U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market Size and Growth
The U.S. medical lifting sling market size was exhibited at USD 242.45 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 495.07 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.4% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
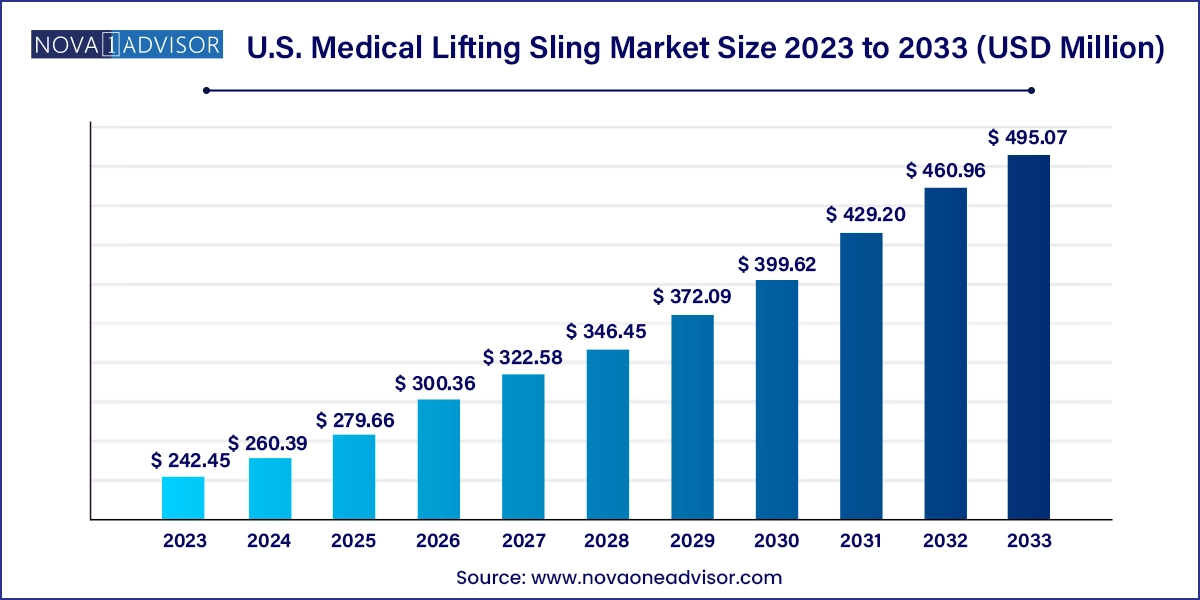
U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market Key Takeaways:
- The nylon segment dominated the market and accounted for a share of around 30.25% in 2023.
- Padded slings held the second largest share based on product in 2023.
- Based on application, the transfer segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share in 2023.
- The universal segment is expected to witness a significant growth rate over the forecast period.
- Based on usage, the reusable segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share in 2023.
- The disposable segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The hospital segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share in 2023.
- The homecare segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. medical lifting sling market has emerged as a critical component of the healthcare mobility and patient handling ecosystem. Designed to assist caregivers in safely lifting, transferring, or repositioning patients with limited mobility, medical slings play a vital role in ensuring dignified care, injury prevention, and operational efficiency in hospitals, elderly care facilities, and home settings. These slings are typically used in conjunction with patient lifts, either manually operated or powered, and are customized to suit different patient needs and body types.
In the U.S., rising demand is fueled by a confluence of factors an aging population, a rise in obesity-related mobility issues, increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses, and a growing emphasis on caregiver injury prevention. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, by 2030, over 20% of the U.S. population will be aged 65 or older. As older adults are more susceptible to fractures, muscular weakness, and degenerative conditions, the need for assistive transfer devices continues to rise. Hospitals and long-term care centers are under increasing pressure to reduce workplace injuries related to manual lifting, making slings an essential component of compliance with occupational safety standards.
Additionally, with the shift toward home-based care and growing awareness around ergonomics and patient dignity, lifting slings are no longer confined to institutional use. Manufacturers are expanding product lines to include slings tailored for bariatric patients, toileting purposes, and standing aids, catering to various levels of dependency. The market is further shaped by technological innovation in materials, design, and compatibility with lift systems. With increasing government and private sector attention to patient-centered care and caregiver safety, the U.S. medical lifting sling market is expected to sustain robust growth in the years ahead.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Increased Adoption in Homecare and Elderly Care Settings: Families and caregivers are investing in slings to manage aging family members at home, enhancing safety and reducing the need for long-term hospitalization.
-
Shift Toward Reusable and Eco-Friendly Materials: Reusable slings made from durable, washable materials are gaining traction due to cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
-
Expansion of Bariatric Sling Offerings: With obesity rates climbing, demand for heavy-duty, comfortable slings capable of supporting higher weight thresholds is rising.
-
Integration with Powered and Automated Patient Lifts: Compatibility with electric lifts and ceiling track systems is influencing purchasing decisions among hospitals and clinics.
-
Customizable and Ergonomic Design Innovations: Manufacturers are incorporating padding, breathable fabrics, anti-shear materials, and adjustable strap systems for improved comfort and usability.
-
Emphasis on Infection Control: Disposable slings are increasingly being used in acute care settings to prevent cross-contamination and comply with hygiene standards.
-
Training and Safety Education for Staff: Institutions are investing in proper training and sling usage education to reduce staff injuries and improve patient outcomes.
-
Growing Influence of Assistive Technologies: Smart lifting solutions integrated with sensors to monitor sling positioning and pressure distribution are under development.
Report Scope of U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 260.39 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 495.07 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 7.4% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, Usage, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Bestcare; Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc (Baxter); Invacare Corporation; GF Health Products, Inc.; Arjo; DiaMedical USA; Joerns Healthcare; Henry Schein, Inc.; SSM Health; Bishop Lifting; Etac AB; Binder Lift Inc.; Winncare |
Market Driver: Growing Aging Population and Mobility Challenges
The leading driver of the U.S. medical lifting sling market is the rapidly aging population and the consequent rise in mobility impairment. With over 55 million Americans aged 65 and older, and the figure projected to exceed 70 million by 2035, healthcare providers are witnessing an escalating demand for transfer and repositioning aids. Aging individuals are more likely to suffer from arthritis, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, hip fractures, and neurological disorders all of which significantly impair mobility and self-sufficiency.
Medical slings provide a safe and practical solution for caregivers to manage daily care routines such as bed-to-chair transfers, toileting, and repositioning in bed. This helps minimize the risk of falls and pressure ulcers while maintaining patient comfort. Hospitals and long-term care facilities are increasingly implementing no-lift policies, making slings essential to meet Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines and reduce worker compensation claims. As the aging demographic continues to expand, the role of medical lifting slings in enabling aging in place, rehabilitation, and institutional care will remain indispensable.
Market Restraint: Cost and Product Accessibility in Non-Institutional Settings
Despite clear benefits, the market faces a significant barrier in the form of cost-related challenges, particularly for non-institutional users. While hospitals and nursing homes may benefit from equipment procurement contracts and insurance reimbursement, individual caregivers often face out-of-pocket costs for lifts and compatible slings. High-quality padded or bariatric slings can range between $200 and $600, and may not always be covered under standard Medicare or private insurance plans unless deemed medically necessary.
This cost barrier discourages adoption in homecare settings, especially in low-income households. Additionally, a lack of awareness and guidance on proper sling selection and application can lead to misuse or underutilization. For facilities operating under tight budgets, replacing worn or soiled slings can become a financial burden, leading to extended use of old equipment and increased safety risks. Addressing these cost and accessibility concerns through better insurance frameworks, training programs, and rental models will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of the market.
Market Opportunity: Increasing Demand in Homecare and Telehealth-Integrated Support
The homecare segment presents a robust opportunity for growth in the U.S. medical lifting sling market. As more families opt to care for loved ones with mobility limitations at home either due to preference, cost savings, or limited access to long-term facilities the need for user-friendly lifting equipment is on the rise. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift toward home-based care, and the trend has continued as the healthcare system emphasizes outpatient recovery and aging in place.
Innovative sling designs optimized for homecare such as lightweight, washable, and quick-drying options are gaining popularity. Furthermore, manufacturers can leverage telehealth platforms to provide virtual consultations for correct sling sizing, positioning guidance, and maintenance tips. Partnerships between lift device suppliers and home health agencies also create opportunities for bundled services that include delivery, installation, and training. As homecare becomes a central pillar of healthcare delivery in the U.S., companies that provide tailored, accessible, and supportive sling solutions stand to gain a competitive edge.
U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market By Product Insights
Padded slings dominated the product category, primarily due to their enhanced patient comfort and versatility. These slings are often preferred in hospital and long-term care settings, where patients require extended time in slings for positioning or transfers. Padded designs help distribute body weight evenly and reduce pressure points, making them ideal for fragile skin and post-surgical recovery. They are commonly used in toileting, transfer, and seated support applications and are often compatible with both loop and clip-style patient lifts.
Mesh slings are among the fastest-growing products, especially in homecare and bariatric care applications. Their breathable structure offers moisture-wicking benefits, crucial for preventing skin breakdown in immobile patients. Mesh slings are also preferred for showering and bathing due to their quick-drying nature. Moreover, the lightweight and flexible design makes them easier for solo caregivers to position and remove. As awareness about hygiene, infection control, and patient skin care grows, mesh slings are likely to see increasing preference across a range of healthcare environments.
U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market By Application Insights
Transfer slings are the most widely used application segment, with widespread deployment in hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers. These slings are engineered to lift patients between beds, wheelchairs, and commodes, forming the backbone of safe patient handling programs. They are available in a wide range of configurations—padded, full-body, divided leg, and more—making them adaptable to various body types and conditions. Transfer slings are indispensable in minimizing caregiver strain and ensuring dignity during mobility assistance.
Bariatric slings are the fastest-growing application, driven by rising obesity rates in the United States. According to the CDC, over 42% of U.S. adults are classified as obese. Bariatric patients require specially designed slings with reinforced stitching, broader straps, and higher weight limits (often exceeding 600 lbs). These slings not only accommodate larger body frames but also address the challenges of safely managing dependent patients in both hospital and home settings. The surge in bariatric procedures, combined with an increase in mobility-related complications among obese patients, underscores the growing need for this segment.
U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market By Usage Insights
Reusable slings held the largest share by usage, particularly in institutional settings where sanitation infrastructure and laundering services are readily available. Reusable slings offer long-term cost advantages, especially for facilities with high patient turnover. Hospitals often standardize reusable sling types to ensure consistency and durability over repeated usage cycles. Moreover, padded and mesh variants are more commonly available in reusable forms, making them favorable for long-term patients.
Disposable slings, however, are seeing the fastest adoption, especially in infection-sensitive environments such as ICUs and COVID-19 isolation wards. These single-use products reduce the risk of cross-contamination and save time on cleaning and maintenance. In facilities that experience frequent patient turnover or transport across departments, disposable slings provide operational efficiency and compliance with stringent hygiene protocols. As infection control remains a top healthcare priority, the demand for disposable slings is expected to grow.
U.S. Medical Lifting Sling Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals were the dominant end-use segment, benefiting from higher patient volumes, advanced lifting equipment, and structured caregiver training programs. From trauma care to post-operative recovery, hospitals rely on slings across departments including orthopedics, geriatrics, neurology, and intensive care. The institutional focus on safe patient handling programs has driven extensive sling adoption, especially for transfer and positioning needs.
Elderly care facilities and homecare services are the fastest-growing end-use areas, reflecting the nation’s demographic shift and the decentralization of care. Assisted living centers, skilled nursing homes, and memory care units are incorporating slings to provide better quality of life and support for residents with degenerative diseases and limited mobility. Homecare, too, is witnessing higher sling usage due to family caregivers seeking safer methods to manage daily care tasks. Portable sling systems and educational resources are increasingly making home-based lifting safer and more manageable.
Country-Level Analysis
The U.S. market for medical lifting slings is characterized by regional variability in healthcare infrastructure, aging demographics, and funding availability. The Northeast region leads in adoption due to its high concentration of advanced medical centers and long-term care facilities. States like New York, Massachusetts, and Pennsylvania have extensive healthcare networks and a higher proportion of elderly populations. These regions also see strong regulatory enforcement of patient handling protocols, encouraging hospitals to adopt comprehensive sling systems.
Conversely, the Southwest region, including Texas and Arizona, is the fastest-growing area for sling adoption. This growth is driven by rapid population expansion, high obesity rates, and rising investment in elder care facilities. Additionally, home health services and hospice care are particularly prominent in this region, supporting increased demand for both reusable and disposable sling systems. The push toward decentralized, community-based elder care is shaping procurement patterns across the state healthcare and private sector landscapes.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. medical lifting sling market include:
- Bestcare
- Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc (Baxter)
- Invacare Corporation
- GF Health Products, Inc.
- Arjo
- Medical Depot
- DiaMedical USA
- Joerns Healthcare
- Henry Schein, Inc.
- SSM Health
- Bishop Lifting
- Etac AB
- Binder Lift Inc.
- Winncare
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. medical lifting sling market
Product
- Nylon
- Padded
- Mesh
- Canvas
- Others
Application
- Transfer
- Universal
- Hammock
- Standing
- Seating
- Toileting
- Bariatric
- Others
Usage
End-use
- Hospital
- Homecare
- Elederly Care
- Other Healthcare Settings
Regional
- West
- Midwest
- Northeast
- Southwest
- Southeast

