U.S. EMS Billing Services Market Size and Research
The U.S. EMS billing services market size was exhibited at USD 4.39 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 11.25 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.86% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
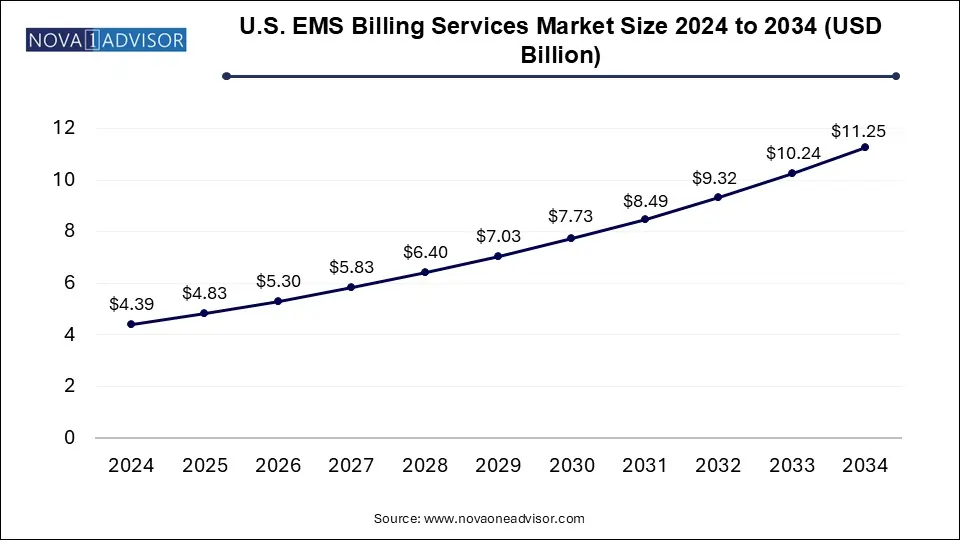
U.S. EMS Billing Services Market Key Takeaways:
- The outsourced segment held the majority of the market share of 57.0% in 2024.
- The in-house segment is expected to witness growth during the forecast period
Market Overview
The U.S. Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Billing Services market plays a pivotal role in supporting ambulance providers, fire departments, and other EMS agencies by streamlining revenue cycle management and ensuring compliance with federal, state, and payer-specific regulations. EMS billing services are critical to maintaining the financial viability of emergency response operations, particularly as EMS systems face growing patient volumes, expanding geographic coverage, and increasing regulatory scrutiny.
EMS billing refers to the documentation, coding, submission, and follow-up of claims for pre-hospital emergency services, often involving complex medical coding and coordination with various payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. In the U.S., EMS agencies may operate under fire departments, private ambulance services, or hospital-owned entities. Given the varied ownership and service structures, billing practices often require customization, expertise, and technological integration.
Historically, many EMS agencies managed billing in-house. However, over the past decade, there has been a strong shift toward outsourcing due to growing complexities in billing regulations, coding standards like ICD-10 and HCPCS, and payer-specific reimbursement requirements. This has fueled the rise of specialized EMS billing firms that offer end-to-end solutions, including claim submissions, appeals, denial management, audit readiness, and analytics-driven insights.
The market continues to evolve in response to industry dynamics such as federal policy changes (like the CMS Cost Data Collection initiative), technological innovation, consolidation of EMS providers, and increasing emphasis on operational efficiency. Overall, the U.S. EMS Billing Services market is experiencing significant transformation—positioned at the intersection of emergency healthcare, compliance, and financial management.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Growing Shift Toward Outsourcing: EMS agencies increasingly rely on third-party billing vendors to manage complex reimbursement processes and reduce administrative overhead.
-
Technology-Driven Solutions: Integration of AI-powered coding, automated claim tracking, and cloud-based billing platforms is becoming widespread.
-
Compliance Emphasis: Increased enforcement of Medicare and Medicaid billing compliance has prompted investment in audit-proof billing systems and training.
-
Consolidation of EMS Providers: Mergers among EMS agencies are leading to centralized billing operations and partnerships with full-suite billing vendors.
-
Rise of Data Analytics: EMS billing firms are offering real-time dashboards and analytics to optimize collection rates and monitor KPIs.
-
Customized Payer Engagement: Vendors are enhancing services to deal with payer-specific rules and documentation needs to reduce claim denials.
-
Staffing Shortages: Shortages of skilled medical coders and RCM professionals are accelerating the move to automated and outsourced solutions.
Report Scope of U.S. EMS Billing Services Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 4.83 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 11.25 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 9.86% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Component |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
EMS Management & Consultants, Inc.; Cvikota EMS; Omni Medical Billing Service, Inc.; Quick Med Claims, LLC.; 911 Billing Services & Consultant, Inc.; Change Healthcare; PCC Ambulance Billing Service; EMS Billing Management, LLC; Pintler Billing Services; AIM EMS Software & Services |
Market Driver: Increasing Complexity of EMS Reimbursement Systems
A critical driver for the EMS billing services market is the increasing complexity of the reimbursement landscape for EMS providers in the U.S. Over the past few years, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has implemented stringent documentation and cost-reporting requirements. Simultaneously, payers have updated claim adjudication rules, and fraud scrutiny has intensified, especially concerning upcoding and transport necessity validations.
EMS providers must now navigate nuanced requirements such as the Ground Ambulance Data Collection System (GADCS), introduced by CMS to collect cost data from EMS agencies to assess payment adequacy. This requires extensive financial and operational reporting—often outside the expertise or bandwidth of in-house billing teams. Additionally, each payer may have unique rules around transport eligibility, mileage documentation, and pre-authorization.
To manage these complexities, EMS agencies are turning to specialized billing vendors who possess domain-specific knowledge, maintain compliance infrastructure, and offer scalable billing solutions. This shift not only enhances claim accuracy and reimbursement speed but also reduces audit risk—a significant concern for public and private EMS entities.
Market Restraint: Data Security and Patient Privacy Challenges
A major restraint in the U.S. EMS billing services market is the ongoing challenge of data security and patient privacy compliance, especially under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). EMS agencies handle highly sensitive patient health information (PHI) under stressful and dynamic conditions. Transmitting this data to billing providers—particularly those using cloud platforms or third-party software—exposes it to potential breaches or misuse.
Cybersecurity threats to healthcare billing systems are rising, with ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, and data leaks affecting organizations of all sizes. EMS agencies are especially vulnerable due to the mobile and decentralized nature of their operations, often relying on laptops, tablets, or handwritten PCRs (Patient Care Reports) in the field. Inadequate encryption or poor endpoint security could result in HIPAA violations, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
Moreover, integrating ePCR systems with billing software requires rigorous data handling protocols and audit trails. Vendors who fail to ensure end-to-end encryption, access controls, and secure cloud hosting risk losing clients. Thus, while outsourcing offers numerous advantages, the risk of compromised data integrity remains a key inhibitor to market expansion, especially among risk-averse municipal EMS providers.
Market Opportunity: Integration of AI and Automation in Billing Workflows
The most promising opportunity in the U.S. EMS billing services market lies in leveraging artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to enhance accuracy and speed in revenue cycle management. As the volume of emergency calls rises, billing teams face enormous pressure to process claims promptly while reducing denials, errors, and manual workload.
AI can assist in auto-coding patient narratives, analyzing PCRs for compliance, predicting claim outcomes, and identifying patterns in denials. Vendors deploying smart platforms can instantly validate claims against payer policies and flag incomplete documentation before submission. RPA, on the other hand, can streamline repetitive tasks like insurance eligibility verification, invoice generation, and payment posting.
For instance, vendors like ZOLL Data Systems and ESO Solutions are increasingly embedding smart billing tools into their EMS software ecosystems. Adoption of such tools is especially valuable for mid-sized EMS agencies seeking to scale operations without proportionally increasing staffing costs. As healthcare continues to digitize, the convergence of EMS billing with AI-based tools is poised to unlock significant productivity gains and competitive differentiation.
U.S. EMS Billing Services Market By Component Insights
Outsourced EMS billing services currently dominate the U.S. market, driven by the need for specialization, compliance assurance, and operational efficiency. Many EMS agencies, including municipal fire departments and private ambulance companies, lack the internal expertise to keep up with evolving payer regulations and audit requirements. Outsourcing allows them to access trained billing specialists, legal counsel, and coders familiar with Medicare/Medicaid nuances. Firms such as Change Healthcare EMS, Digitech, and Intermedix offer end-to-end services that reduce claim cycle times and maximize reimbursement potential.
Outsourced services have also gained favor due to their ability to offer value-added features like analytics dashboards, payer portal integrations, and dedicated denial resolution teams. For example, large-scale providers like AMR (American Medical Response) leverage outsourcing to maintain consistent billing standards across multiple states. The scalability, compliance infrastructure, and guaranteed service-level agreements make outsourcing the default choice for new EMS agencies or those undergoing restructuring.
However, the in-house segment, while declining in relative share, still plays a role among large hospital-owned EMS departments or fire-based systems with dedicated administrative teams. These entities maintain internal billing departments to retain tighter control over patient data and revenue cycles. For example, the Los Angeles Fire Department uses its internal revenue management system integrated with city-wide financial tools. Yet, maintaining an in-house team requires significant investment in training, software, and compliance management—burdens that many smaller providers find unsustainable.
Despite its historical roots, the in-house billing segment is expected to grow modestly in niche scenarios where customization or data sovereignty is prioritized. Still, unless paired with modern automation tools and strong IT support, in-house teams may struggle to match the speed and precision offered by specialized vendors.
Country-Level Analysis
The EMS billing ecosystem in the United States is shaped by a decentralized healthcare model, where funding mechanisms and regulations vary by state, municipality, and agency ownership type. More than 21,000 EMS agencies operate across the country, including fire departments, private ambulance services, and hospital-based providers. As of 2024, Medicare remains the largest payer for EMS services, making up nearly 60% of total EMS transports, especially for patients over 65 or with disabilities.
The U.S. government's Cost Data Collection program, initiated by CMS, is significantly influencing billing practices. Participating EMS agencies must now submit detailed annual financial reports, which inform future Medicare reimbursement rates. This has compelled agencies to adopt advanced billing systems capable of generating real-time cost analytics and documentation validation.
Moreover, various state-level EMS oversight bodies, such as the California Emergency Medical Services Authority (EMSA) and Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS), impose unique requirements for transport documentation, payer coordination, and electronic reporting. Navigating this patchwork of regulations is a key challenge—driving the need for billing providers with localized expertise.
Additionally, the growing popularity of mobile integrated healthcare (MIH) and community paramedicine programs is expanding EMS roles beyond transport to include chronic disease management and post-discharge follow-ups. This shift may require the development of new billing codes, payer agreements, and reimbursement protocols—creating further demand for flexible and informed billing partners.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. EMS billing services market include:
- EMS Management & Consultants, Inc.
- Cvikota EMS
- Omni Medical Billing Service, Inc.
- Quick Med Claims, LLC.
- 911 Billing Services & Consultant, Inc.
- Change Healthcare
- PCC Ambulance Billing Service
- EMS Billing Management, LLC
- Pintler Billing Services
- AIM EMS Software & Services
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: ESO Solutions announced a strategic partnership with Healthcare Management Partners (HMP) to integrate AI-based auditing tools into EMS billing workflows, enhancing compliance and reducing denial rates across major metropolitan clients.
-
February 2025: Change Healthcare launched a new feature in its EMS billing platform that incorporates payer-specific rulesets for real-time claim validation. The update aims to reduce claim denials due to missing mileage or medical necessity data.
-
January 2025: Digitech unveiled its new cloud-native EMS billing suite designed for multi-agency operations. The platform offers customizable dashboards, real-time KPI tracking, and ePCR integration for better documentation-to-billing sync.
-
December 2024: ZOLL Data Systems expanded its customer base by signing a five-year EMS billing contract with a leading New York-based ambulance company, focused on automating its full revenue cycle operations.
-
October 2024: Intermedix rebranded to Logis Solutions, highlighting its expansion beyond billing into full-cycle EMS administration and resource deployment optimization.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. EMS billing services market
By Component

