Non-specific Endonucleases Market Size Trends Analysis and Forecast till 2034
The global non-specific endonucleases market size was estimated at USD 362.55 million in 2024 and is expected to hit USD 667.26 million in 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 6.29% during the forecast period of 2025 and 2034. The market growth is driven by the rising demand for advanced gene-editing tools, expanding applications in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research, increasing adoption in biomanufacturing and nucleic acid purification processes, and advancements in recombinant enzyme technologies.
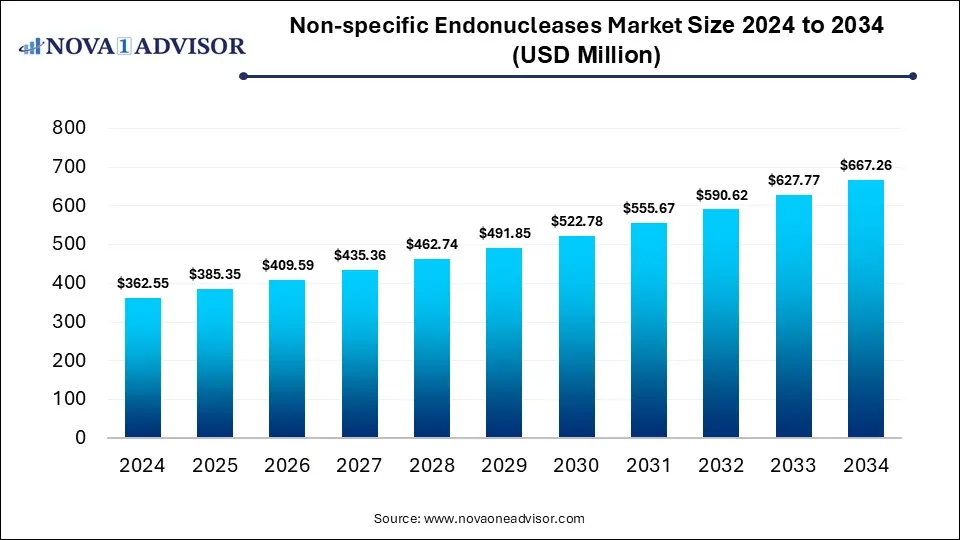
Key Takeaways
- By region, North America held the largest share of the non-specific endonucleases market in 2024.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to experience the fastest growth between 2025 and 2034.
- By type, the 25kU segment led the market in 2024.
- By type, the 100kU segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR over the projected timeframe.
- By application, the biological laboratory segment led the market in 2024.
- By application, the university research room segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR over the projection period.
Impact of AI on the Non-Specific Endonucleases Market
AI is significantly transforming the non-specific endonucleases market by accelerating enzyme discovery, optimization, and customization. AI-driven predictive modelling and machine learning algorithms enable faster identification of enzyme variants with improved stability, specificity, and activity for various biotechnological applications. In bioprocessing, AI is being used to optimize reaction conditions and streamline quality control, reducing time and cost in enzyme manufacturing. Moreover, AI-powered data analytics facilitate better understanding of enzyme-substrate interactions, accelerating innovation in gene editing and nucleic acid purification. Overall, the integration of AI is driving precision, scalability, and innovation across the non-specific endonuclease value chain.
- In June 2024, Basecamp Research and the Ferruz Lab at the Institute of Molecular Biology of Barcelona launched ZymCTRL, an AI model for enzyme design. Inspired by large language models like ChatGPT, ZymCTRL generates new enzyme sequences from a simple input: an enzyme ID and desired activity.
Market Overview
The market growth is attributed to the rising demand for recombinant therapeutics, increasing adoption of gene editing and cell therapy technologies, and ongoing advancements in enzyme engineering. Additionally, expanding biopharma R&D and the integration of automation and AI in bioprocess workflows further propel market expansion. The non-specific endonucleases market refers to the industry focused on enzymes that cleave nucleic acids at random sites within DNA or RNA molecules, playing a crucial role in genetic engineering, biopharmaceutical manufacturing, and molecular biology research.
These enzymes are widely used for nucleic acid removal in bioprocessing, DNA fragmentation in sequencing, and cell lysis applications due to their high efficiency and broad substrate specificity. Key advantages include improved product purity, enhanced process scalability, and reduced contamination risks in downstream purification processes.
- In 2025, Roche launched EndoCleave, a non-specific endonuclease derived from Serratia marcescens (expressed in E. coli) designed for viral vector, oncolytic virus, and vaccine purification. It boasts broad-spectrum DNA/RNA cleavage, GMP quality, and features tailored for large-scale manufacturing.
What are the Major Trends in the Non-Specific Endonucleases Market?
- Advancements in Enzyme Engineering and Recombinant Technology
Innovations in protein engineering are enabling the development of endonucleases with enhanced stability, activity, and compatibility across diverse bioprocess conditions. Recombinant production methods also support large-scale, cost-effective enzyme manufacturing.
- Increasing Focus on Sustainable and High-Purity Bioprocessing
Manufacturers are adopting environmentally friendly, high-efficiency enzyme formulations that reduce chemical waste and improve purification performance. This aligns with the global shift toward greener, more sustainable biomanufacturing practices.
- Growth in Biopharma & Gene / Cell Therapy
The increasing production of biologics, vaccines, and cell & gene therapies is pushing demand for endonucleases that help remove residual nucleic acids in upstream/downstream processes. For example, viral vector based therapeutics (AAV, lentivirus) require removal of host/plasmid DNA/RNA, boosting use of high performance, GMP grade non specific endonucleases.
Report Scope of Non-specific Endonucleases Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 385.35 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 667.26 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 6.29% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
By Type, By Application, By Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rising Demand for Biopharmaceuticals
The rising demand for biopharmaceuticals is a major factor driving the growth of the non-specific endonucleases market, as these enzymes play a crucial role in ensuring product purity and regulatory compliance during biologics manufacturing. In processes such as vaccine, monoclonal antibody, and recombinant protein production, non-specific endonucleases are used to efficiently remove residual host-cell DNA and RNA contaminants. The growing global focus on high-quality, safe, and effective biologic therapies has intensified the adoption of these enzymes across large-scale bioprocessing operations. Additionally, as more biopharma companies invest in advanced production technologies and gene-based therapies, the need for reliable nucleic acid removal tools continues to rise.
- In January 2024, the AccuSignal Nuclease ELISA Kit was introduced to detect specific endonucleases, such as Benzonase, DENARASE, and Turbonuclease, which help biopharmaceutical manufacturers in their quality control processes.
Growth in Genetic Engineering and Molecular Biology Research
The growth in genetic engineering and molecular biology research is significantly fueling the expansion of the non-specific endonucleases market by increasing the demand for efficient tools that facilitate DNA and RNA manipulation. Non-specific endonucleases are essential for applications such as cloning, gene expression studies, and nucleic acid purification, where precise and effective cleavage of nucleic acids is required. As research institutions and biotech companies intensify efforts in areas like gene editing, synthetic biology, and recombinant protein production, the use of these enzymes becomes even more critical. Additionally, advancements in molecular techniques and the availability of high-purity recombinant endonucleases are enhancing workflow efficiency and experimental accuracy.
Restraints
High Production and Purification Costs
The market growth is hindered by high costs associated with enzyme manufacturing and purification, as it involves complex biotechnological processes and stringent quality control measures. Producing these enzymes in recombinant systems requires advanced fermentation, purification, and validation techniques, which increase overall production expenses. Small and medium-sized biopharma companies often face financial constraints in adopting high-cost enzyme solutions, limiting market penetration. Additionally, maintaining enzyme stability and activity during large-scale production further adds to operational costs.
Regulatory & Quality Compliance Burdens
Regulatory and quality compliance burdens restrain the growth of the market by increasing development time, cost, and complexity. Manufacturers must meet stringent standards for purity, consistency, and safety, particularly for enzymes used in biopharma and clinical applications. Achieving compliance with agencies like the FDA or EMA requires extensive validation, documentation, and quality control systems, which can be resource-intensive. These requirements often deter smaller companies and delay product launches, limiting innovation and market expansion.
Opportunities
Rising Development of Cell and Gene Therapies
Rising development of cell and gene therapies creates immense opportunities in the market, as these enzymes are essential for ensuring the purity and safety of therapeutic products. In gene therapy production, non-specific endonucleases are used to remove residual host-cell nucleic acids from viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing preparations, meeting strict regulatory requirements. The increasing number of gene therapy approvals and expanding pipeline of cell-based treatments are driving demand for high-efficiency, GMP-grade enzymes. Moreover, advancements in bioprocessing technologies and scalable manufacturing systems are encouraging the integration of endonucleases into commercial production workflows
Expansion in Genomics, Diagnostics & Precision Medicine
The rapid expansion of genomics, diagnostics, and precision medicine is creating significant opportunities in the non-specific endonucleases market. These enzymes are essential for nucleic acid sample preparation, cleanup, and fragmentation in workflows such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), liquid biopsies, and PCR-based diagnostics. As demand for fast, accurate, and high-throughput testing grows, so does the need for reliable, high-purity endonucleases that can streamline and enhance these processes. This surge in genomic and diagnostic applications is driving both increased consumption and innovation in enzyme formulations, opening new avenues for market growth.
How Macroeconomic Variables Influence the Non-specific Endonucleases Market?
Economic Growth and GDP
Economic growth and rising GDP generally lead to positive growth, as higher national income levels lead to increased investments in biotechnology, pharmaceutical R&D, and healthcare infrastructure. Countries with strong economic performance allocate more resources toward advanced bioprocessing technologies and life sciences innovation, boosting enzyme adoption. Conversely, slower economic growth can limit funding for research and biomanufacturing, temporarily restraining market expansion.
Inflation & Drug Pricing Pressures
It can negatively affect the growth of the, as rising production costs and tighter profit margins limit spending on high-cost bioprocessing materials and enzymes. Pharmaceutical and biotech companies may delay or reduce investments in premium enzyme formulations to control overall manufacturing expenses. Additionally, global pricing pressures on biologics and gene therapies further challenge the affordability and widespread adoption of advanced endonucleases.
Exchange Rates
Exchange rate fluctuations can both positively and negatively impact the market, depending on currency trends and trade dynamics. Favorable exchange rates can lower import costs for enzymes and raw materials, supporting market expansion in developing regions. However, volatile or unfavorable currency movements increase production and procurement expenses for international manufacturers, thereby restraining growth and profitability in global trade.
Segment Outlook
Type Insights
Why Did the 25kU Segment Dominate the Non-specific Endonucleases Market in 2024?
The 25kU segment dominated the market with the largest share in 2024. This is because of the widespread adoption in large-scale biopharmaceutical and vaccine manufacturing processes. This concentration offers an optimal balance between enzyme quantity, cost-effectiveness, and processing efficiency, making it ideal for commercial bioprocessing applications. Biopharma companies prefer the 25kU format for its scalability, consistent performance, and compatibility with GMP-grade production environments. Additionally, its high yield and ability to effectively remove residual nucleic acids from biologic products contribute to improved product purity and regulatory compliance.
The 100kU segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the projection period, owing to the increasing adoption in large-scale biopharmaceutical and gene therapy manufacturing. This high-capacity format offers superior efficiency for industrial bioprocessing, enabling the removal of nucleic acids from bulk volumes of biologics and viral vectors. As companies move toward continuous and high-throughput production systems, the demand for larger enzyme quantities that ensure consistent performance and process scalability is rising. Additionally, the 100kU segment supports cost optimization by reducing the frequency of enzyme replenishment and streamlining workflow operations.
Non-specific Endonucleases Market By Type, 2024-2034 (USD Million)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| 5kU |
101.52 |
106.35 |
111.4 |
116.67 |
122.16 |
127.88 |
133.83 |
140.03 |
146.47 |
153.18 |
160.14 |
| 25kU |
94.26 |
99.81 |
105.68 |
111.89 |
118.46 |
125.42 |
132.79 |
140.58 |
148.84 |
157.56 |
166.82 |
| 50kU |
79.76 |
84.78 |
90.11 |
95.78 |
101.8 |
108.21 |
115.01 |
122.25 |
129.94 |
138.11 |
146.8 |
| 100kU |
65.26 |
70.13 |
75.37 |
80.98 |
87 |
93.45 |
100.37 |
107.8 |
115.76 |
124.3 |
133.45 |
| ≥100kU (Bulk Pack) |
21.75 |
24.28 |
27.03 |
30.04 |
33.32 |
36.89 |
40.78 |
45.01 |
49.61 |
54.62 |
60.05 |
Application Insights
Why Did the Biological Laboratory Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The biological laboratory segment dominated the non-specific endonucleases market in 2024 due to its extensive use of these enzymes in molecular biology, genetic engineering, and bioprocess research. Laboratories across academic, clinical, and industrial settings depend on non-specific endonucleases for essential applications such as nucleic acid removal, cloning, and sequencing. The widespread adoption of enzyme-based techniques in genomic research, coupled with the increasing number of biotech laboratories worldwide, has significantly boosted demand. Additionally, advancements in life sciences research and the growing focus on precision medicine have intensified the use of these enzymes in experimental workflows.
The university research room segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR in the coming years. This is mainly due to the rising focus on academic research and innovation in molecular biology and biotechnology. Universities are increasingly utilizing non-specific endonucleases for experiments related to gene editing, DNA sequencing, and protein expression, driving consistent enzyme demand. Enhanced government funding and research grants aimed at advancing life sciences are further supporting the adoption of these enzymes in academic settings. Moreover, growing collaboration between universities and biotech industries is promoting knowledge exchange and access to high-quality enzyme technologies.
Non-specific Endonucleases Market By Application, 2024-2034 (USD Million)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Biological Laboratory |
210.28 |
221.96 |
234.29 |
247.29 |
260.98 |
275.44 |
290.66 |
306.73 |
323.66 |
341.51 |
360.33 |
| University Research Room |
97.89 |
103.27 |
108.95 |
114.93 |
121.24 |
127.88 |
134.88 |
142.25 |
150.02 |
158.2 |
166.81 |
| Others |
54.38 |
60.12 |
66.35 |
73.14 |
80.52 |
88.53 |
97.24 |
106.69 |
116.94 |
128.06 |
140.12 |
Regional Analysis
What Made North America the Dominant Region in the Market?
North America sustained dominance in the non-specific endonucleases market while holding the largest share in 2024. The region’s growth is primarily attributed to its strong biotechnology and pharmaceutical infrastructure, coupled with extensive investments in bioprocessing and genetic research. The region benefits from a high concentration of leading biopharma companies and research institutions that extensively utilize non-specific endonucleases in biologics production and molecular biology applications. Stringent regulatory standards set by agencies like the FDA encourage the use of high-quality, GMP-grade enzymes for ensuring product safety and purity. Additionally, ongoing advancements in gene and cell therapy manufacturing, along with strong government and private funding for life sciences R&D, further fuel market growth.
The U.S. is a major contributor to the North American non-specific endonucleases market due to its advanced biotechnology ecosystem and strong presence of leading biopharmaceutical companies. The country’s high investment in gene therapy, recombinant protein production, and molecular biology research fuels extensive demand for non-specific endonucleases. Additionally, well-established research infrastructure, favorable regulatory frameworks, and government funding initiatives support continuous innovation in enzyme technologies.
What Makes Asia Pacific the Fastest-Growing Market?
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market for non-specific endonucleases. This is due to the rapid expansion of the biotechnology and biopharmaceutical sectors across countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Increasing government investments in life sciences research, coupled with rising demand for vaccines, biosimilars, and gene therapies, are driving enzyme adoption in the region. The establishment of new biomanufacturing facilities and collaborations between local research institutions and global biotech firms further support market expansion. Additionally, the growing focus on affordable biologics production and process optimization has encouraged the use of high-efficiency non-specific endonucleases.
China is a major player in the Asia Pacific non-specific endonucleases market due to its rapidly advancing biotechnology industry and strong government support for biopharmaceutical innovation. The country has made significant investments in gene therapy, vaccine production, and molecular biology research, all of which heavily rely on non-specific endonucleases for nucleic acid removal and purification. Additionally, China’s growing network of biomanufacturing facilities and partnerships with global life science companies are accelerating the adoption of high-quality recombinant enzymes.
Region-Wise Market Outlook
| Region |
Approximate Market Size in 2024 |
Projected CAGR (next 5-10 years) |
Major Growth Factors |
Key Restraints / Challenges |
Growth |
| North America |
USD 150.8 Billion |
5.88% |
Strong biotech & pharmaceutical infrastructure, large R&D investments, government / private funding, regulatory emphasis on purity & safety. |
High cost of GMPâ€grade enzymes, stringent regulatory and quality requirements. |
Dominant region |
| Asia-Pacific |
USD 105.9 Billion |
7.03% |
Rapid expansion of biotech/biopharma manufacturing, increasing R&D investment (governments & private sector). |
Some challenges in regulatory harmonization, quality consistency. |
Region with the fastest growth |
| Europe |
USD 84.7 Billion |
9.93% |
Strong biotech & pharma base, regulatory oversight, high adoption of diagnostics and rare disease/gene therapy pipelines. |
High production/compliance costs. |
Steady growth |
| Latin America |
USD 29.3 Billion |
4.69% |
Growing interest in diagnostics, increasing investment in local biotech R&D. |
Infrastructure & regulatory limitations, lower ability to afford high-grade enzymes. |
Emerging region with steady growth |
| Middle East & Africa |
USD 18.6 Billion |
3.38% |
Increasing healthcare infrastructure investment, rising awareness of molecular diagnostics. |
Significant regulatory, cost and supply chain challenges. |
High growth potential |
Non-specific Endonucleases Market Value Chain Analysis
1. Raw Material Sourcing & Enzyme Production
This stage involves sourcing biological raw materials such as microbial cultures (e.g., Serratia marcescens), recombinant DNA, and cell substrates used in the synthesis of non-specific endonucleases. Companies at this stage focus on high-purity, GMP-grade enzyme extraction and purification to ensure performance consistency and regulatory compliance.
- Key Players: Merck KGaA (Sigma-Aldrich), Takara Bio Inc., and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
2. Product Development & Formulation
In this stage, manufacturers optimize enzyme formulations for different purity levels and applications (e.g., 25kU, 100kU grades). R&D teams develop enzyme variants that offer improved activity, stability, and compatibility with biopharmaceutical and diagnostic processes. Continuous innovation in enzyme engineering and formulation drives differentiation and cost efficiency.
- Key Players: Roche CustomBiotech, BioVision Inc., and Qiagen N.V.
3. Manufacturing & Quality Control
At this stage, large-scale manufacturing of non-specific endonucleases is carried out under strict GMP conditions. Quality control measures, such as activity assays, endotoxin testing, and stability validation, are implemented to ensure batch consistency and regulatory approval. Automation and bioreactor technologies play a key role in scaling up production while maintaining purity.
- Key Players: Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Merck KGaA, and Agilent Technologies
4. Distribution & Supply Chain
Distributors and suppliers ensure the timely and safe delivery of enzymes to end-users such as research labs, universities, and biopharmaceutical companies. This stage also includes logistics, inventory management, and compliance with international shipping standards for biological materials. Global distributors maintain cold-chain logistics to preserve enzyme integrity.
- Key Players: Fisher Scientific, VWR International (Avantor Inc.), and Merck Life Science.
5. End-Use Applications
End-users utilize non-specific endonucleases in biopharmaceutical production (DNA removal from biologics), genetic engineering, molecular diagnostics, and academic research. Growing adoption in cell and gene therapy manufacturing, as well as in CRISPR and recombinant protein production, drives this stage. Feedback from end-users also supports product improvements and innovations.
- Key Players: Amgen Inc. and Pfizer Inc., Harvard University and Stanford University, and Novartis AG
Non-Specific Endonucleases Market Companies
| Tier |
Companies Included |
Description / Why in This Tier |
Approximate Cumulative Share of Global Market |
| Tier I |
Thermo Fisher Scientific; Merck KGaA; New England Biolabs |
These are large, well established players with broad enzyme portfolios, strong regulatory/compliance capabilities, global distribution, and leading positions in revenue. |
40-50% |
| Tier II |
GenScript; Yeasen Biotechnology; Vazyme Biotech; Takara Bio; Bio Techne; Promega |
These are medium to large firms, strong in specific regions or product lines (e.g. recombinant or engineered enzymes), growing fast, but not yet as dominant globally as Tier I. |
25-35% |
| Tier III |
ACROBiosystems; ArcticZymes; Worthington Biochemical; RayBiotech; TransGen Biotech; Beyotime Biotechnology; possibly smaller/regional players |
These contribute more modestly, often specialized, regional, newer entrants, or narrower product ranges. |
20-30% |
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, Avantor, Inc. launched two innovative products, the J.T.Baker® Cell Lysis Solution and J.T.Baker® Endonuclease, designed to optimize the gene therapy harvest process sustainably and at scale.
- In June 2024, Basecamp Research launched ZymCTRL, the world’s first open-source, generative AI enzyme design tool. Developed in collaboration with the Ferruz Laboratory, ZymCTRL allows users to generate entirely new enzyme sequences by simply inputting an enzyme identification code, eliminating the need for a seed sequence.
Exclusive Analysis on the Non-Specific Endonucleases Market
The global non-specific endonucleases market is poised at a pivotal inflection point, underpinned by a confluence of technological advancement, biopharmaceutical expansion, and structural shifts in genomics-driven workflows. Characterized by high-margin, value-added enzymatic products, the market is witnessing accelerating integration across critical applications including bioprocessing, gene and cell therapy, nucleic acid diagnostics, and synthetic biology. The heightened regulatory stringency around host cell DNA clearance and residual nucleic acid thresholds is driving a paradigm shift from legacy purification protocols to enzyme-enabled solutions, positioning non-specific endonucleases as indispensable bioprocess auxiliaries.
Moreover, the convergence of AI-enabled protein engineering and the emergence of thermostable, recombinant-grade variants is catalyzing the development of next-gen formulations with enhanced activity, reduced cold chain dependency, and scalability for GMP-grade deployment. The expanding biomanufacturing footprint in emerging economies, particularly across Asia-Pacific, further augments demand tailwinds, supported by localized enzyme production and government-backed R&D pipelines. Despite legacy barriers such as cost intensity and regulatory overhead, the addressable market remains structurally underpenetrated, suggesting outsized growth potential for innovators capable of aligning with evolving modality-agnostic platform requirements.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- 5kU
- 25kU
- 50kU
- 100kU
- 100kU
By Application
- Biological Laboratory
- University Research Room
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa

