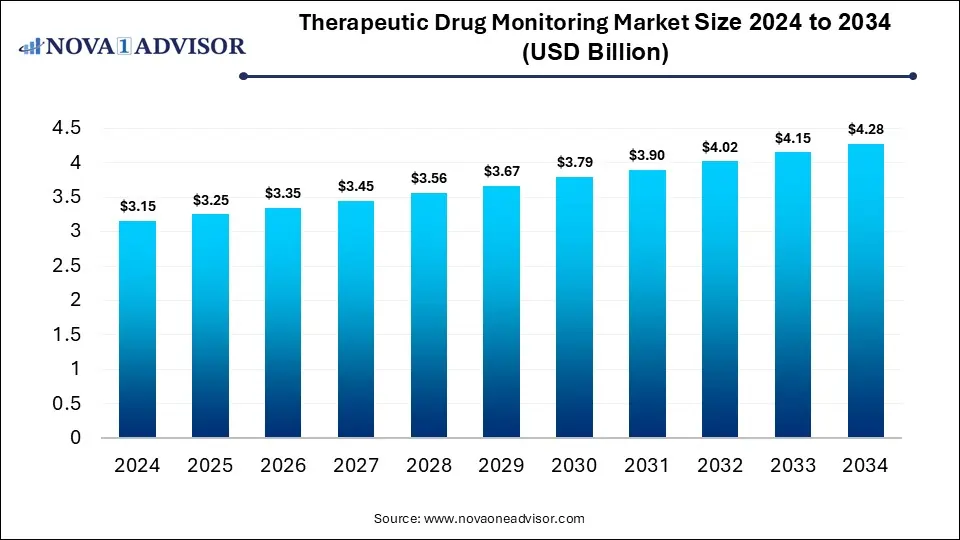
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the global therapeutics drugs monitoring market in 2024 with a revenue share of 43%.
- The U.S. dominated the market in the region with a market share of market share of 89% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific therapeutics drugs monitoring market is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 4.1% over the forecast period.
- The consumables segment dominated the market share with 66% in 2024.
- The equipment segment is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period.
- The antiarrhythmic segment dominated the market in 2024.
- The immunosuppressants segment is expected to grow fastest, with a compounded annual growth rate of 5.13% over the forecast period.
- The hospital segment dominated the market share in 2024.
- The diagnostics segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The global Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM) market is gaining significant traction as personalized medicine becomes central to clinical decision-making. TDM is a specialized clinical practice that involves measuring specific drug levels in a patient’s blood to maintain a constant concentration within a therapeutic window. It is primarily used for drugs that have a narrow therapeutic range, considerable inter-patient variability, or the potential for adverse drug reactions.
The increased prevalence of chronic diseases such as epilepsy, cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and autoimmune diseases has led to widespread adoption of complex drug regimens. This, in turn, necessitates the use of TDM to optimize dosing, improve therapeutic efficacy, and reduce toxicity risks. Additionally, rising concerns over adverse drug reactions—which remain one of the leading causes of hospitalization and mortality globally—have made TDM essential in modern clinical settings.
Technological advancements in laboratory instruments, increasing access to healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies, and growing awareness among healthcare providers about the importance of precision dosing are driving the expansion of the market. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into pharmacokinetics is opening new frontiers for real-time therapeutic monitoring.
With the continuous innovation of high-throughput testing devices and bioanalytical methods such as immunoassays, chromatography, and mass spectrometry, TDM is moving beyond traditional hospital labs into specialized diagnostic centers and even near-patient testing environments. As the global healthcare landscape shifts toward personalized, data-driven medicine, the TDM market is set to become a cornerstone in managing therapeutic interventions for complex disease profiles.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of Personalized and Precision Medicine: TDM is becoming a foundational tool in tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenomics.
-
Shift Toward High-Sensitivity Analyzers: Clinical labs are increasingly adopting advanced chromatography and mass spectrometry technologies for greater sensitivity and specificity.
-
Integration of AI and Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models are being developed to analyze TDM data and support dose prediction, enhancing clinical decisions.
-
Expansion of TDM to Biologics and Monoclonal Antibodies: As the use of biologic therapies rises, especially in oncology and autoimmune diseases, TDM is expanding beyond small-molecule drugs.
-
Outsourcing to Diagnostic Laboratories: Hospitals are increasingly outsourcing TDM services to accredited third-party diagnostic labs with specialized instruments.
-
Increased Focus on Pediatric and Geriatric Dosing: Age-specific pharmacokinetic variations are prompting the use of TDM in vulnerable populations.
-
Regulatory Push for Safe Drug Use: Guidelines from health bodies such as the FDA and EMA are emphasizing therapeutic monitoring to mitigate drug-related complications.
Where is AI Finding Applications in the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market?
Artificial intelligence (AI) can potentially transform therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) workflows. AI algorithms can be used for analyzing patient data such as genetic makeup and medical history for predicting patient response to a particular medication. Machine learning algorithms can be applied for predicting drug-drug interactions, further uncovering potential interactions among different drugs and mitigating the risk of adverse drug events, leading to improved patient outcomes. Automation of several aspects of TDM, including data collection, analysis and interpretation with AI-powered tools can potentially enhance the accuracy and efficiency of results.
Integration of AI and machine learning methodologies in Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP) can enable creation of accurate and efficient models facilitating better understanding of drug and disease mechanisms. Additionally, development of Electronic Health Records (EHR)- integrated Clinical Decision Support (CDS) tools with the help of AI can offer real-time guidance to healthcare providers (HCPs) for dosage optimization and making informed treatment decisions.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.25 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 4.28 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 3.11% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Drug Class, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott; ALPCO; Beckman Coulter, Inc; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; Chromsystems Instruments & Chemicals GmbH; F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Randox laboratories Ltd; Siemens Healthineers AG.; biomérieux, Inc. |
Market Driver: Growing Prevalence of Chronic and Autoimmune Disorders
The increasing burden of chronic and autoimmune diseases is a primary driver of the TDM market. Conditions such as epilepsy, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and transplant rejections require long-term administration of medications that must be carefully monitored to avoid toxicity and therapeutic failure. For example, immunosuppressants like tacrolimus and cyclosporine used in transplant patients have narrow therapeutic indices and show high inter-patient variability.
According to the CDC, nearly 6 in 10 adults in the U.S. suffer from at least one chronic disease, and these numbers are expected to rise globally due to aging populations and lifestyle changes. TDM provides a cost-effective strategy for optimizing treatment outcomes in such cases by ensuring therapeutic compliance and adjusting doses according to individual metabolic responses. Its use is especially critical in high-risk populations, such as cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, where accurate dosing can drastically impact survival and quality of life.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Equipment and Skilled Personnel
Despite its benefits, the high cost of TDM instrumentation and the requirement for skilled professionals to operate them pose significant restraints, particularly in resource-limited settings. Advanced technologies like LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry) and automated immunoassay analyzers, although precise and effective, entail high capital investments, maintenance expenses, and technical training.
This financial burden is especially significant for small-scale hospitals or diagnostic centers that may not have the patient volumes to justify the investment. Additionally, the shortage of trained laboratory technicians capable of performing and interpreting complex tests limits the scalability of TDM in rural and underserved regions. While outsourcing to centralized labs is a partial solution, it often leads to delays in results, undermining the real-time utility of TDM in critical care scenarios.
Market Opportunity: Integration of TDM with Pharmacogenomic Testing
A transformative opportunity lies in integrating therapeutic drug monitoring with pharmacogenomic testing. Pharmacogenomics studies how genes affect a person’s response to drugs and can significantly improve dosing accuracy. When combined with TDM, clinicians can gain a holistic understanding of both drug concentration and individual metabolic capability, allowing for truly personalized medicine.
This dual approach is particularly useful in fields like oncology, psychiatry, and neurology, where drug responses can be highly patient-specific. For instance, genotyping a patient for CYP2C19 or CYP2D6 can predict how they metabolize antidepressants or anti-epileptic drugs, while TDM can confirm serum levels for therapeutic efficacy. This integration will likely become standard in the near future as sequencing costs decline and EHRs (Electronic Health Records) begin to incorporate genomic data, offering immense growth potential for TDM solution providers.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market By Product Insights & Trends
The Equipment segment dominates the TDM market owing to its critical role in performing drug assays, especially in high-volume clinical settings. Instruments such as immunoassay analyzers, chromatography systems, and mass spectrometers form the technological backbone of TDM. Immunoassay analyzers, in particular, are widely used due to their automation, high throughput, and relatively low operational complexity, making them suitable for routine monitoring of drugs like antiepileptics and immunosuppressants. Major diagnostic labs and hospital-based laboratories continue to invest in these technologies, with vendors like Roche, Thermo Fisher, and Siemens offering highly integrated platforms.
However, the Consumables segment is emerging as the fastest-growing category. Reagents, assay kits, columns, cartridges, and sample preparation tools are recurrently required for TDM procedures, providing steady revenue streams. As the installed base of instruments expands, the demand for high-quality consumables that ensure accuracy and consistency rises concurrently. Additionally, the shift toward point-of-care and decentralized diagnostics is pushing manufacturers to develop easy-to-use kits tailored for smaller labs or remote clinics, further fueling segment growth.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market By Drugs Class Insights & Trends
The Immunosuppressants drug class segment dominated the market due to their widespread use in organ transplantation and autoimmune disease management. Drugs like cyclosporine, tacrolimus, and sirolimus require close monitoring due to their narrow therapeutic range and high variability among patients. TDM is standard protocol in transplant centers worldwide to ensure that the immune system is sufficiently suppressed without leading to infection or toxicity. The U.S. alone performs over 40,000 organ transplants annually, all of which demand long-term immunosuppressive therapy backed by consistent TDM.
In contrast, Antiepileptic Drugs represent the fastest-growing drug class. With a rise in global epilepsy incidence and growing recognition of the need for individualized dosing, TDM is being increasingly used in neurological care. Drugs such as phenytoin, valproic acid, and carbamazepine are routinely monitored to avoid adverse effects like drowsiness, hepatotoxicity, and cognitive dysfunction. Furthermore, the emergence of newer antiepileptics with complex metabolism underscores the importance of combining TDM with pharmacogenomic insights for optimized patient outcomes.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market By End Use Insights
Hospitals held the largest market share in the end-use segment due to their integrated infrastructure, patient load, and access to skilled clinical pathologists. TDM is most often conducted in tertiary and quaternary care hospitals where complex drug therapies are managed. In-house labs offer the advantage of quicker turnaround time, essential in intensive care units and oncology wards. Leading hospitals are also integrating TDM platforms with patient EHRs to automate result interpretation and support clinical decision-making.
However, Diagnostic Centers are the fastest-growing end-use segment. The outsourcing trend, combined with cost efficiency and technological sophistication, has made diagnostic labs pivotal in expanding TDM access. Central laboratories and independent diagnostic chains now offer specialized TDM panels, often with courier pickup and digital result delivery. This shift is democratizing access to TDM in smaller towns and private practices, particularly in emerging markets where standalone labs are more common than advanced hospital setups.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market By Regional Insights
North America dominated the global TDM market, led by the United States. The region benefits from an advanced healthcare ecosystem, early adoption of precision medicine, and strong reimbursement frameworks. High prevalence of chronic diseases, rising organ transplantation rates, and the presence of major pharmaceutical and diagnostic companies further boost demand. Regulatory support from agencies like the FDA, which encourages pharmacovigilance and safe medication practices, has catalyzed the integration of TDM into clinical workflows. The U.S. also leads in pharmacogenomic research, paving the way for combined genomic-TDM services. Leading players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Abbott Laboratories, and Quest Diagnostics are headquartered in the region, enabling rapid innovation and distribution.
U.S. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Trends
U.S. is a leading contributor the therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) market in North America. The market growth can be attributed to the presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure, rising chronic disease burden, increased focus on patient safety, adoption of telemedicine platforms, and shift towards personalized medicine approaches and pharmacogenomics. Advancements in analytical techniques like liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and development of high-throughput immunoassays and automated systems are improving the accuracy and efficiency of TDM in clinical settings. Supportive government initiatives and favourable reimbursement policies through programs like Medicare are improving patient access to TDM services. Additionally, the rise in number of organ transplants is necessitating immunosuppressant drug monitoring.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by increasing healthcare investments, improving access to diagnostics, and growing awareness among clinicians. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are witnessing a surge in organ transplants, cancer treatments, and chronic disease management—all of which require therapeutic monitoring. Government initiatives to modernize healthcare infrastructure and expand diagnostic capabilities are playing a significant role. Additionally, collaborations between global diagnostics firms and local laboratories are improving access to high-end equipment and training. As the region moves toward universal health coverage, TDM will become a standard tool in clinical decision-making.
Japan Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Trends
Japan is experiencing strong growth in the therapeutic drug monitoring market in the Asia Pacific region, driven by the rising prevalence of chronic conditions, especially in the aging population, often requiring and long-term medications with complex regimens, creating the need for robust TDM systems to optimize drug dosages and minimizing side effects. The nation’s strong healthcare infrastructure, continuous advancements in precision medicine, rise of telemedicine platforms and innovations in TDM testing equipment and methods backed by advancements such as digital pathology tools and lab-on-a-chip miniaturization are bolstering the market growth. Japan’s national health insurance system is improving access and adoption of TDM services. Additionally, funding of drug development programs by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) and the presence of robust pharmaceutical industry are expanding the market potential.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Top Key Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the therapeutic drug monitoring market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Abbott
- ALPCO
- Beckman Coulter, Inc
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Chromsystems Instruments & Chemicals GmbH
- F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Randox laboratories Ltd
- Siemens Healthineers AG.
- biomérieux, Inc.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Prometheus Laboratories Inc., a leading precision healthcare company, expanded its precision-guided dosing tests portfolio with the launch of PredictrPK VDZ and PredictrPK UST for adults with with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) receiving vedolizumab (VDZ) and ustekinumab (UST) treatment.
- In July 2025, Pillbox Health LLC, an innovator in medical adherence and medication reminder app technology, launched its new Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) feature via the PillPal app.
- In June 2025, at the 73rd American Society for Mass Spectrometry (ASMS) Conference, Bruker Corporation through its Applied Mass Spectrometry (Applied MS) division showcased its two important innovations: the integration of RECIPE’s ClinMass and ClinDART assay kits with Bruker’s EVOQ DART-TQ⺠system for therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) and drugs of abuse (DoA) applications, and the launch of the new timsMetabo platform for PFAS and environmental contaminant detection.
- In May 2025, Revvity Inc., launched its innovative CE marked and FDA listed device, the new new IDS i20 analytical random access platform from EUROIMMUN which will enable fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassays (ChLIA). The IDS i20 instrument allows its users to simultaneously run 20 analytes on single device from six diagnostic specialties, including allergy and autoimmune and infectious disease testing, endocrinology, testing for Alzheimer’s disease and therapeutic drug monitoring.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring market.
By Product
- Equipment
- Immunoassay Analyzers
- Clinical Chemistry Analyzers
- Chromatography & MS Detectors
- Consumables
By Drug Class
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs
- Immunosuppressants
- Antiepileptic Drugs
- Others
By End Use
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

