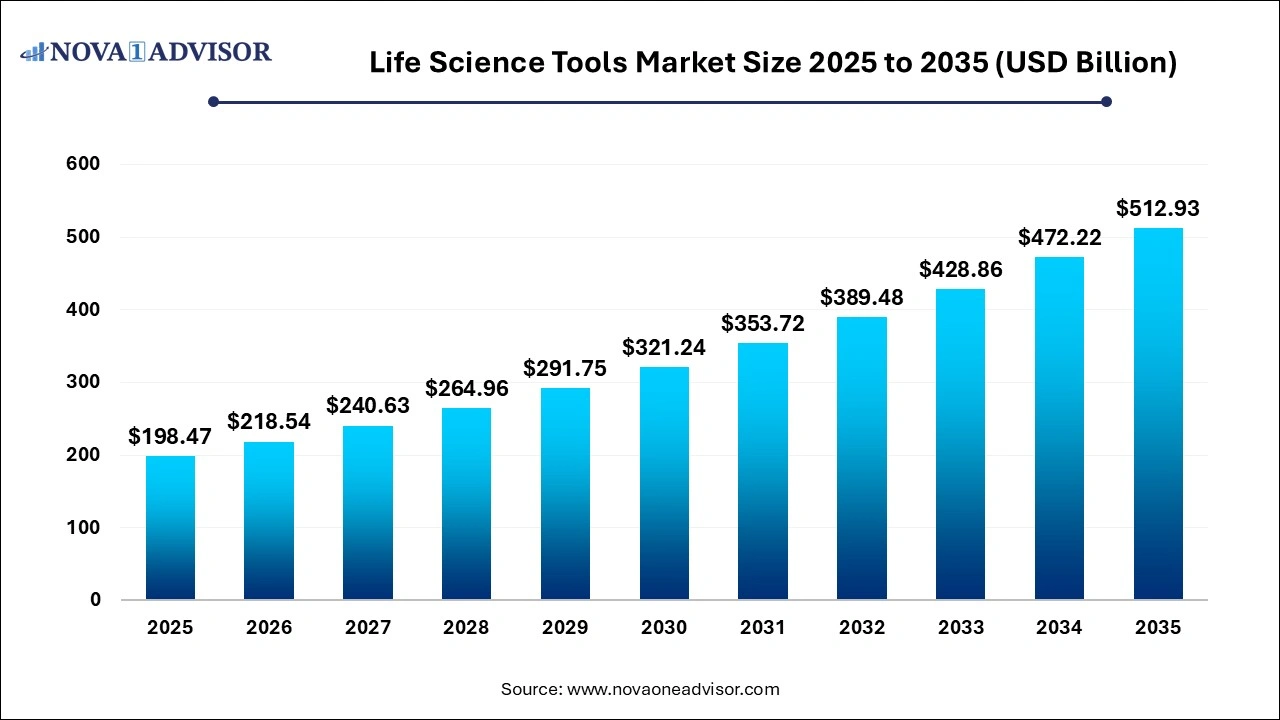
The global life science tools market size was estimated at USD 198.47 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 512.93 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 9.96% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035. The life science tools market growth is driven by the rising R&D expenditure, ongoing launch of innovative technologies, increasing demand for advanced diagnostic tools and supportive government initiatives.
Key Takeaways:
- North America accounted for a dominant revenue share of over 40% in 2025.
- The Asia Pacific region will grow at the highest rate during the projected period.
- In 2025, cell biology technology accounted for the largest share of over 36%.
- The genomics technology segment is expected to grow at a significant rate over the forecast period.
- In 2025, cell culture systems and 3D cell culture segment held the largest share of over 23%.
- Next-generation sequencing is anticipated to exhibit the fastest growth rate of 21.2% from 2026 to 2035.
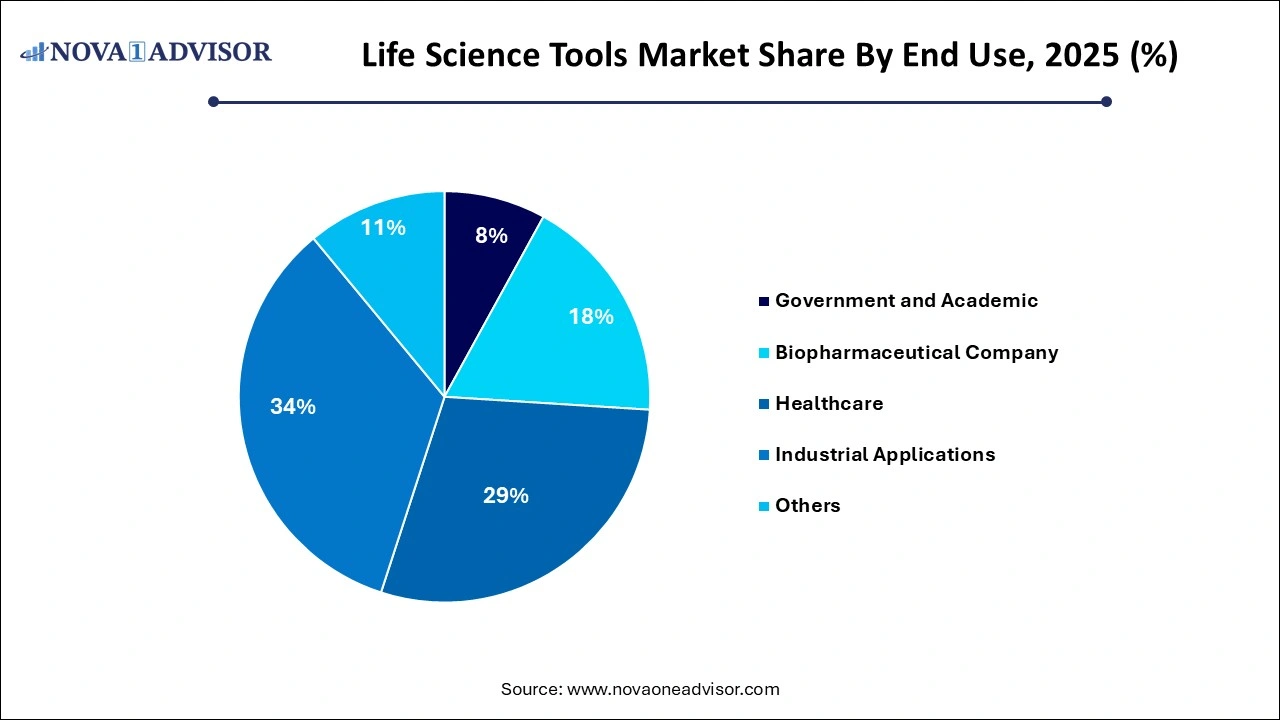
- The healthcare segment captured the largest share of over 34% in 2025.
The growth in revenue is mainly due to rapid advancements by the life science tools companies in sequencing, MS, chromatography, NMR, and other various products. Moreover, investments and funding for the development of advanced therapeutics along with continuous demand for novel medicine and treatments due to rising incidence of diseases such as cancer, kidney and thyroid disorders, and diabetes will drive the market. The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted several industries and the associated supply chains across the globe. This is due to disruption in the supply of key materials such as scarcity of raw materials and labor. In addition, the transportation of raw materials across regions had been put on hold. These factors have led to a shortage of medical supplies, such as molecular and immunoassay kits, digital solutions, life-support machines, and drugs in different regions of the globe.
Besides this, the pandemic had a positive impact on the market as the race for developing rapid diagnostics for the SARS-CoV-2 virus led manufacturers to provide innovative breakthroughs. Some of these tests detect the SARS-CoV-2 nucleic material using the PCR technique or via nucleic acid hybridization-related methods or while others are serological and immunological assays that detect antibodies produced in response to the virus. For example, in December 2021, Siemens Healthineers received Emergency Use Authorization from the U.S. FDA for its COVID-19 rapid test, CLINITEST Rapid COVID-19 Antigen Self-Test that can be used for self-testing by individuals aged 14 and above. The pandemic-related new developments, government funding, product approvals, and continuous launches will drive the market.
The growth of gene and cell therapies and their rising demand is anticipated to boost market growth. With the growing demand for robust disease treatment therapies, companies have focused their efforts to accelerate their R&D for effective gene therapies that target the cause of disease at the genomic level. With a rise in the number of FDA-approved products, a healthy outlook for gene therapies is expected in the near future. In addition, advancements in recombinant DNA technology are expected to expand the number of ongoing clinical trials for gene therapy. For instance, in 2021, FDA expected more than 200 applications annually for cell and gene therapy clinical trials by 2034.
The increased understanding of drug interaction with the genetic makeup of patients has led to improvements in targeted therapies. The life science industry is now capitalizing on novel innovations such as predictive analytics to enhance the manufacturing of biological therapeutics to meet the growing demand. This combined with low-cost and robust genetic profiling will improve treatment outcomes and help reduce the drug development cost. The rise in demand for biologics is expected to propel market growth as most biologics are manufactured with the help of recombinant DNA technology.
Furthermore, monoclonal antibodies are rapidly evolving in the field of cancer therapy. For instance, according to an article published in January 2021, by mAbxience, 27 monoclonal antibodies have been approved for treating different types of cancer. Moreover, FDA approvals of monoclonal antibodies in diagnostics and cancer therapy are increasing the applications of biologics. For instance, in January 2022, FDA approved Tebentafusp-tebn monoclonal antibody that aids in the treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma. Government support coupled with rising demand for novel therapeutics will boost the growth of the market.
- Industry Growth Overview: Between 2025 and 2030, this market is expected to rise significantly due to the rise in number of biotechnology companies along with increasing demand for plasma therapies for treating cancers.
- Major Investors: Numerous market players are actively entering this market, drawn by partnerships, R&D and product launches. Several life science tools companies such as Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Bruker Corporation; Danaher Corporation and some others have started investing rapidly for developing high-quality life science tools to cater the needs of the end-users.
- Startup Ecosystem: Various startup brands are engaged in developing several types of life science tools for the end-users. The prominent startup companies dealing in life science tools comprises of Unifize, Leucine, BrainSightAI and some others.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of Single-cell Technologies: Tools enabling single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics are transforming cell biology research.
-
Miniaturization and Automation: Instruments are becoming more compact and automated, supporting high-throughput applications and reducing human error.
-
Cloud-based Data Analysis: Bioinformatics tools are increasingly being integrated with cloud platforms to process massive genomic and proteomic datasets.
-
Increased Investment in Personalized Medicine: Life science tools are critical in supporting genomic medicine and individualized therapy development.
-
Emergence of CRISPR and Genome Editing Platforms: Demand is rising for reagents and kits tailored to gene editing applications.
-
Focus on 3D Cell Culture and Organoid Models: Researchers are using 3D systems to mimic in vivo environments, improving drug screening accuracy.
-
Expansion of AI-integrated Analytical Tools: Artificial intelligence is being deployed for predictive analytics in drug discovery and molecular diagnostics.
The deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) in life science tools is improving the accuracy and efficiency of workflows. AI algorithms can be used for analyzing genomic data, for predicting protein structures, to design novel drug candidates as well as for optimizing clinical trial designs, leading to breakthroughs in drug discovery and with enhanced decision-making. Analysis of patient data with AI-powered tools can enable development of more personalized and effective therapies. AI-powered biomarkers can be applied for analyzing omics data for identification of biomarkers, necessary for predicting severity of diseases and patient outcomes.
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 218.54 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 512.93 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 9.96% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
By Technology, By Product, By Application, By End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Agilent Technologies, Inc.; Becton; Dickinson and Company; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Danaher Corporation; Illumina, Inc.; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc; QIAGEN N.V.; Merck KGaA; Shimadzu Corporation; Hitachi Ltd.; Bruker Corporation; Oxford Instruments plc; Zeiss International |
Driver: Surge in Biopharmaceutical R&D Activities
One of the most significant driving forces for the life science tools market is the escalating research and development expenditure by biopharmaceutical companies. In an era where biologics and cell-based therapies are emerging as front-line treatments, pharmaceutical companies are significantly investing in R&D to identify, validate, and produce novel therapeutics. These efforts demand advanced instrumentation and consumables that can deliver high-accuracy results in high-throughput settings.
For example, companies working on mRNA-based vaccines and therapies heavily rely on nucleic acid purification kits, PCR systems, and transfection reagents to evaluate gene expression, optimize formulations, and validate efficacy. This growth is also fueled by public-private partnerships and funding from governmental bodies such as the NIH, which further stimulates innovation and demand for research tools.
Restraint: High Cost of Advanced Equipment
Despite the promising landscape, the high cost associated with cutting-edge analytical equipment remains a major restraint for the life science tools market. Instruments like high-resolution mass spectrometers, cryo-electron microscopes, and next-generation sequencers can cost several hundred thousand dollars, making them unaffordable for small-scale academic institutions and emerging biotech startups.
Moreover, maintenance and calibration of such sophisticated tools demand specialized technicians and regular service contracts, adding to the operational burden. The cost barrier is particularly pronounced in developing countries where research infrastructure is still evolving. As a result, these regions rely heavily on grants and collaborative projects to gain access to such high-end technologies.
Opportunity: Expanding Application in Personalized Medicine
An exciting opportunity lies in the expansion of life science tools in the field of personalized and precision medicine. The shift from "one-size-fits-all" treatments to therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup has fueled the need for tools that can provide accurate, real-time data about patients’ biomolecular profiles.
For instance, in oncology, next-generation sequencing tools help identify specific mutations in tumors, guiding the choice of targeted therapies. Similarly, mass spectrometry is increasingly used to profile protein biomarkers that can predict disease progression or treatment response. The integration of such tools into clinical workflows opens new revenue streams and applications beyond the traditional research space, particularly in diagnostics and monitoring.
By Technology Insights
Genomic technology has been the dominant segment due to its broad application in identifying gene variants, understanding gene expression, and detecting mutations. The use of whole-genome sequencing, exome sequencing, and targeted panels is common in both academic research and clinical diagnostics. For instance, companies like Illumina and Thermo Fisher Scientific are constantly innovating their sequencers to improve throughput and accuracy, catering to population-scale genomics initiatives such as the UK Biobank and the NIH’s All of Us project.
On the other hand, proteomics technology is the fastest-growing segment. It is increasingly being applied in drug discovery, biomarker identification, and systems biology. The complexity of the proteome and the growing need to understand post-translational modifications have propelled demand for advanced mass spectrometry systems, bioinformatics software, and chromatography tools. Proteomics is expected to play a vital role in next-generation therapeutic strategies and disease diagnostics.
By Product Insights
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) products dominate the product category due to their indispensable role in genomics and transcriptomics research. The instrument sub-segment leads in revenue, thanks to major platforms from Illumina, PacBio, and Oxford Nanopore. Meanwhile, consumables, particularly sequencing reagents, contribute substantially to recurring revenue for companies. Services are also gaining prominence, especially as more research organizations outsource complex sequencing tasks.
3D cell culture systems are the fastest-growing product segment. These systems better replicate human physiology compared to traditional 2D cultures and are being rapidly adopted in drug toxicity testing, regenerative medicine, and cancer research. Companies like Corning, Lonza, and Thermo Fisher have developed advanced scaffolds, bioreactors, and organoid models that are pushing the boundaries of preclinical modeling.
By End-use Insights
Biopharmaceutical companies are the largest end-users of life science tools. These firms invest heavily in R&D for monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, gene therapies, and small molecules. The need for accurate, reproducible data and compliance with regulatory guidelines drives adoption of high-end instrumentation and services.
Meanwhile, the academic and government research segment is expected to register the fastest growth. An increasing number of public health initiatives, NIH grants, and academic-industry collaborations have led to a boom in the usage of research tools across public universities and research institutes.
The U.S. life science tools market size reached USD 60.00 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 154.33 billion by 2035, poised to grow at a CAGR of 9.91% from 2026 to 2035.
.webp) North America, particularly the United States, continues to lead the global life science tools market. The region benefits from strong governmental support, high healthcare expenditure, advanced infrastructure, and a concentration of key players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, and Illumina. The presence of leading academic institutions and life science clusters like Boston-Cambridge and the Bay Area further contributes to market dominance. Initiatives such as the Cancer Moonshot and large-scale genomics projects have created sustained demand for sequencing, proteomics, and cell-based assay tools.
North America, particularly the United States, continues to lead the global life science tools market. The region benefits from strong governmental support, high healthcare expenditure, advanced infrastructure, and a concentration of key players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, and Illumina. The presence of leading academic institutions and life science clusters like Boston-Cambridge and the Bay Area further contributes to market dominance. Initiatives such as the Cancer Moonshot and large-scale genomics projects have created sustained demand for sequencing, proteomics, and cell-based assay tools.
Asia-Pacific, especially countries like China, India, and South Korea, is witnessing the fastest growth. Factors such as rising healthcare investment, increasing biotechnology startups, government-led R&D funding, and growing academic output are fueling market expansion. For example, China’s “Healthy China 2030” initiative has significantly boosted its life sciences ecosystem. Additionally, companies in the region are becoming competitive in manufacturing and innovation, contributing to a more localized supply of instruments and reagents.
China Life Science Tools Market
China is expected to grow significantly in the life science tools market in Asia Pacific, driven by factors such as the increasing investments by pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions in R&D activities, growing emphasis on precision medicine and regenerative therapies, rising prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases as well as demand the need for reliable and efficient diagnostic tools and reagents. These factors are driving the demand for advanced life science tools for various applications. Advancements in biotechnology with the development of new technologies such as gene editing tools like CRISPR, next-generation sequencing (NGS), high-throughput screening, automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are expediting drug discovery and development workflows.
U.S. life science tools market trends
The rise in number of biopharma companies and clinical diagnosis centers has increased the demand for life science tools, thereby driving the market expansion. Additionally, numerous government initiatives aimed at developing the healthcare sector is playing a vital role in shaping the industrial landscape.
Why Europe is a significant contributor of the life science tools market?
Europe is a significant contributor of the life science tools market. The growing demand for high-quality life science tools from the healthcare sector in numerous countries such as Germany, Italy, France, UK and some others has driven the market growth. Additionally, the presence of several market players coupled with technological advancements in the healthcare sector is expected to drive the growth of the life science tools market in this region.
Germany life science tools market analysis
The rising adoption of robotic surgery for treating chronic ailments has increased the demand for transfection devices, thereby driving the industrial expansion. Additionally, rapid investment by government for developing the healthcare sector is contributing to the industry in a positive manner.
What is the role of Latin America in the life science tools industry?
Latin America has played a prominent role in the life science tools market. The increasing emphasis of healthcare providers to expand the medical services across numerous nations including Argentina, Brazil, Peru and some others has boosted the market expansion. Also, rapid investment by government for developing the healthcare sector is expected to boost the growth of the life science tools market in this region.
Argentina life science tools industry trends
The growing incidences of lungs cancers and cardiovascular diseases has increased the demand for advanced surgical procedures, thereby driving the market growth. Also, the surging adoption of sustainable materials for manufacturing medical tools is playing a vital role in shaping the industrial landscape.
Why Middle East and Africa held a notable share of the life science tools market?
Middle East and Africa held a notable share of the life science tools industry. The rise in number biotech research and development centers in numerous countries including Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Qatar, UAE and some others has boosted the market expansion. Moreover, rapid investment by market players for opening up new medical tools production centers is expected to drive the growth of the life science tools market in this region.
UAE life science tools market analysis
The rapid expansion of the biopharma industry coupled with rising incidences of different types of chronic diseases has driven the industrial growth. Also, the growing popularity of tissue culture along with rise in number of government hospitals is contributing to the industry in a positive manner.
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, West Pharmaceutical Services announced the opening of a new, state-of-the-art analytical laboratory in Stolberg. The new purpose-built laboratory will expand company’s service offerings in order to meet rising needs of their clients for analytical chemistry and microbiological testing.
- In July 2025, Yourgene Health, a globally leading molecular group, launched the LightBench Discover, which is highly precise 3-in-1 instrument used by genomic research labs carrying long-read sequencing.
- In January 2025, ONI (Oxford Nanoimaging), a life science tools company dedicated to develop super-resolution microscopy, launched the Aplo Scope, which is a single molecule super-resolution microscope that allows scientists for observing and measuring the molecular interactions within cells and tissues with exceptional accuracy.
- In January 2025, Takara Bio USA Holdings, Inc., acquired Curio Bioscience, a company dedicated to spatial genomics. The strategic acquisition brings together two novel spatial biology platforms along with Takara Bio’s flagship portfolio of single-cell genomics tools.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
The market is highly competitive due to the presence of multiple players with similar product offerings. These players are continuously expanding product portfolios and launching new platforms with intensive R&D to sustain market position. Furthermore, strategic initiatives by major firms including collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, and new product launches are fueling the market growth along with intensifying the competition.
For instance, in February 2022, Agilent Technologies, Inc. partnered with Biosciences, Inc. to integrate the AVITI System with SureSelect target enrichment panels for enhanced customer access to genomic tools. The initiative was expected to create new growth opportunities for the company. Some prominent players in the global life science tools market include:
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2026 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Life Science Tools market.
By Technology
- Genomic Technology
- Proteomics Technology
- Cell Biology Technology
- Other Analytical & Sample Preparation Technology
- Lab Supplies & Technologies
By Product
- Cell Culture Systems & 3D Cell Culture
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Cell & Tissue Culture Services
- Liquid Chromatography
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Mass Spectrometry
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Flow Cytometry
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Cloning & Genome Engineering
- Kits, Reagents, and Consumables
- Services
- Microscopy & Electron Microscopy
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Next Generation Sequencing
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- PCR & qPCR
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Nucleic Acid Preparation
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Nucleic Acid Microarray
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Sanger Sequencing
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Transfection Devices & Gene Delivery Technologies
- Equipment
- Reagents
- NMR
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Other Separation Technologies
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
- Other Products & Services
- Antibodies
- General Supplies
- Others
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
By Application
- Drug Discovery and Development
- Clinical Diagnostics
- Genomic and Proteomic Research
- Cell Biology Research
- Others
By End-use
- Government & Academic
- Biopharmaceutical Company
- Healthcare
- Industrial Applications
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


.webp) North America, particularly the United States, continues to lead the global life science tools market. The region benefits from strong governmental support, high healthcare expenditure, advanced infrastructure, and a concentration of key players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, and Illumina. The presence of leading academic institutions and life science clusters like Boston-Cambridge and the Bay Area further contributes to market dominance. Initiatives such as the Cancer Moonshot and large-scale genomics projects have created sustained demand for sequencing, proteomics, and cell-based assay tools.
North America, particularly the United States, continues to lead the global life science tools market. The region benefits from strong governmental support, high healthcare expenditure, advanced infrastructure, and a concentration of key players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, and Illumina. The presence of leading academic institutions and life science clusters like Boston-Cambridge and the Bay Area further contributes to market dominance. Initiatives such as the Cancer Moonshot and large-scale genomics projects have created sustained demand for sequencing, proteomics, and cell-based assay tools..webp)